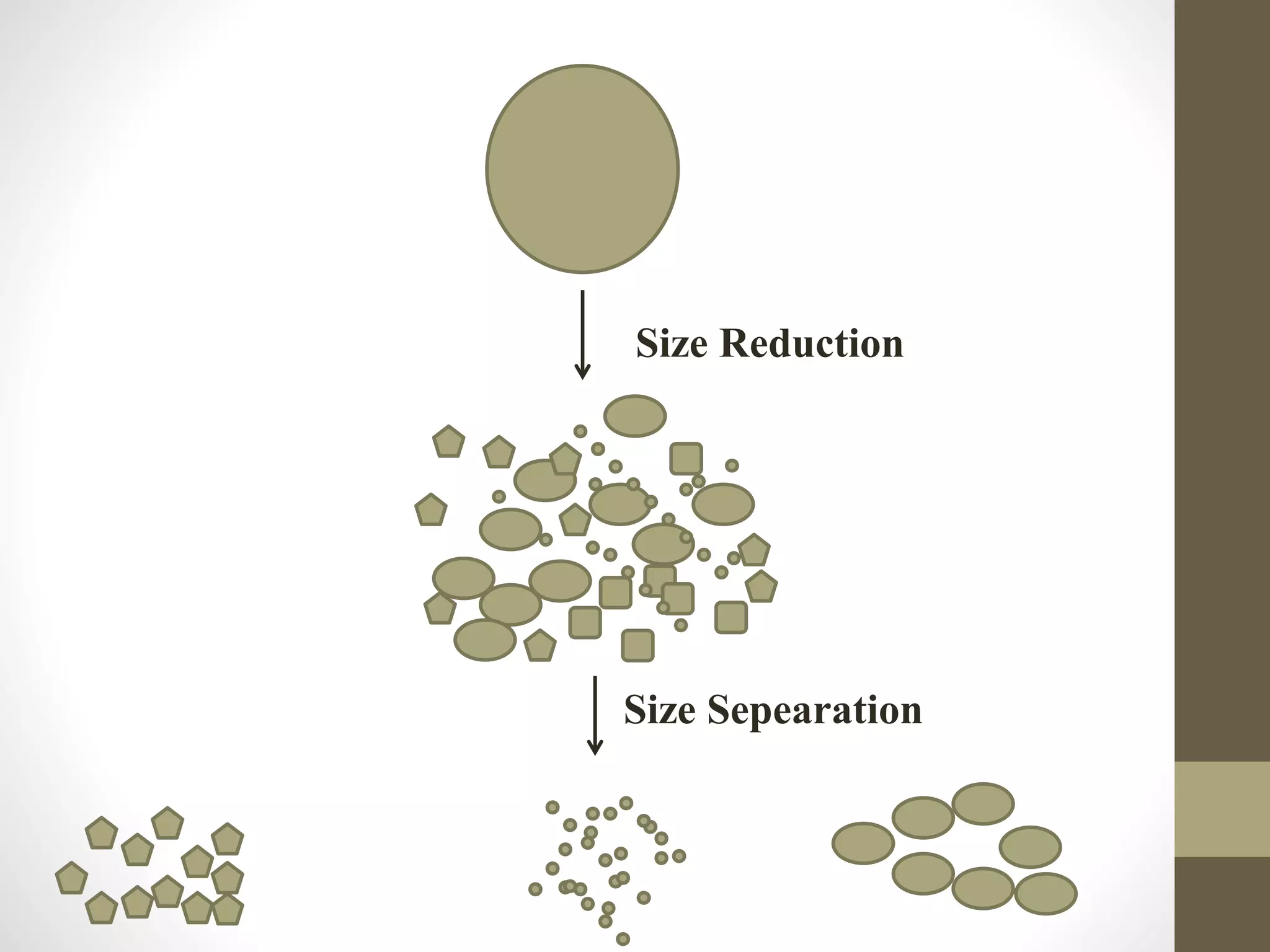
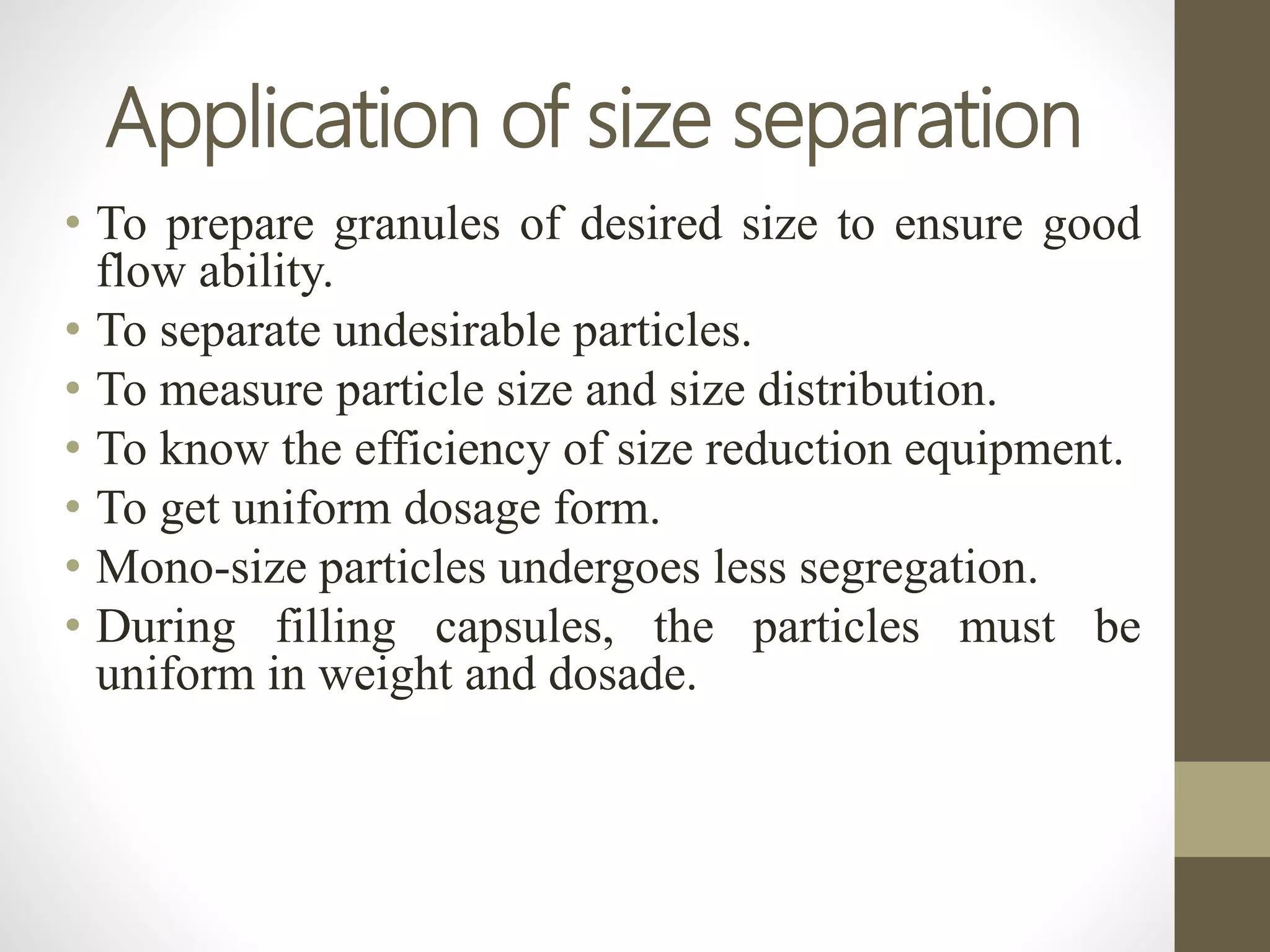
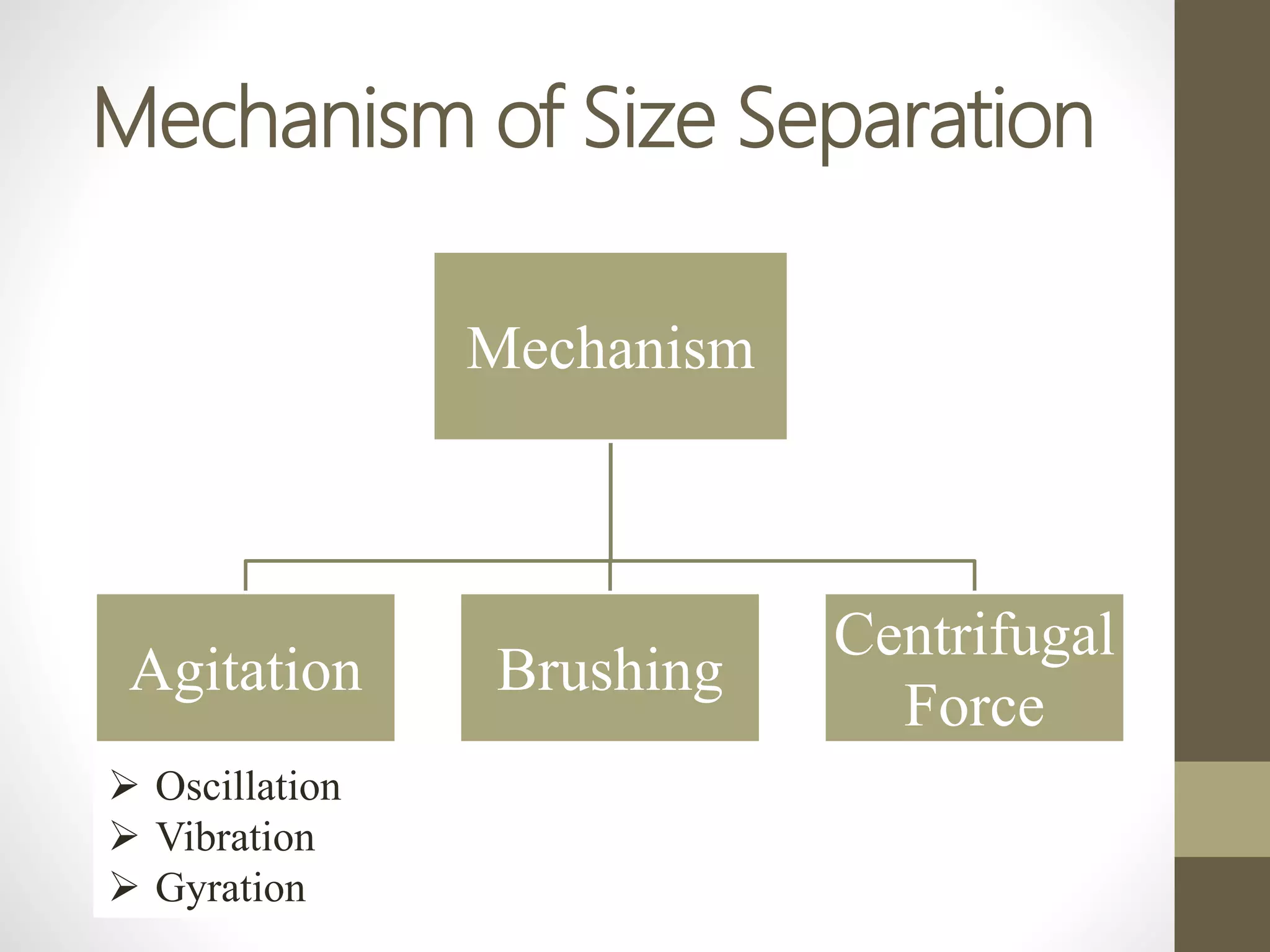
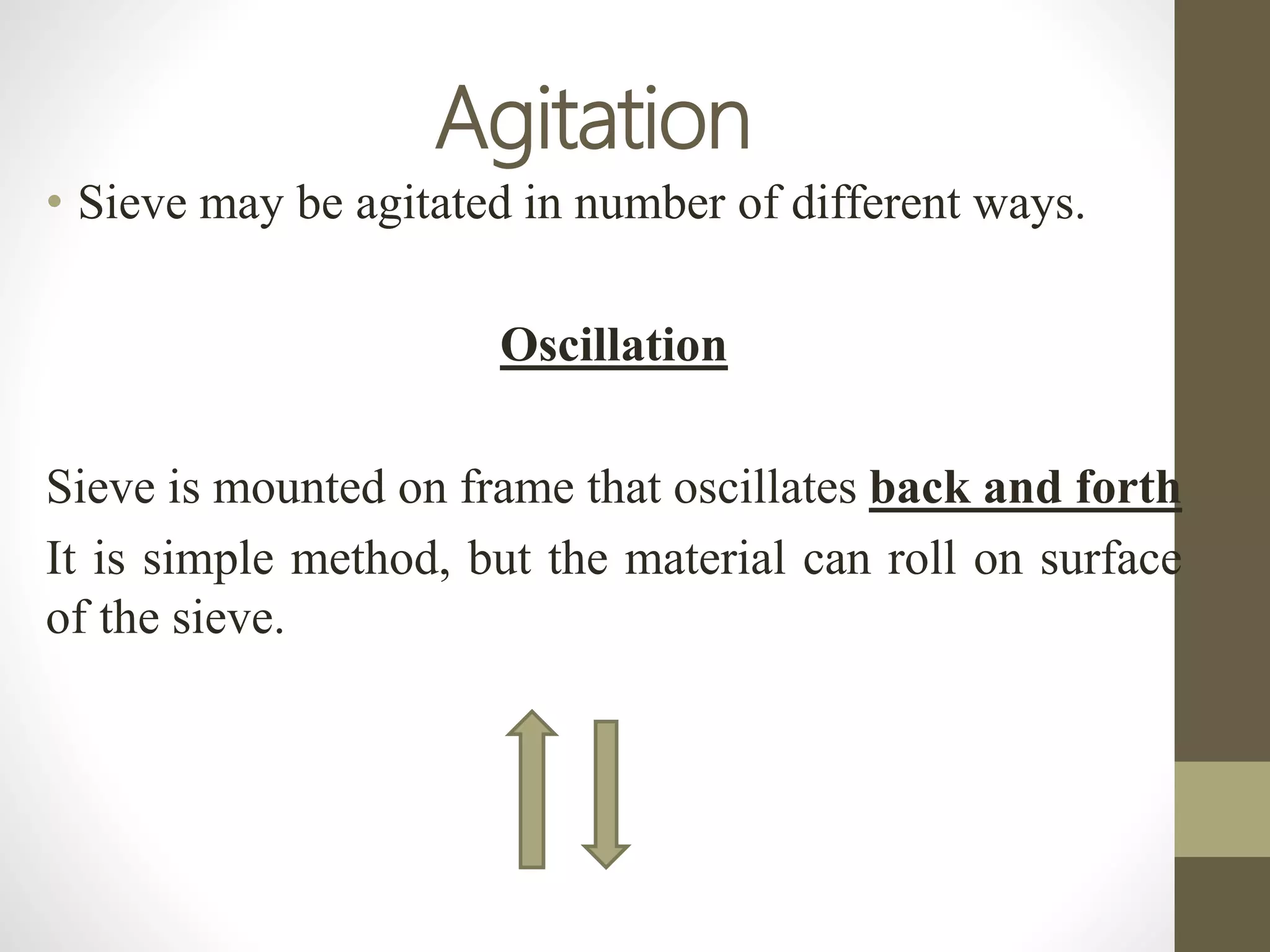
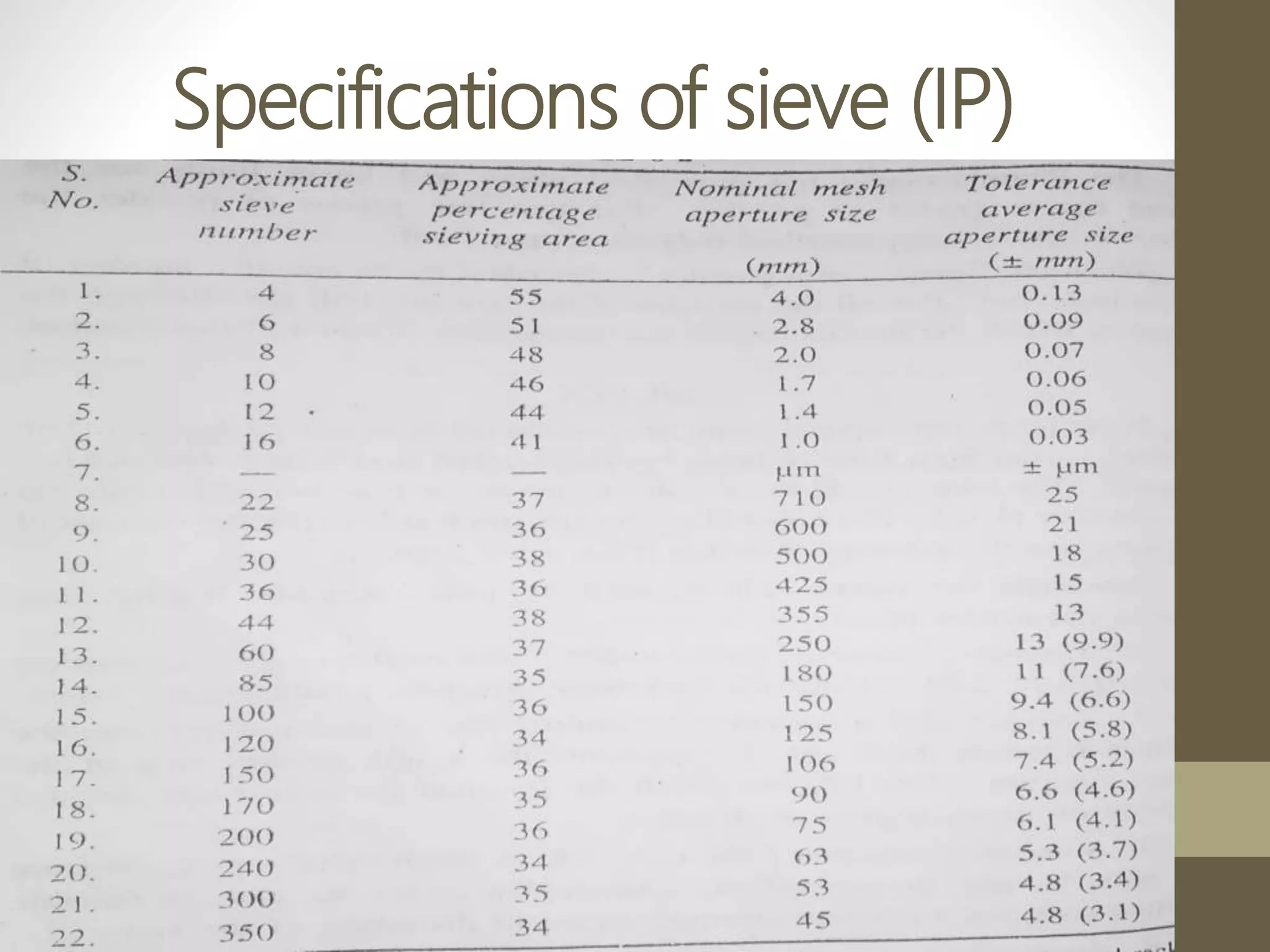
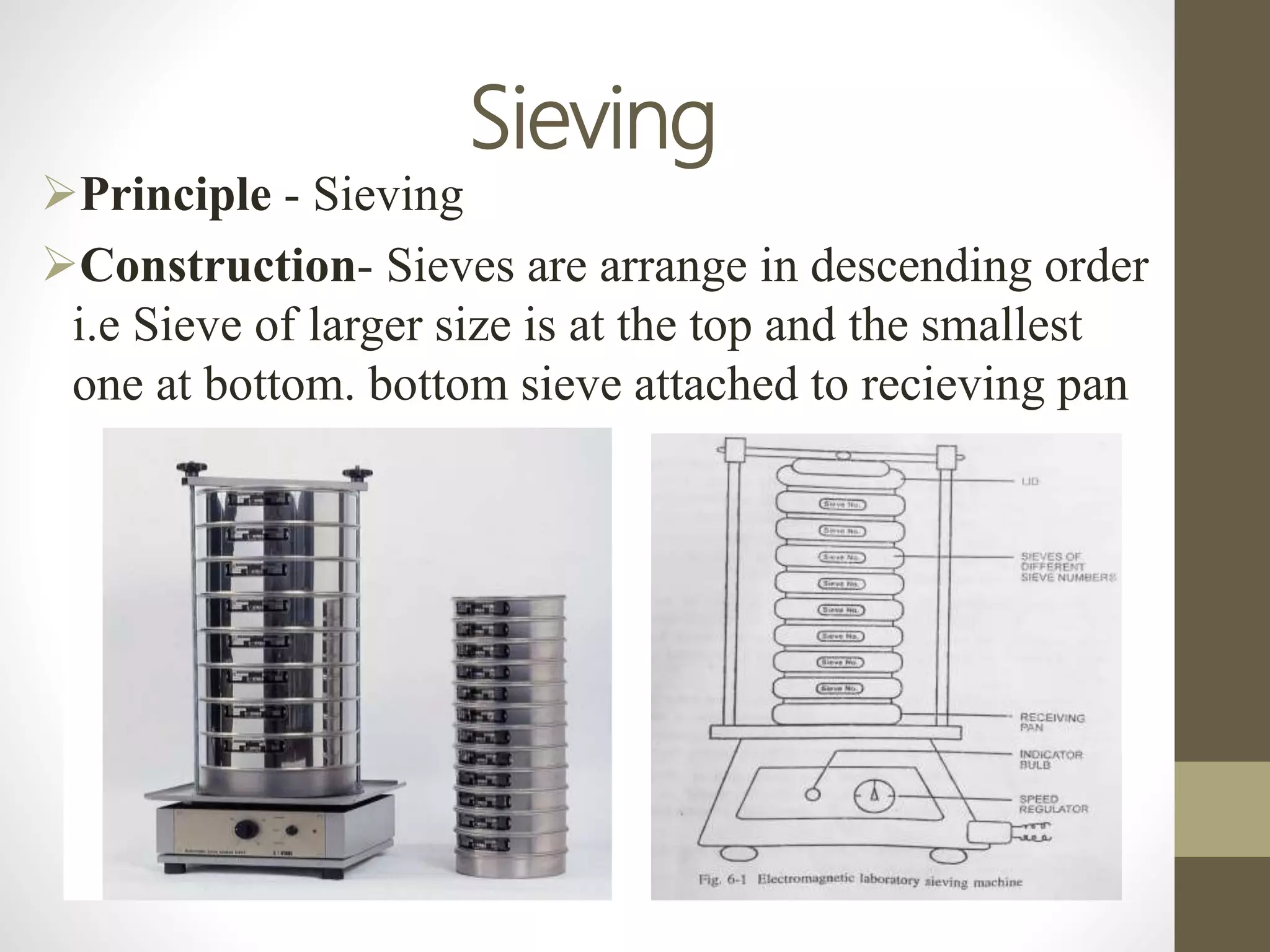
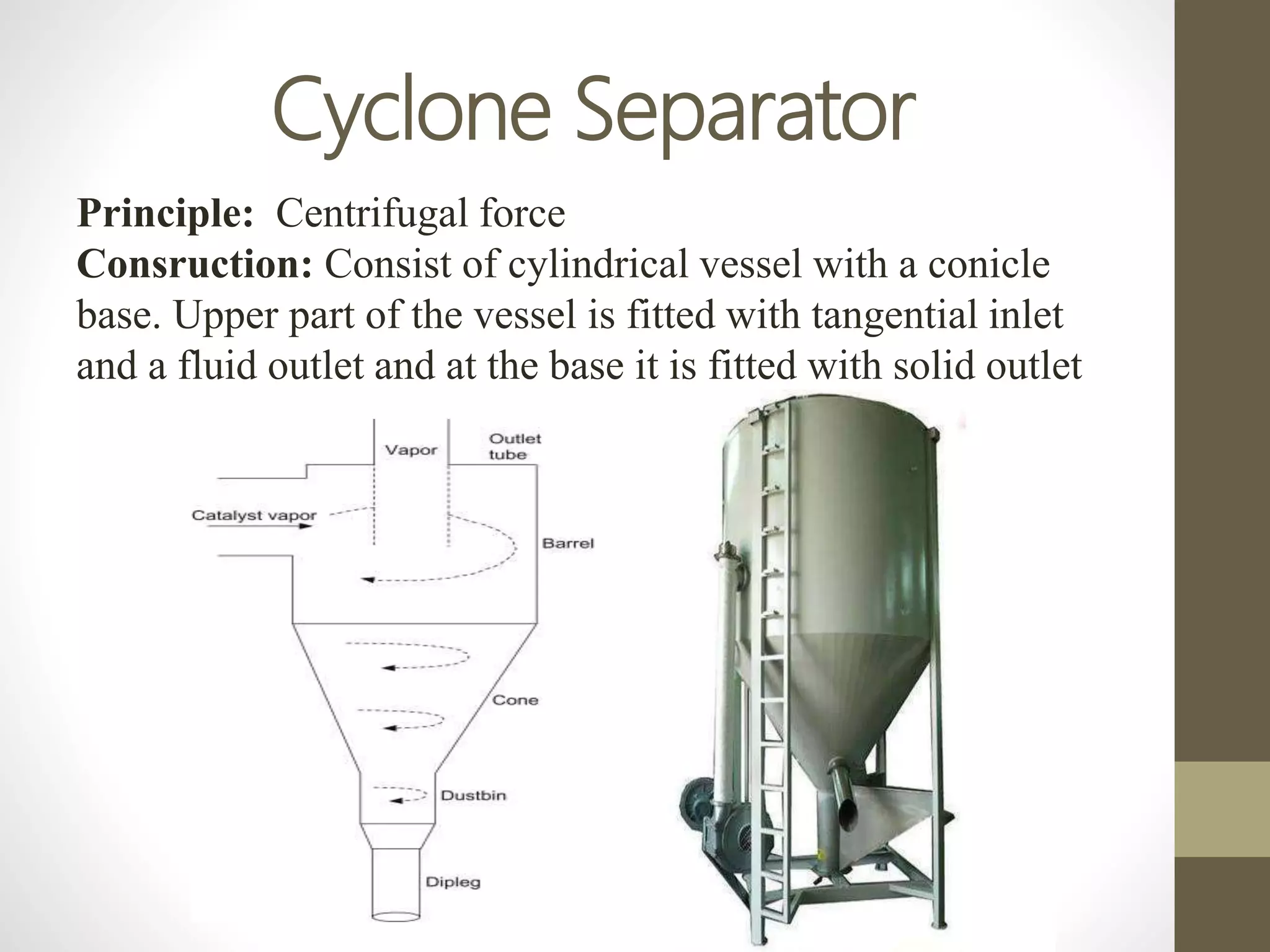
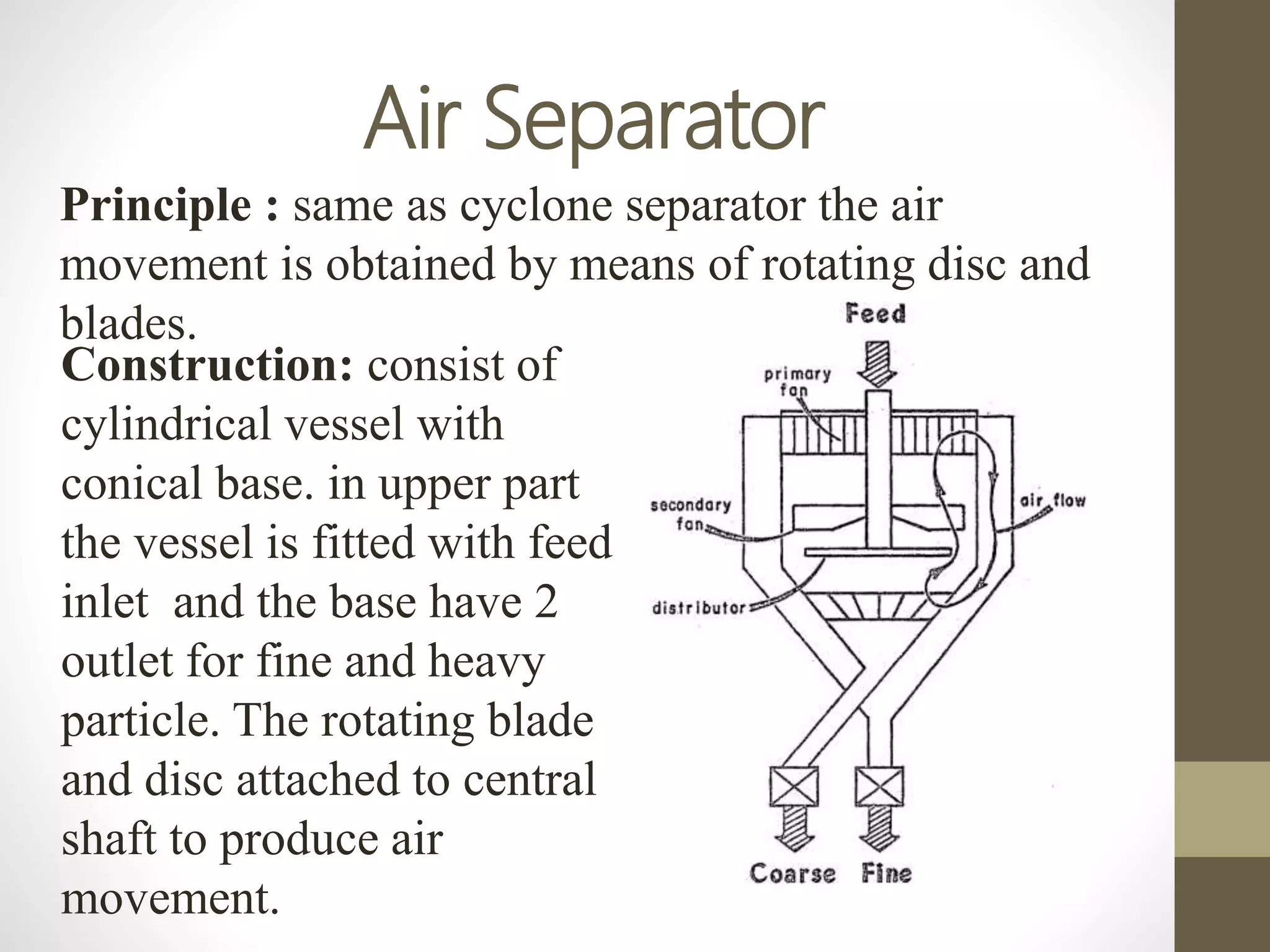
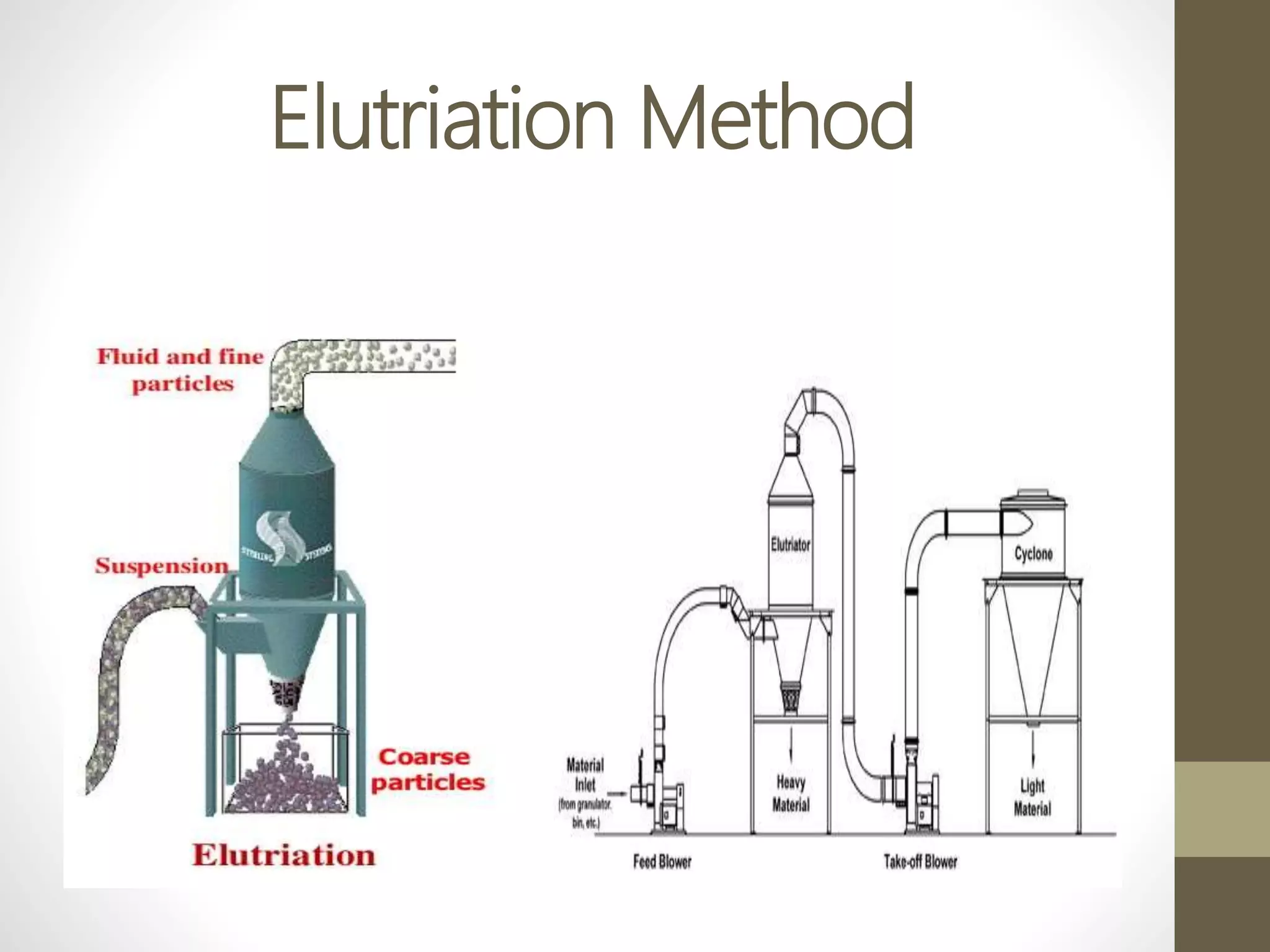
The document discusses size separation processes, their objectives, applications, and mechanisms, specifically in the context of powder production in pharmaceuticals. Methods such as sieving, cyclone separation, air separation, and elutriation are detailed, including their workings, advantages, and disadvantages. Official standards for sieve sizes and specifications are also provided, emphasizing the importance of size separation in ensuring uniformity and quality in pharmaceutical products.