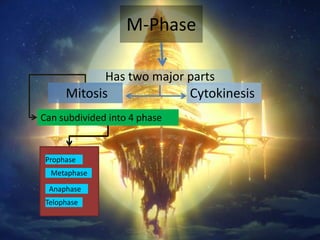
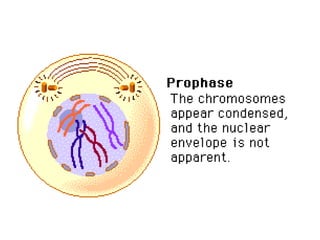
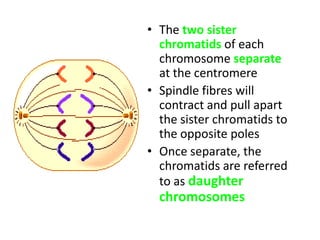
M-phase consists of mitosis and cytokinesis. Mitosis is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the chromosomes condense and duplicate, align at the metaphase plate, separate into daughter chromosomes, and decondense. Cytokinesis then occurs, where in animal cells the cell membrane invaginates at the cleavage furrow to divide the cytoplasm, and in plant cells a cell plate forms between nuclei that fuses with the parent cell membrane to divide the cell.