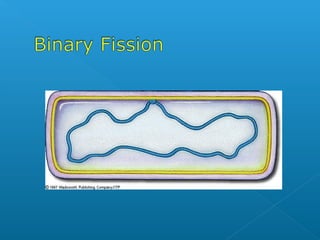
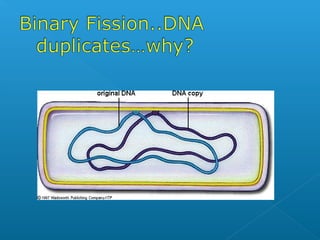
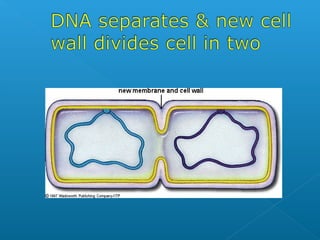
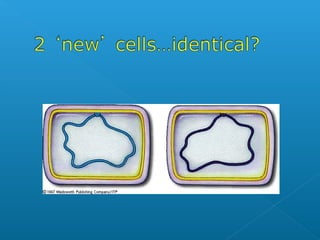
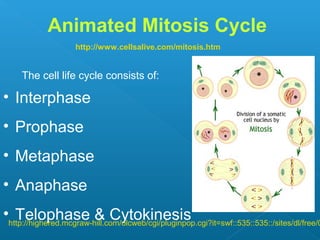
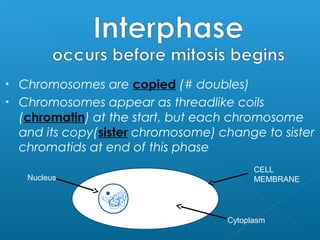
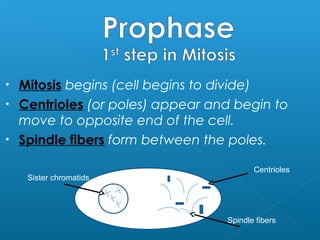
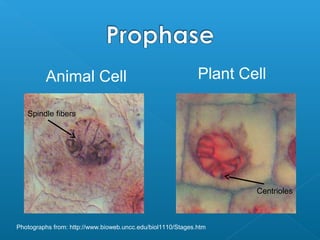
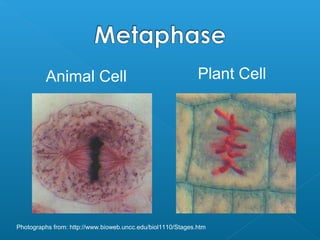
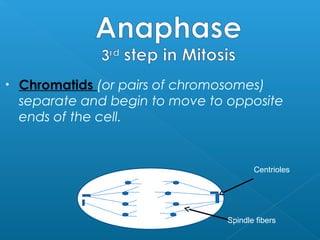
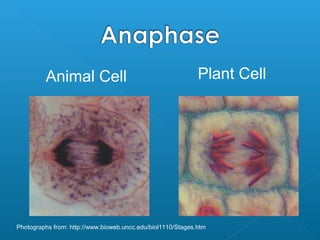
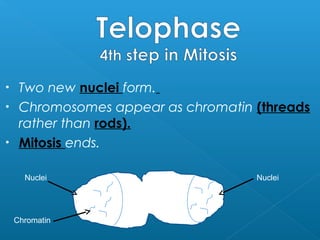
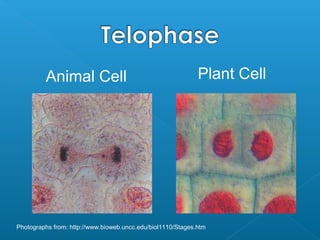
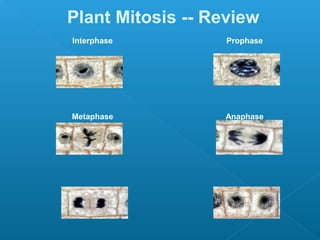
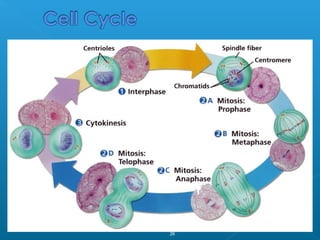
The document discusses how multicellular organisms grow. It states that growth occurs through cell division, not by individual cells increasing in size. It also notes that for binary fission to occur in bacteria, the cell must grow in size and duplicate its DNA so that each new cell has its own copy.