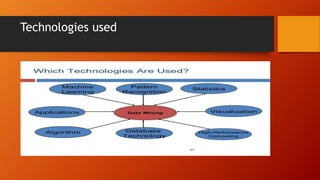
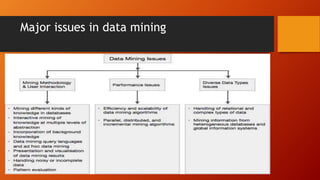
The document introduces data mining, outlining its prerequisites, including knowledge of databases, data warehousing, and OLAP. It defines data mining as the practice of examining large databases to generate new information and highlights various applications such as market analysis and fraud detection. The document also details types of OLAP, kinds of knowledge to be mined, and the technologies used in data mining.