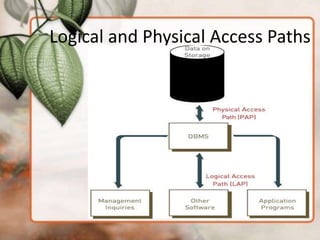
This document lists the members of a group for the Royal University of Phnom Penh including Chan Pisey, Chhann Seakquech, Bun Seng, and others. It then covers 6 topics about database management: 1) Storing and retrieving data through logical and physical access paths, 2) Manipulating data and generating reports using SQL, 3) The roles of database administrators, 4) Popular systems like Microsoft Access, Oracle, and open-source options, 5) Special-purpose databases for specific industries, and 6) Important factors to consider when selecting a database system like size, cost, users, and vendor.