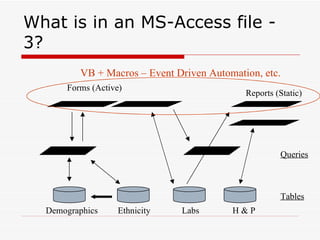
This document provides an overview and introduction to Microsoft Access. It discusses what Access is, when it should be used over Excel or SPSS, its advantages over other database management systems like Oracle, the structure of Access files, best practices for data storage and relationships, and how queries work. Resources for further learning about Access are also provided.