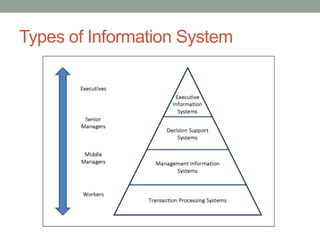
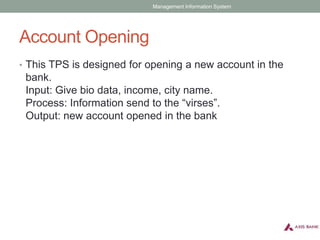
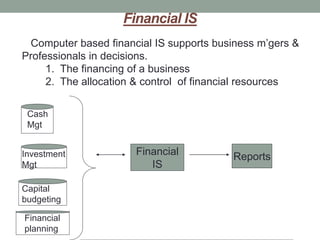
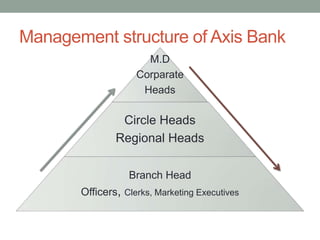
Management information systems (MIS) produce reports from transaction data to inform managers' structured and semi-structured decisions. MIS gather internal and external data, process and store it centrally, and make it available to authorized users. They support functions like decision support systems, resource planning, and customer relationship management. MIS help identify business process improvements and provide overall business insights through data analysis.