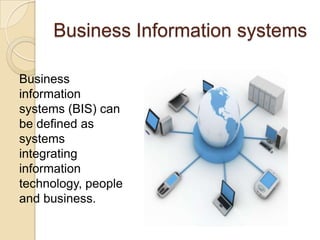
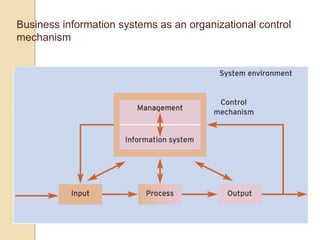
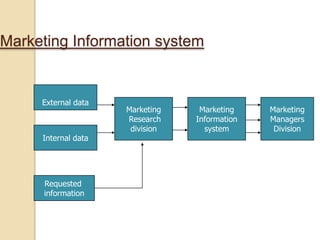
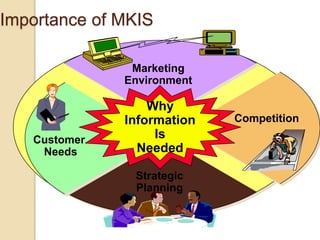
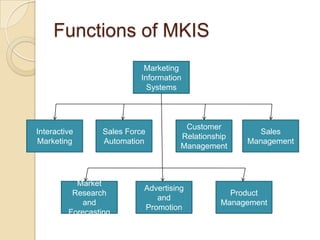
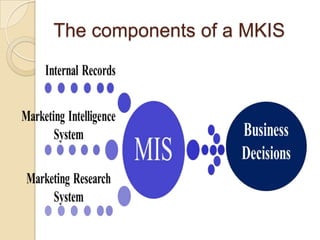
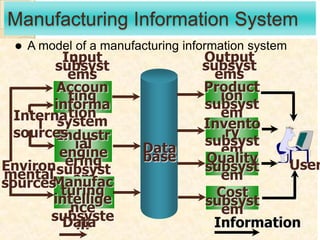
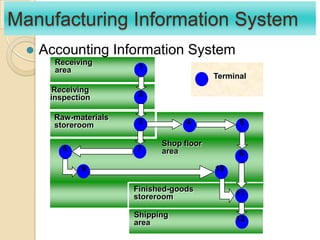
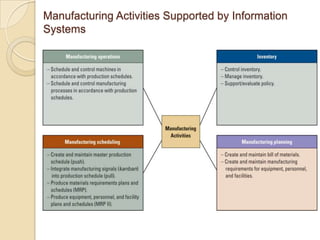
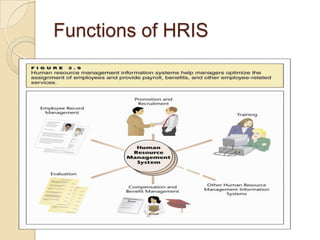
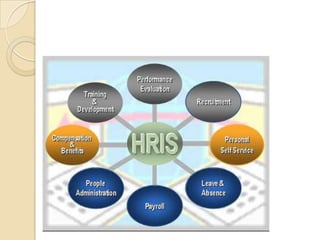
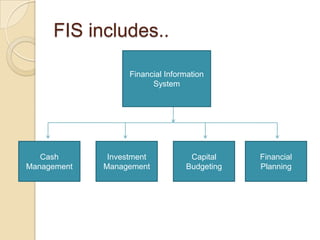
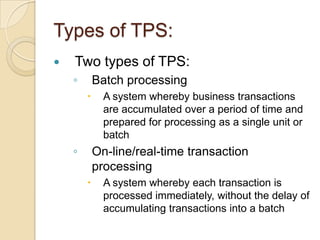
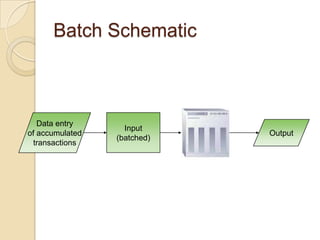
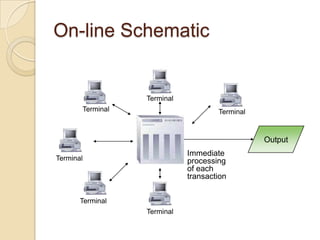
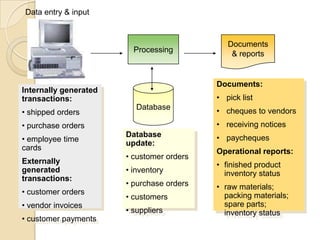
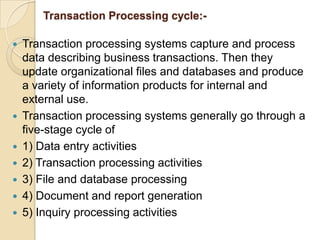
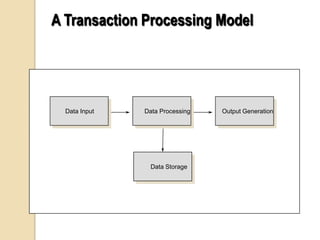
Business information systems support business functions through integrated technology, people and processes. They include marketing, manufacturing, human resources, financial and transaction processing systems. Transaction processing systems specifically collect, store, modify and retrieve organizational transactions for processing, updating files/databases, and generating documents and reports. They are essential for supporting day-to-day business operations through functions like order processing, purchasing, and payroll. Well-designed information systems provide important benefits like increased efficiency, effectiveness and quality of decision-making across business activities.