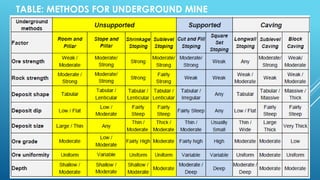
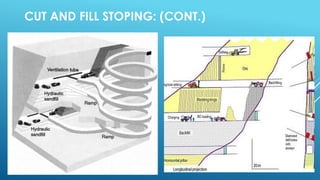
This document discusses different types of underground mining methods. It focuses on cut and fill stoping, describing the process as mining the orebody in horizontal slices from the bottom up while backfilling the voids left behind. The ore is drilled, blasted, loaded onto vehicles and transported out of the mine through ramps and passes. Once a slice is emptied, the space is partially backfilled to provide support for mining the next slice upwards. Both overhand and underhand cut and fill stoping are discussed. Advantages include selective mining with minimal dilution while disadvantages include being labor intensive and cyclical with safety issues from working under freshly cut roof rock.