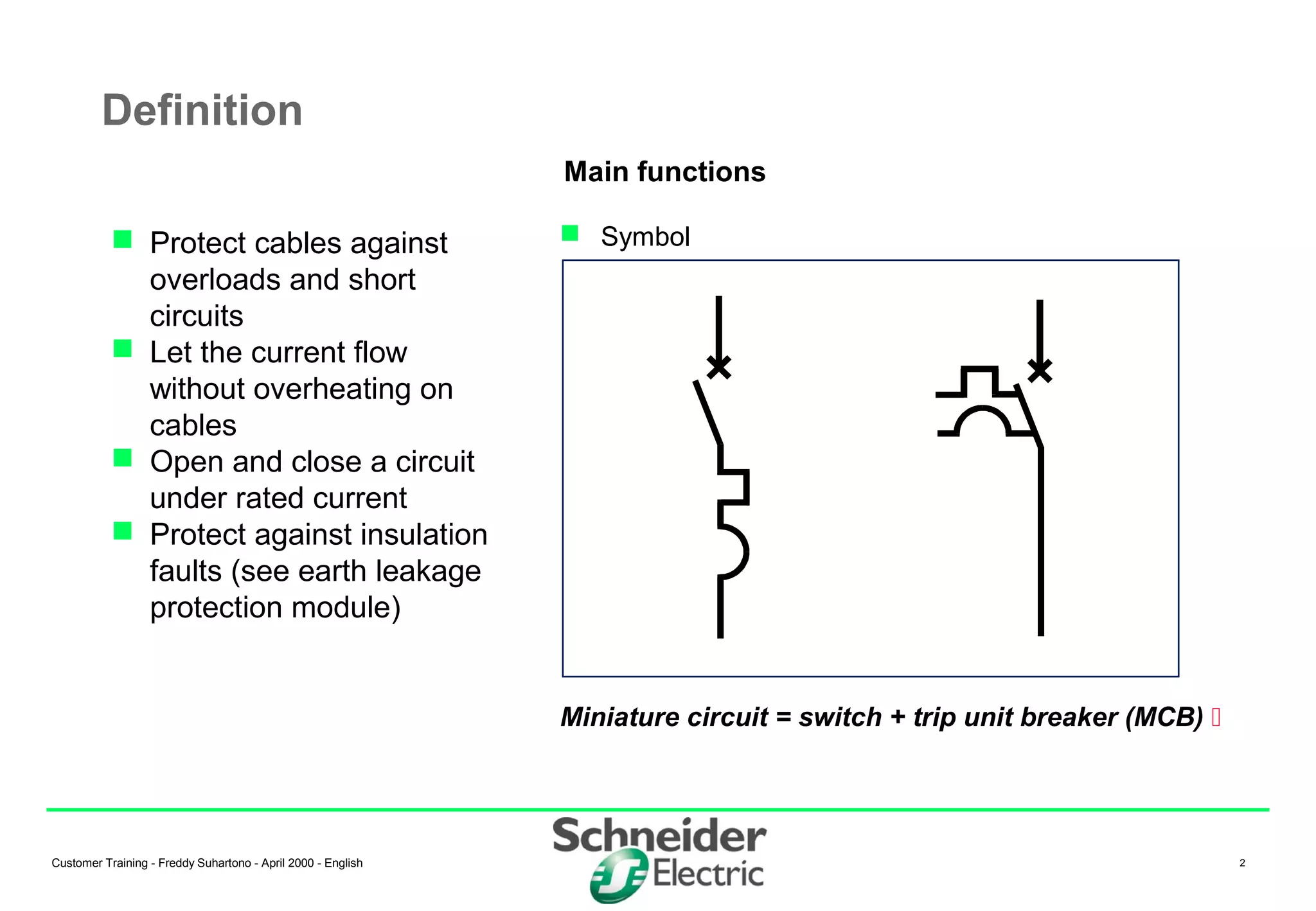
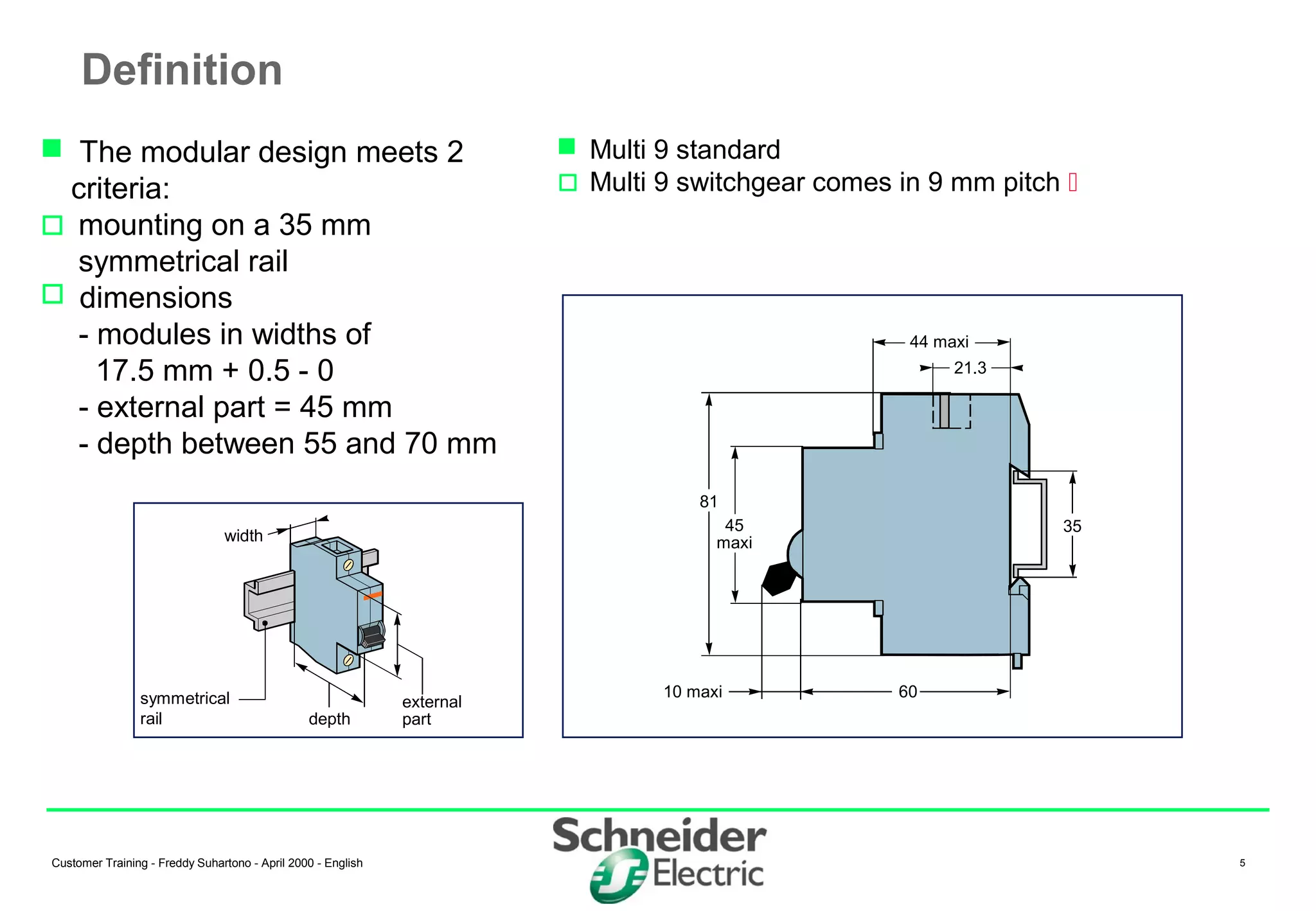
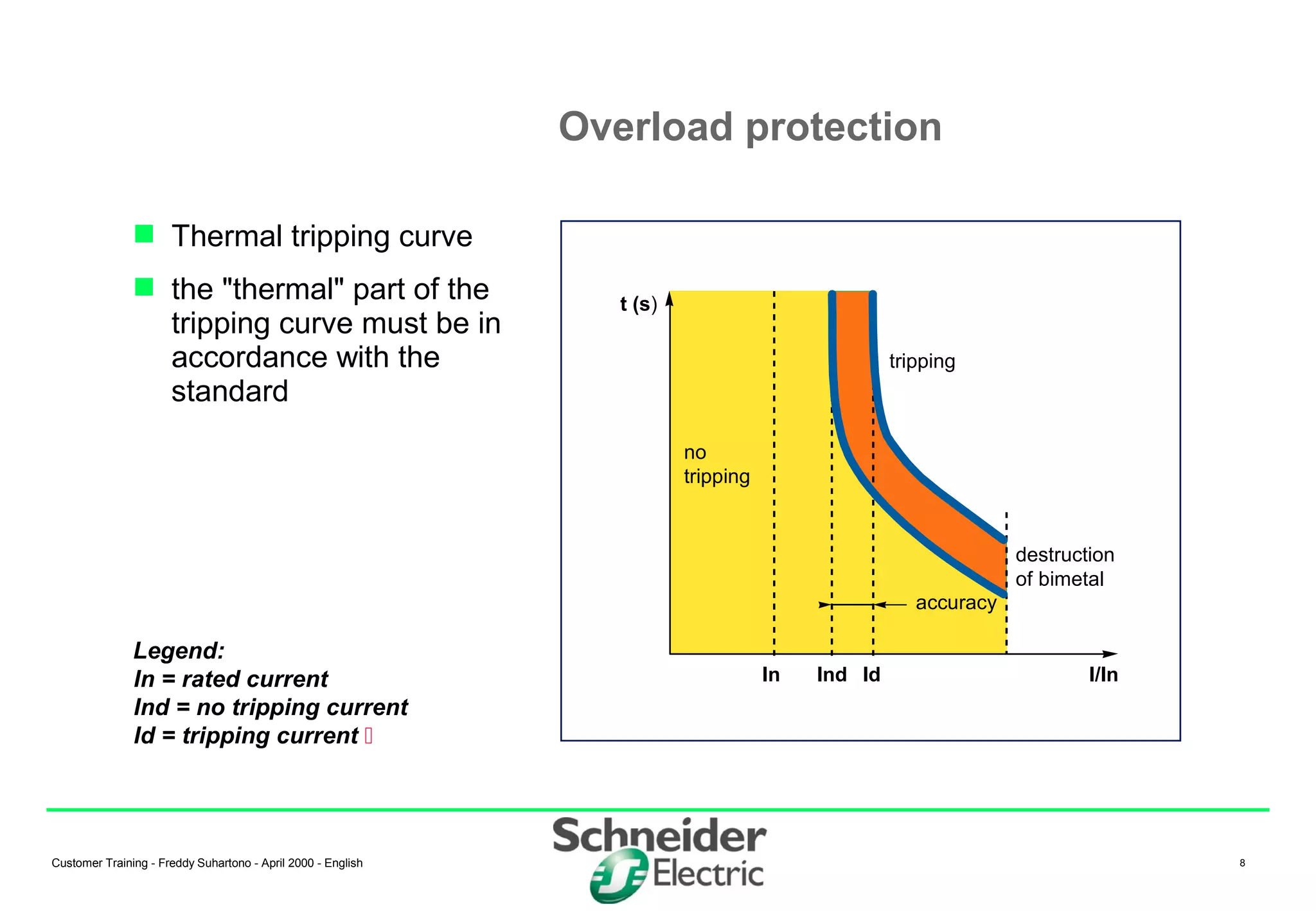
(1) Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) are devices that protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits. They contain a switch and trip unit that can open and close a circuit under rated current. (2) MCBs have standardized modular dimensions and fit into distribution boards. They use a bimetal strip to detect overloads and a magnetic trip to detect short circuits. (3) The tripping characteristics of MCBs can be selected using different curves (B, C, D, etc.) to provide appropriate protection for different circuit types like transformers or motors.