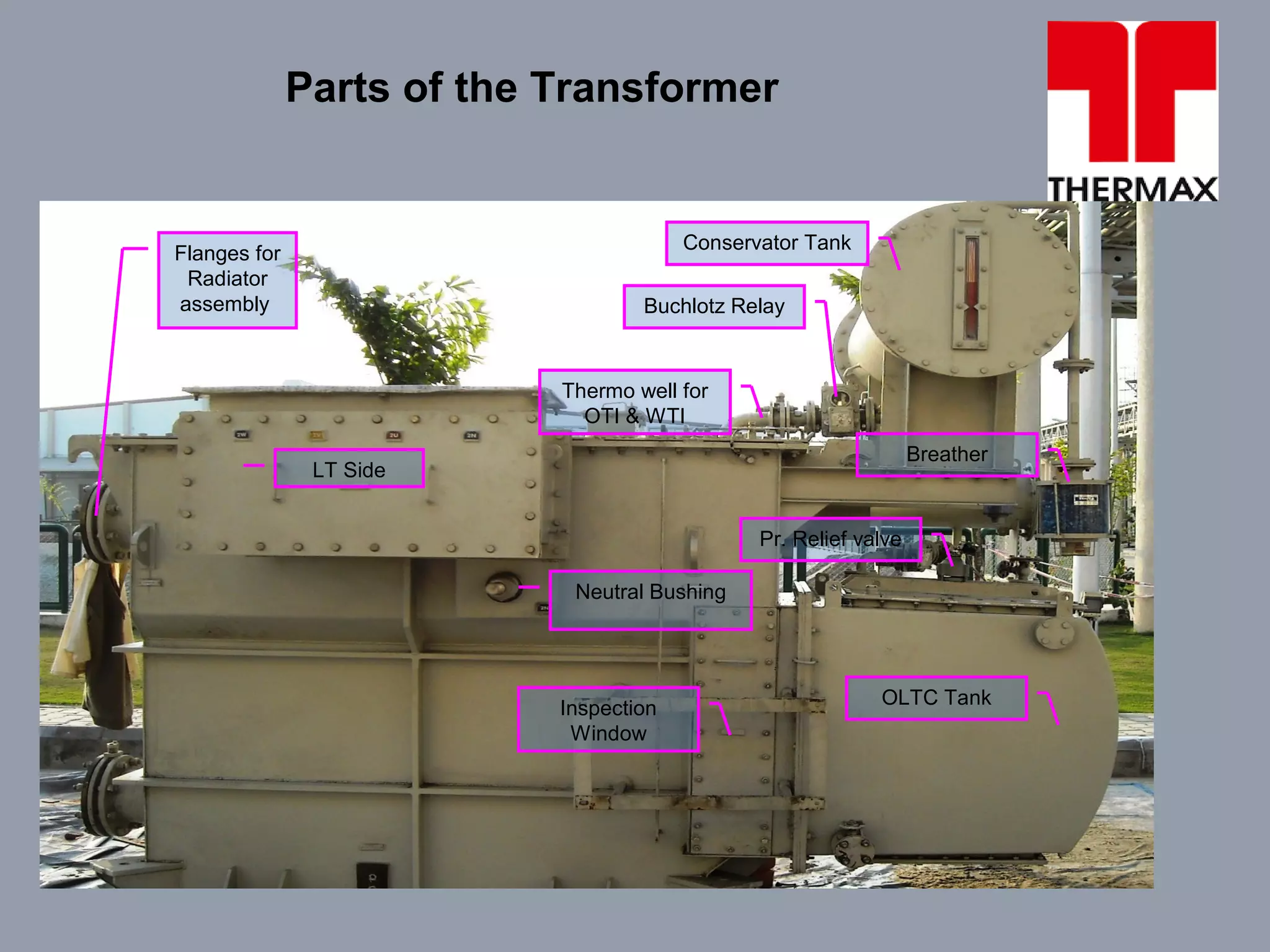
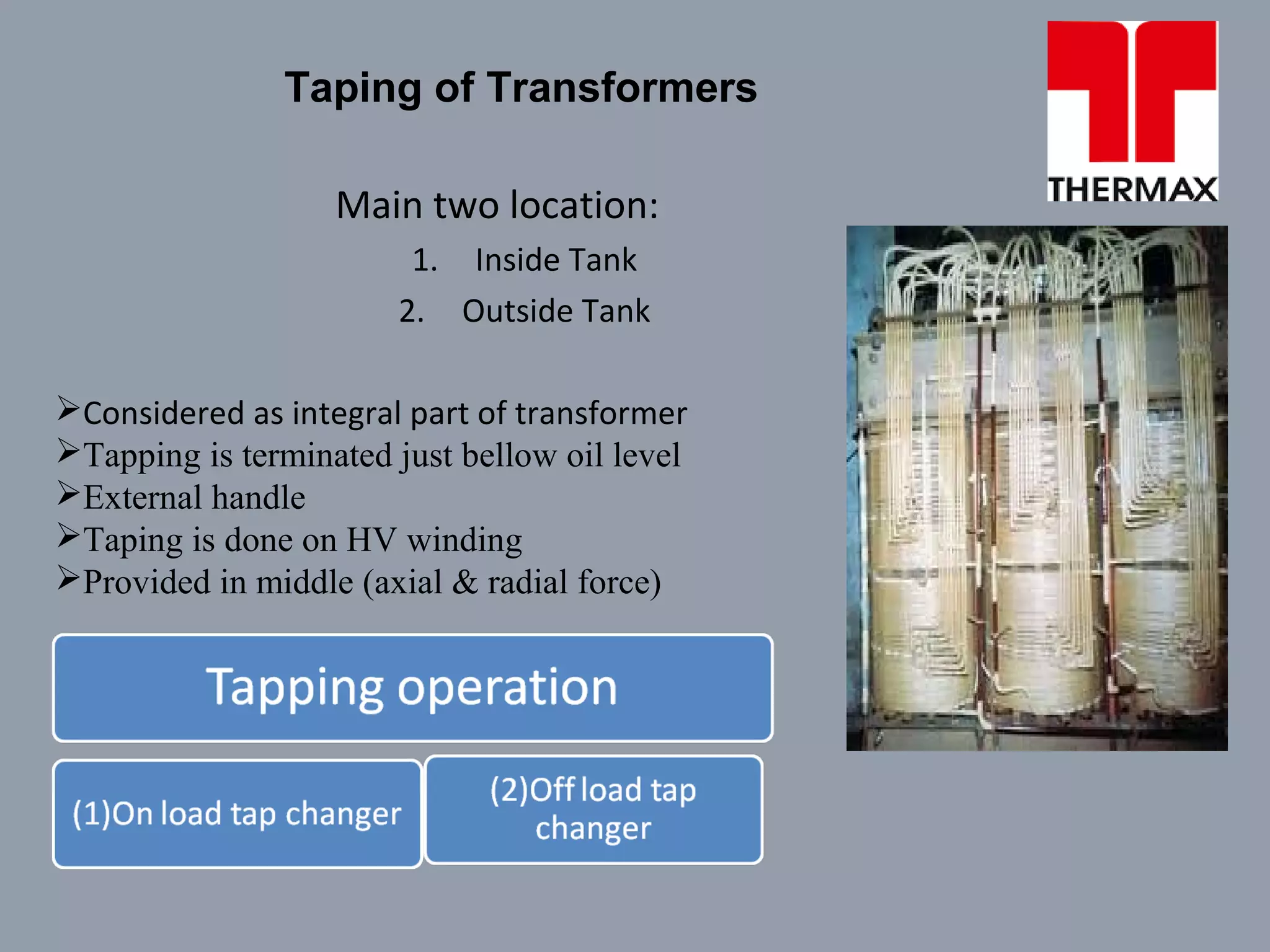
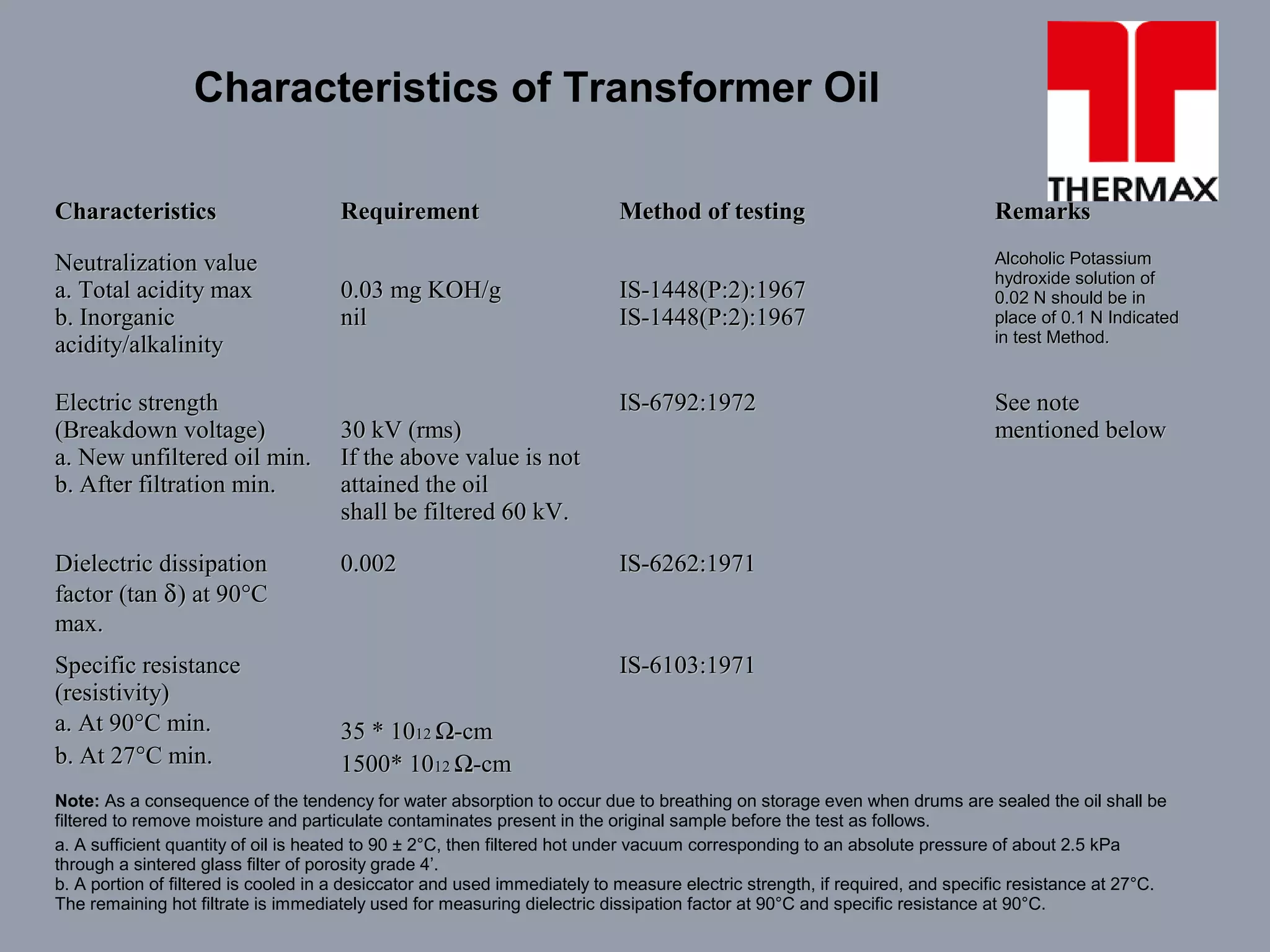
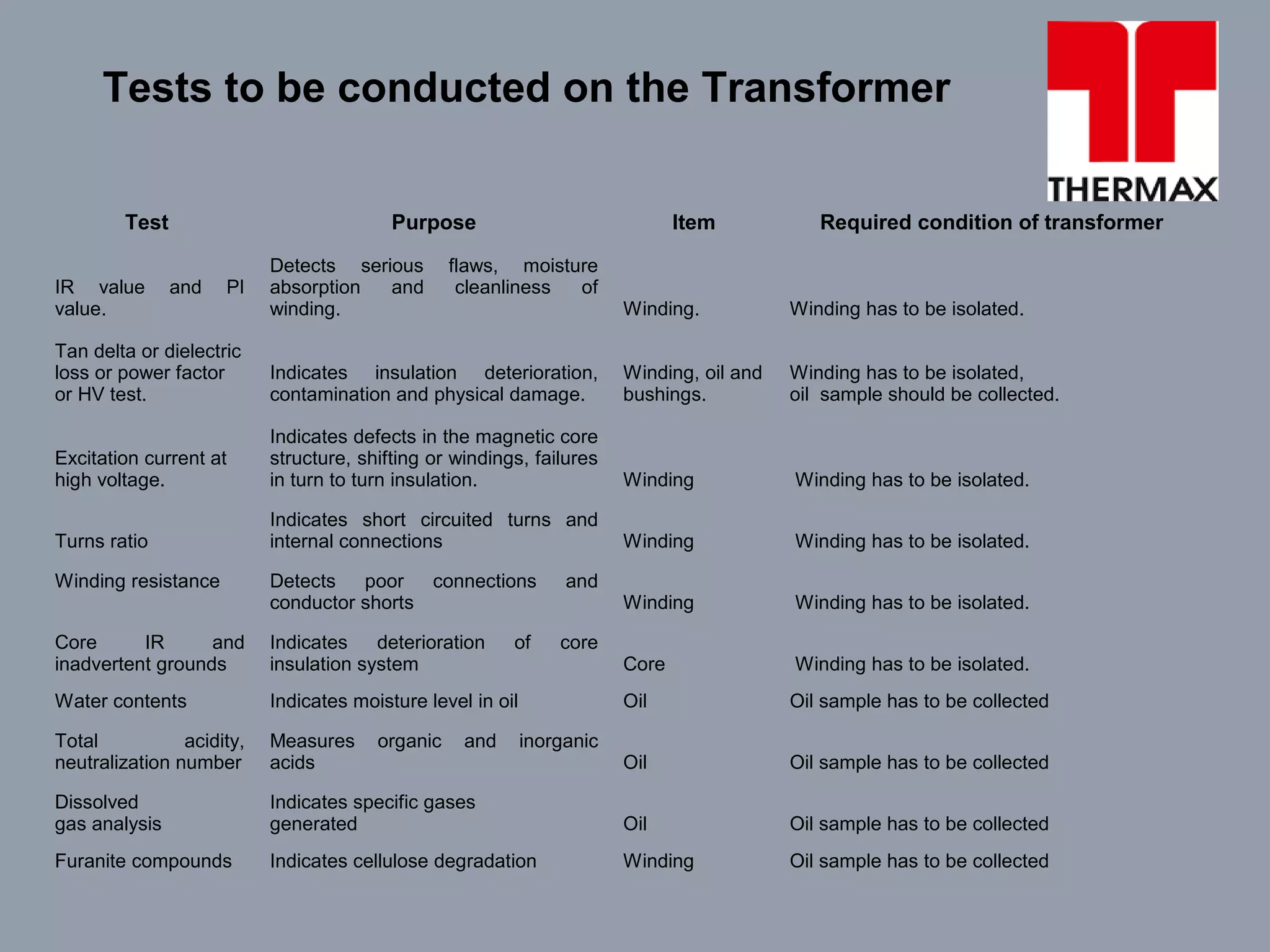
The document provides information on operation and maintenance of distribution transformers. It defines transformers and describes their working principle of mutual electromagnetic induction. It then discusses transformation ratios, the purposes of transformers, their advantages, types, parts, insulation, testing, and maintenance procedures. Key points covered include daily, quarterly and yearly maintenance checks, oil testing parameters, and common transformer tests like ratio, no load, short circuit and insulation tests.