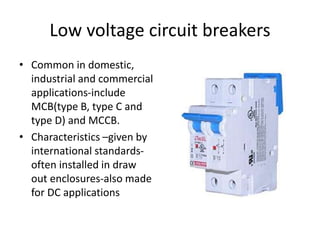
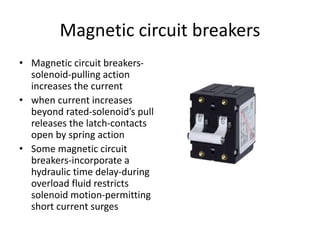
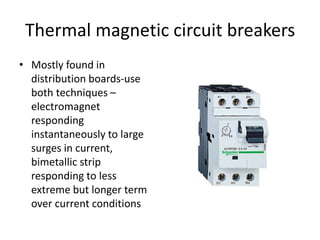
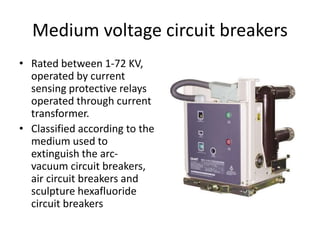
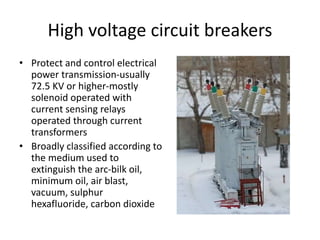
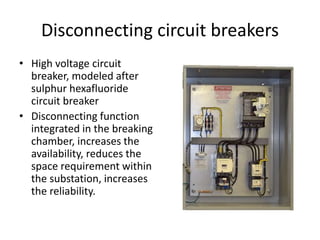
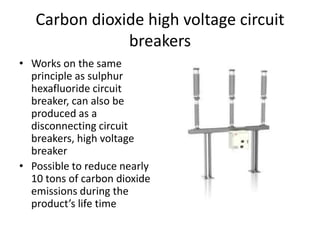
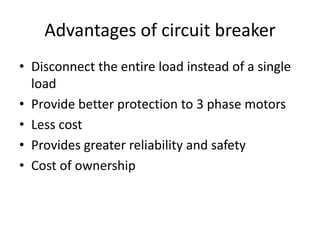
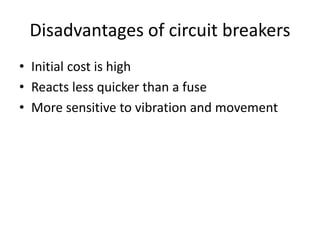
The document discusses different types of circuit breakers, their origins, operations, and uses. It begins by introducing circuit breakers and their basic functions of fault detection and current interruption. It then discusses the early development of circuit breakers by Thomas Edison in 1879 and the modern miniature circuit breaker patented in 1924. The remainder of the document describes the operations, components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of various low voltage, medium voltage, high voltage, magnetic, thermal-magnetic, common trip, disconnecting, sulfur hexafluoride, vacuum, and carbon dioxide circuit breakers.