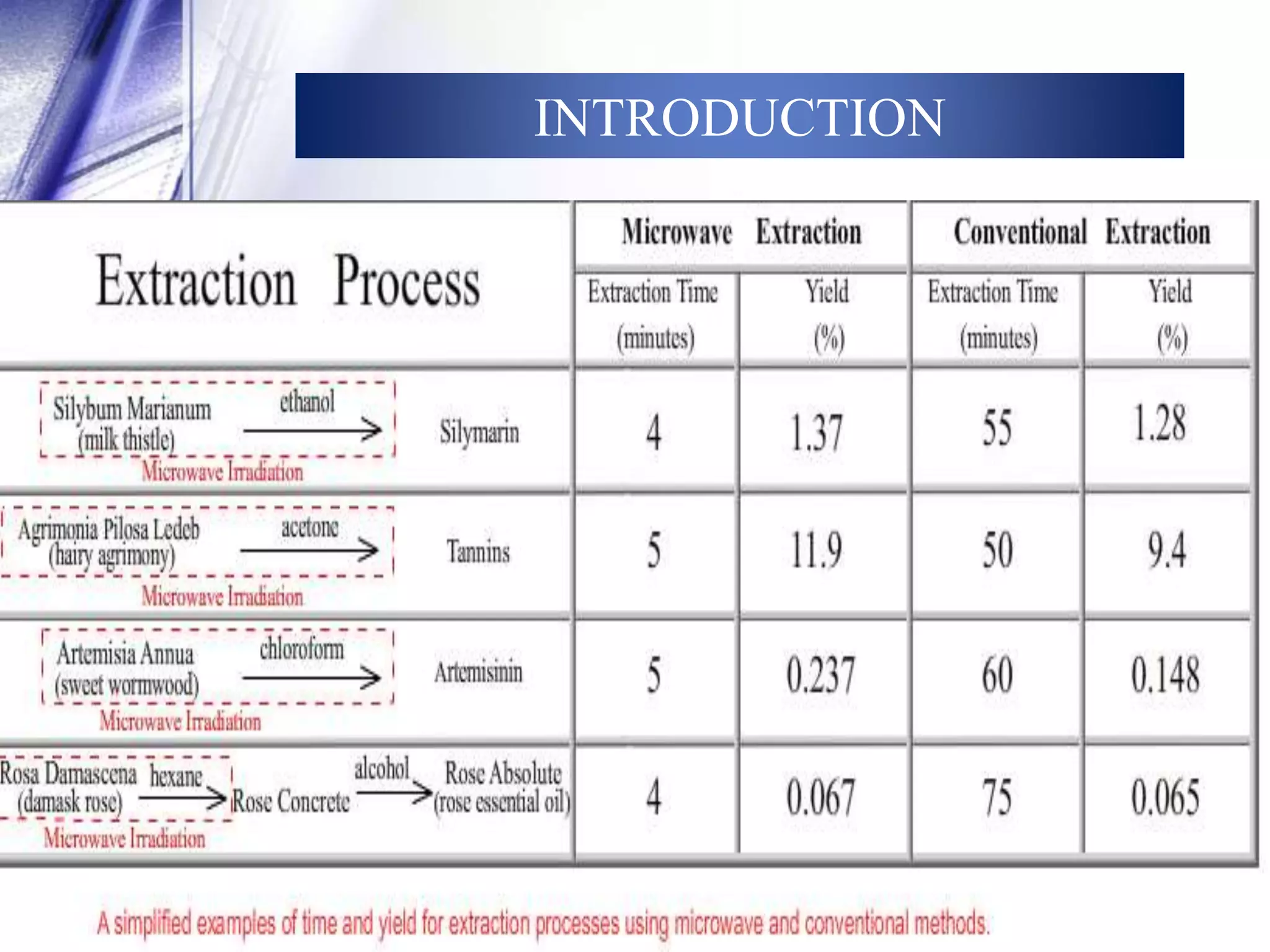
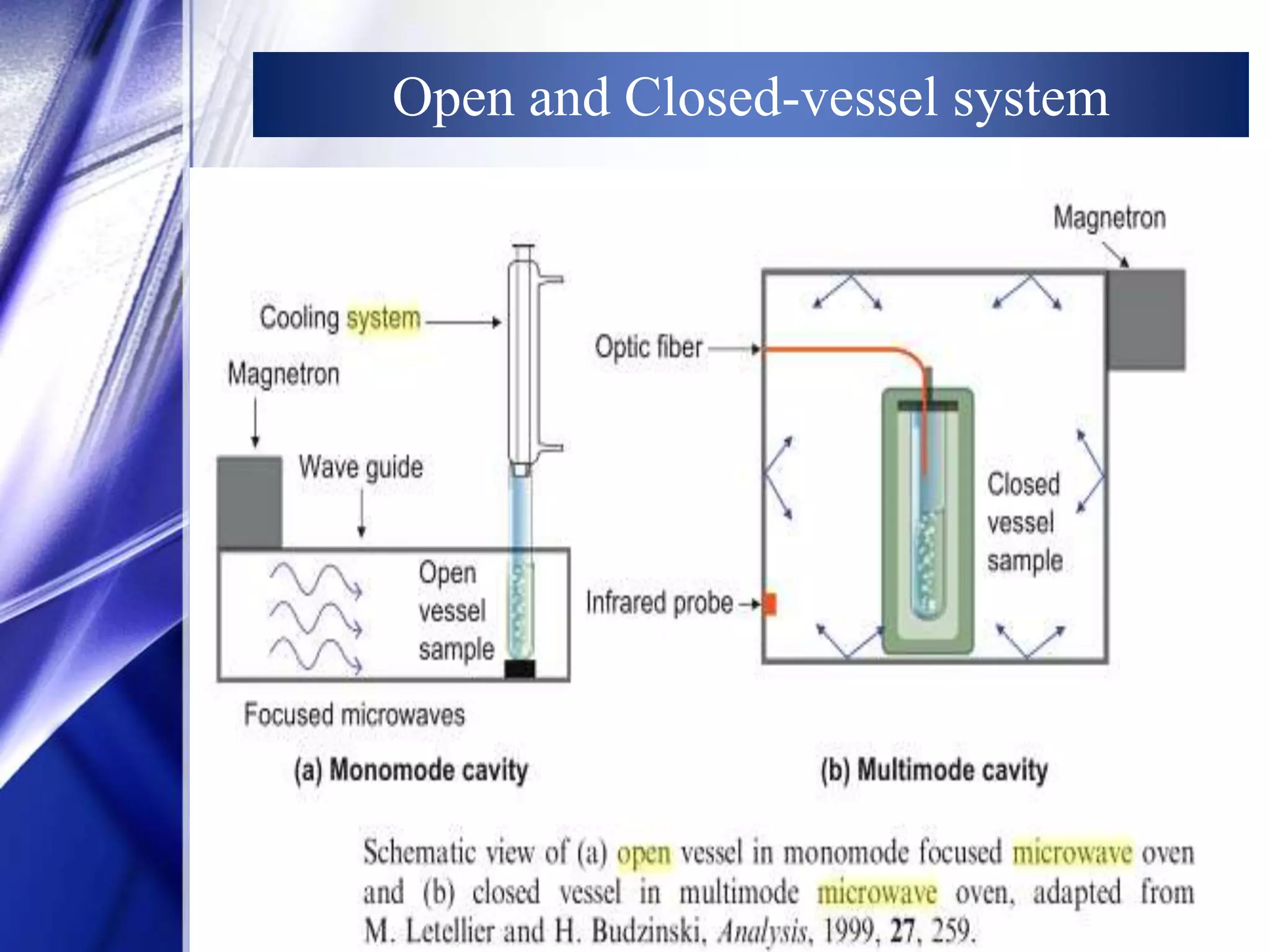
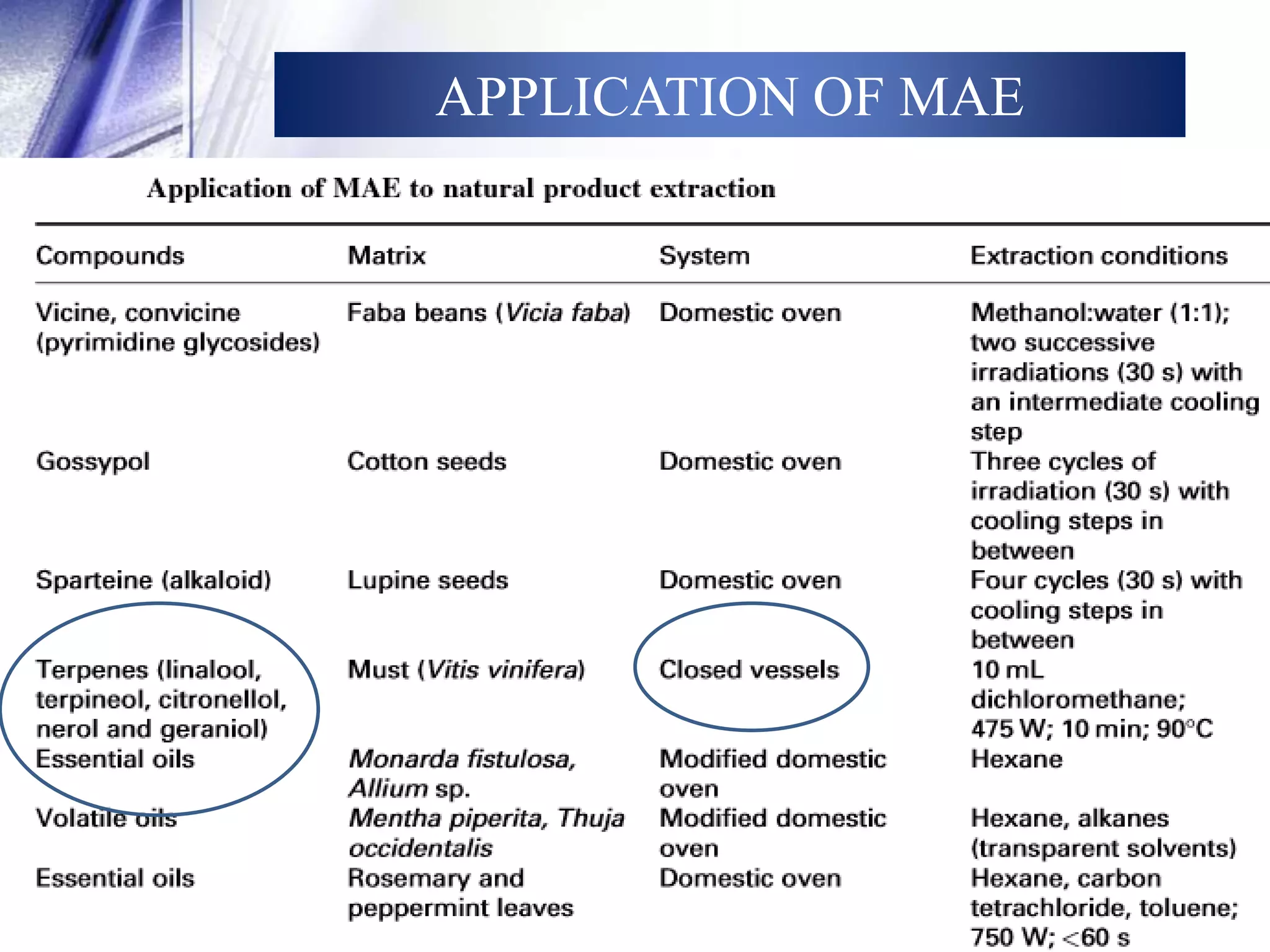
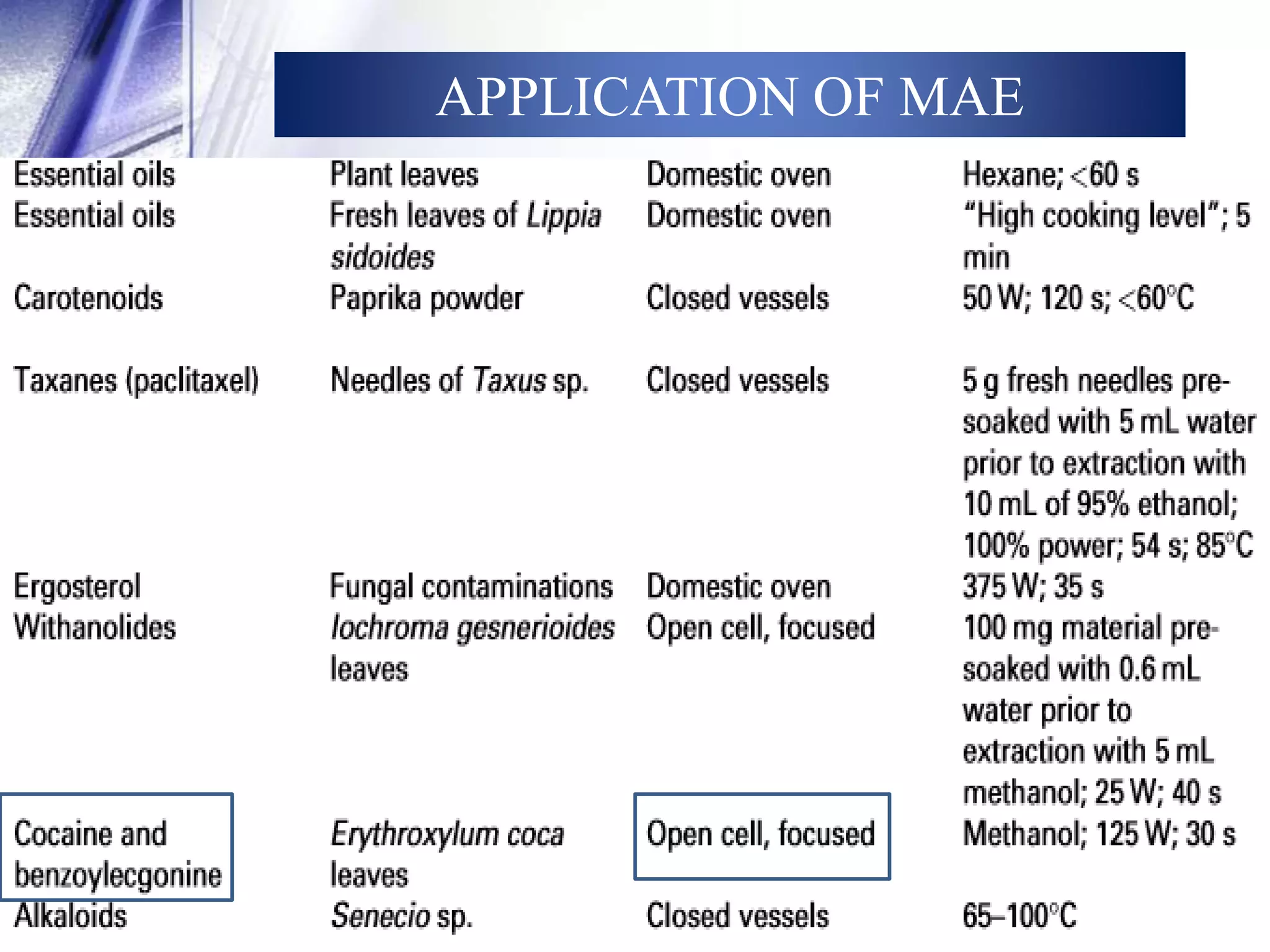
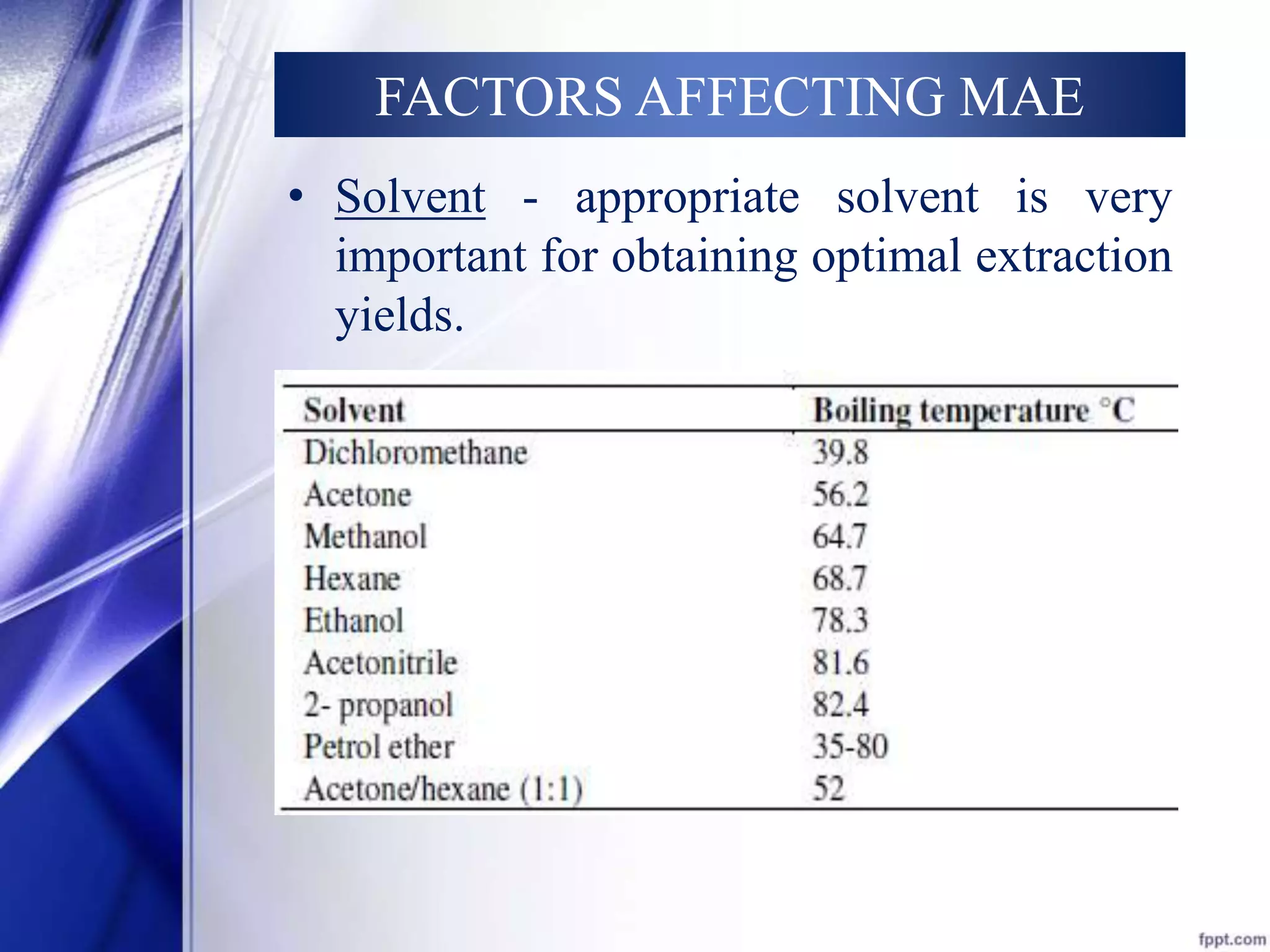
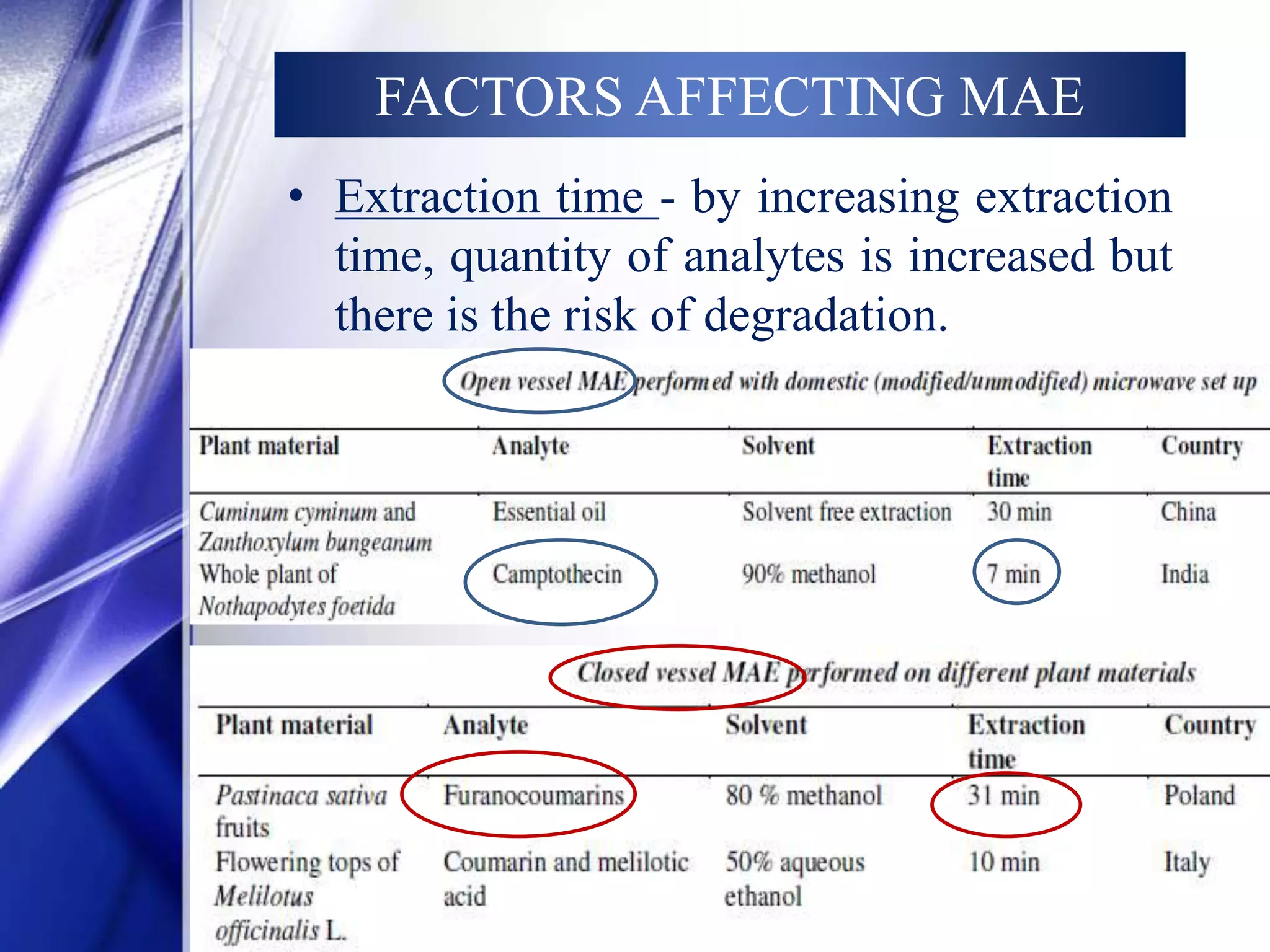
This document discusses microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), an efficient method for deriving natural compounds from plants. MAE uses microwave energy to heat plant materials mixed with solvents, extracting compounds faster than conventional methods. It describes the principles of microwave heating, closed and open vessel extraction systems, factors affecting MAE like solvent, time, power and temperature, and its applications. MAE provides benefits of reduced extraction time, improved yields, and ability to extract thermolabile substances.