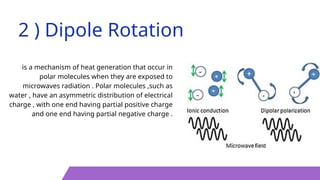
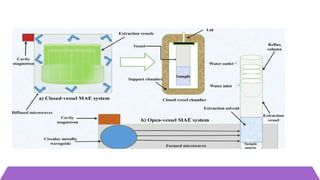
Microwave Assisted Extraction (MAE) is an advanced technique that utilizes microwaves to efficiently extract bioactive compounds from plant materials by generating heat through ionic conduction and dipole rotation. It offers rapid extraction, reduced solvent usage, improved yields, and avoids thermal degradation. MAE can be conducted using closed vessel or atmospheric systems, making it a convenient and effective method for isolating desired compounds.