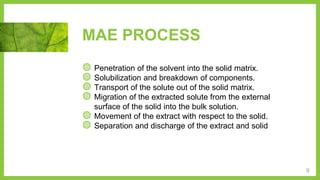
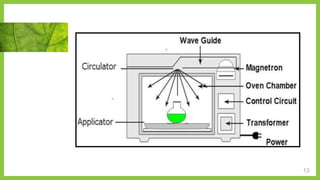
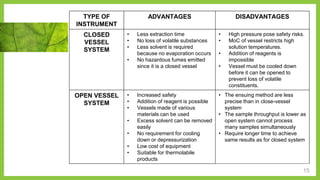
The document discusses microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), a technique that utilizes microwaves to enhance the efficiency of extracting phytoconstituents from solid matrices compared to conventional methods. It highlights the advantages of MAE, including reduced extraction time and lower solvent consumption, while also addressing factors affecting its effectiveness such as solvent choice, microwave power, and temperature. The document compares closed and open vessel systems for MAE, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages.