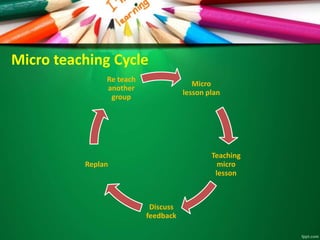
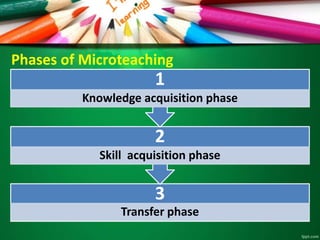
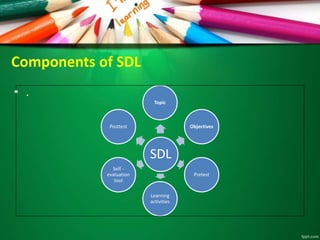
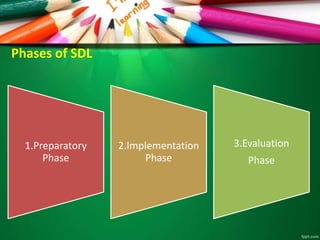
This document discusses microteaching and self-directed learning. It defines microteaching as a scaled down teaching session with 5-10 students over 5-20 minutes, focusing on developing one teaching skill at a time. The microteaching cycle involves planning, teaching, receiving feedback, and reteaching. Self-directed learning allows learners to take initiative for their own learning by identifying needs, goals, and resources without a teacher. It uses modules with objectives, learning activities, and assessments. Both microteaching and self-directed learning aim to help teachers and learners respectively improve their skills through practice and feedback in a structured way.