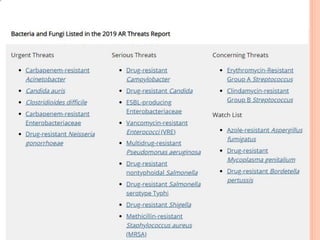
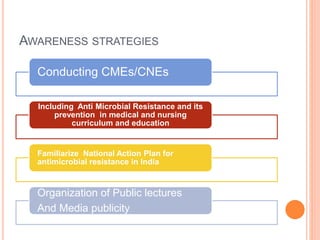
This document outlines 10 strategies to tackle antimicrobial resistance in India. It begins by discussing the magnitude of antimicrobial resistance, noting that in the US at least 2.8 million people get antibiotic-resistant infections each year resulting in over 35,000 deaths. In India, antimicrobial resistance poses a significant public health problem and India has high rates of resistance in both humans and food animals. The strategies proposed include increasing awareness among doctors, nurses, and the public; implementing surveillance and reporting; establishing antibiotic policies in hospitals; developing standard operating procedures; tailoring antibiotic doses; and promoting evidence-based practices.