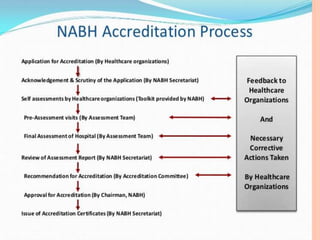
The document discusses the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH) and its Nursing Excellence certification program. It provides an overview of NABH, including that it has 10 chapters, 100 standards, and 683 objective elements. It then describes NABH Nursing Excellence, which contains 7 chapters and 48 standards focused on evaluating nursing services. The chapters cover topics like nursing resource management, nursing care of patients, management of medication, and nursing quality indicators. Obtaining NABH Nursing Excellence certification provides benefits like ensuring quality nursing care and services as well as opportunities for professional growth.