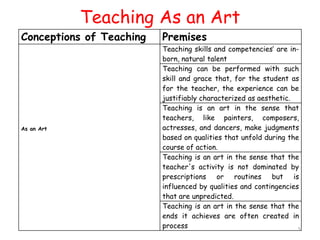
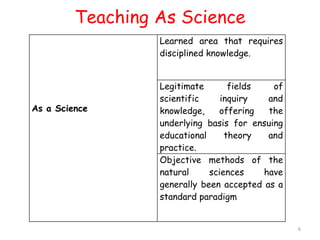
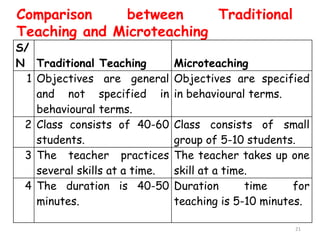
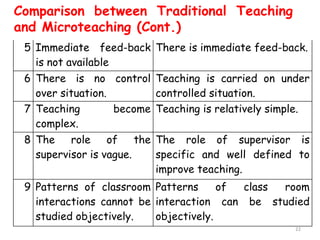
The document discusses microteaching and teacher education. It defines microteaching as a scaled-down teaching experience used to practice specific teaching skills. Microteaching allows pre-service teachers to focus on skills like lesson planning, questioning techniques, and classroom management in a low-stakes environment. The document also outlines the four components of teacher education: general education, subject preparation, general professional education, and specialized professional education. Microteaching is presented as a technique within professional education that allows new teachers to develop their instructional skills before full-time teaching.