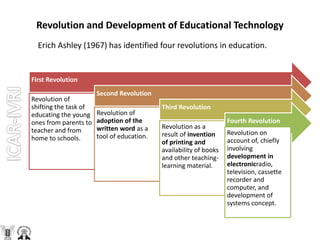
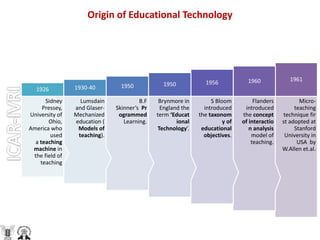
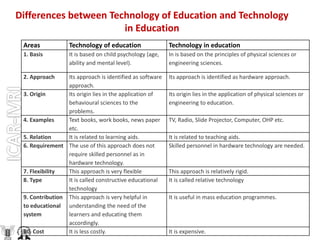
Educational technology refers to the application of scientific knowledge about learning to practical learning situations. It incorporates both the application of physical sciences and engineering technology to provide mechanical instruments for instruction (hardware approach), as well as the application of scientific principles to instruction through strategies like programmed instruction (software approach). The key components of educational technology are planning instruction, organizing content presentation, leading teaching activities, and evaluating student learning. It aims to make the teaching-learning process more effective and objective.