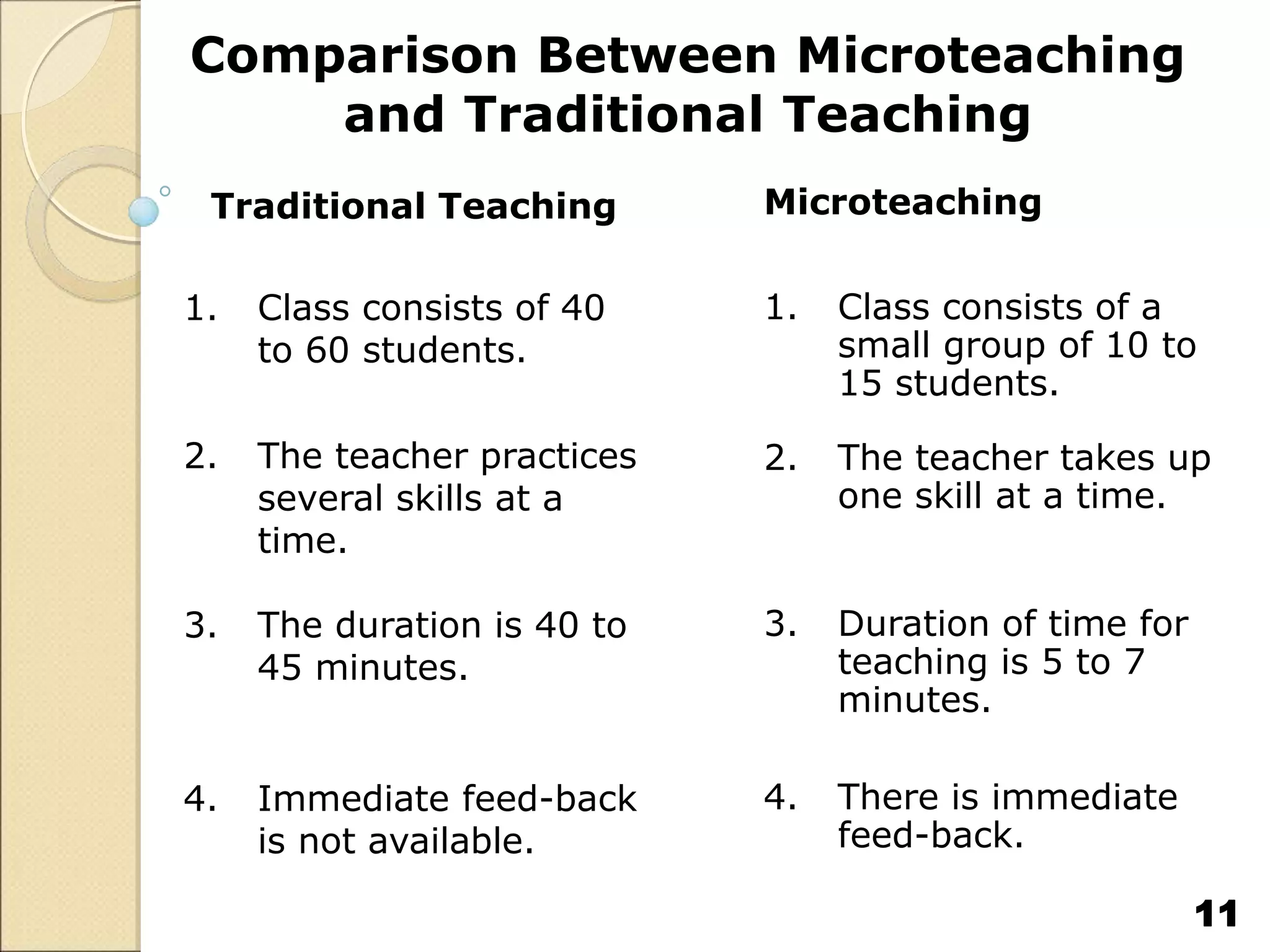
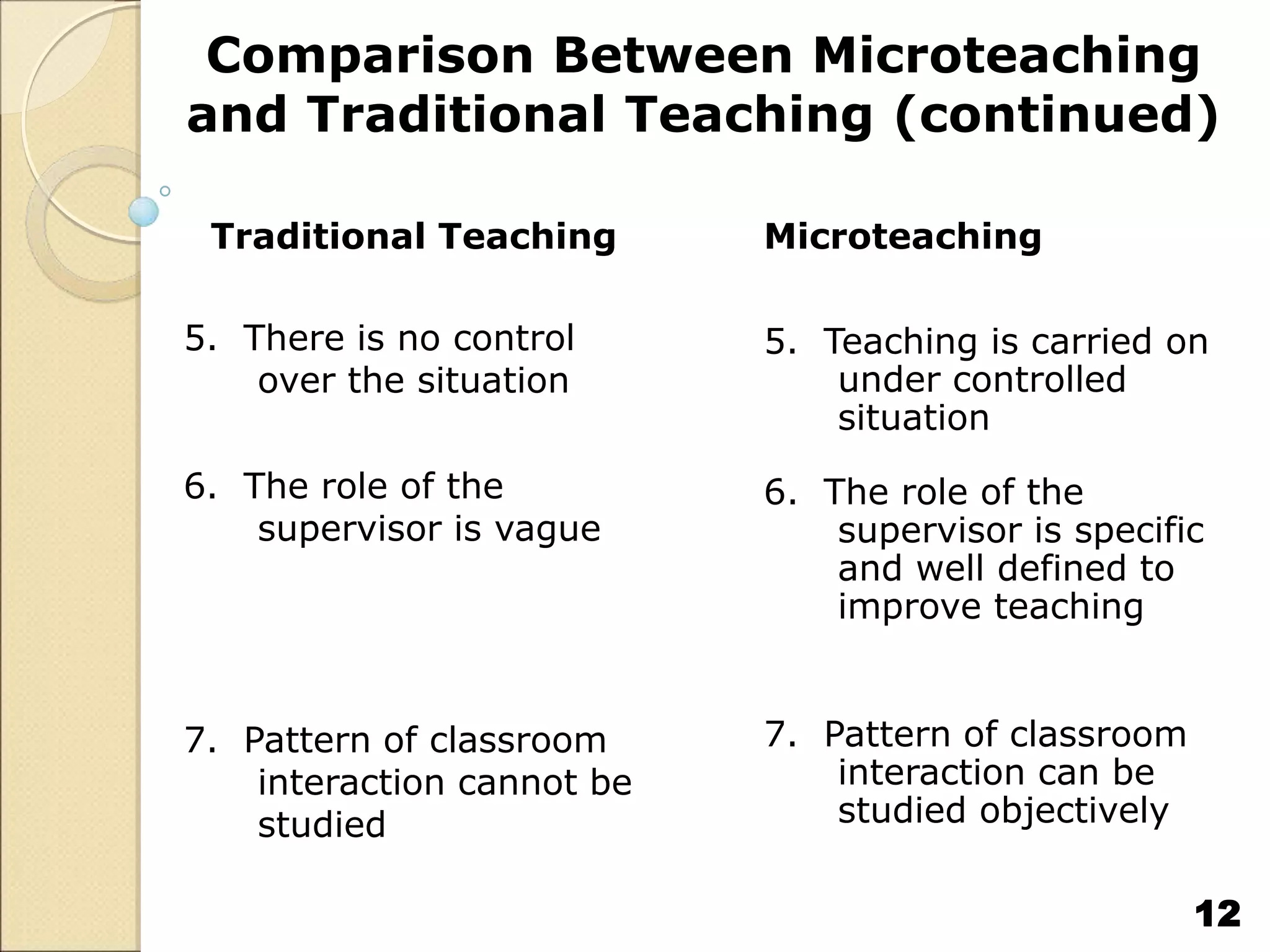
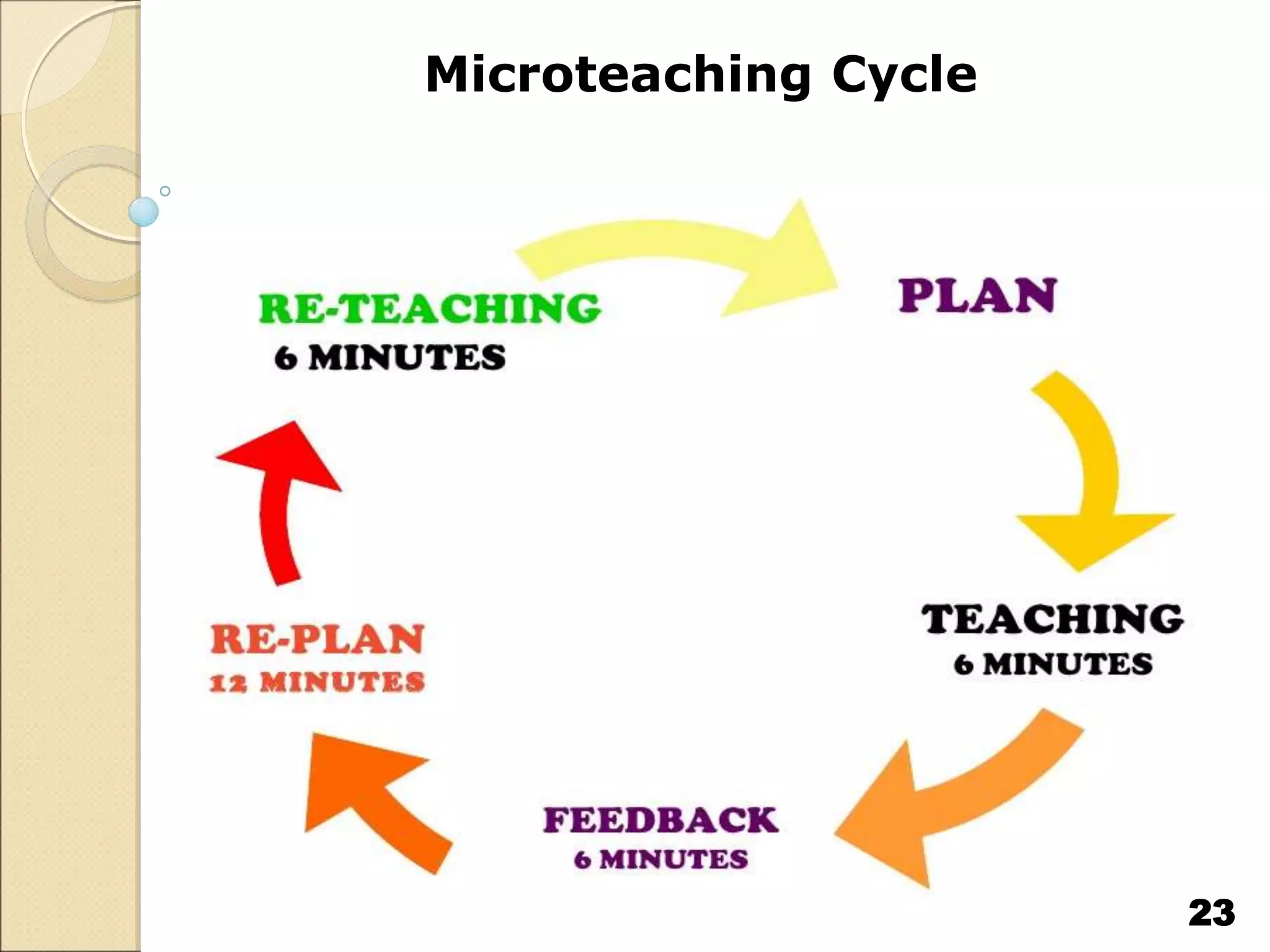
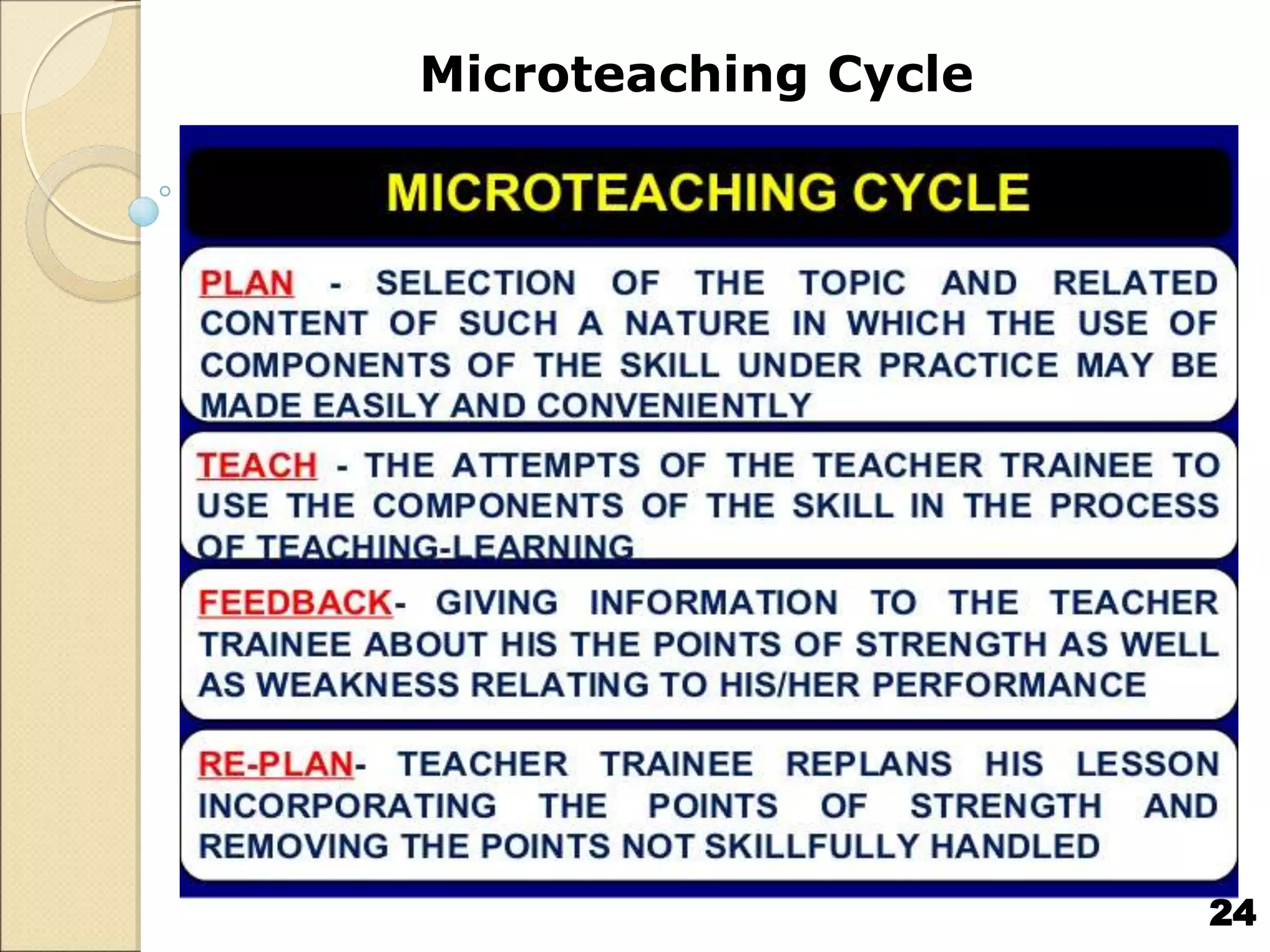
Microteaching is a technique used to train teachers. It involves teaching short lessons (5-7 minutes) to small groups of students (10-15) while focusing on one teaching skill at a time. The microteaching cycle includes planning, teaching, receiving feedback, re-planning, and re-teaching. Microteaching aims to help teachers develop and improve skills like introducing lessons, asking probing questions, explaining concepts, stimulating students, using the blackboard, integrating technology, and concluding lessons. It allows teachers to practice skills in a controlled environment and receive immediate feedback to enhance their teaching abilities.