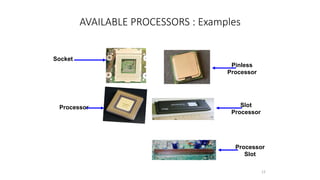
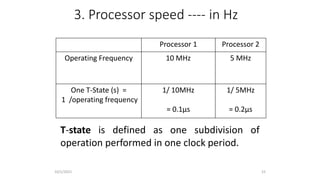
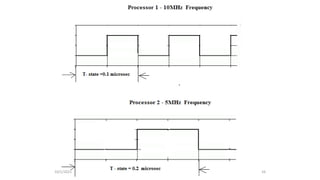
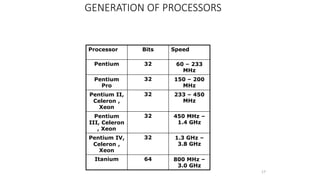
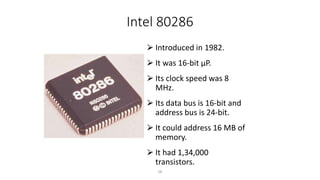
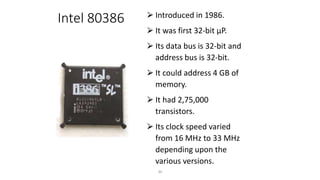
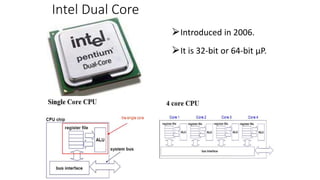
The document discusses the evolution of microprocessors from 1971 to present. It describes several key developments:
- The first microprocessor was the Intel 4004 released in 1971 which was a 4-bit chip designed for calculators.
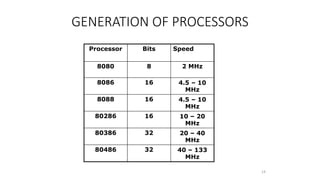
- Subsequent generations included 8-bit processors like the Intel 8008 and 8080, and 16-bit processors like the 8086. These had higher speeds and capabilities.
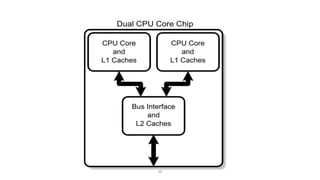
- Major advances included the 32-bit Intel 80386 in 1985 and 64-bit processors like the Itanium in 2000. Modern processors are multi-core and have speeds measured in gigahertz.
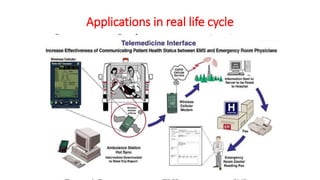
- Applications have grown from calculators to include instruments, traffic controls, military systems, and personal computers