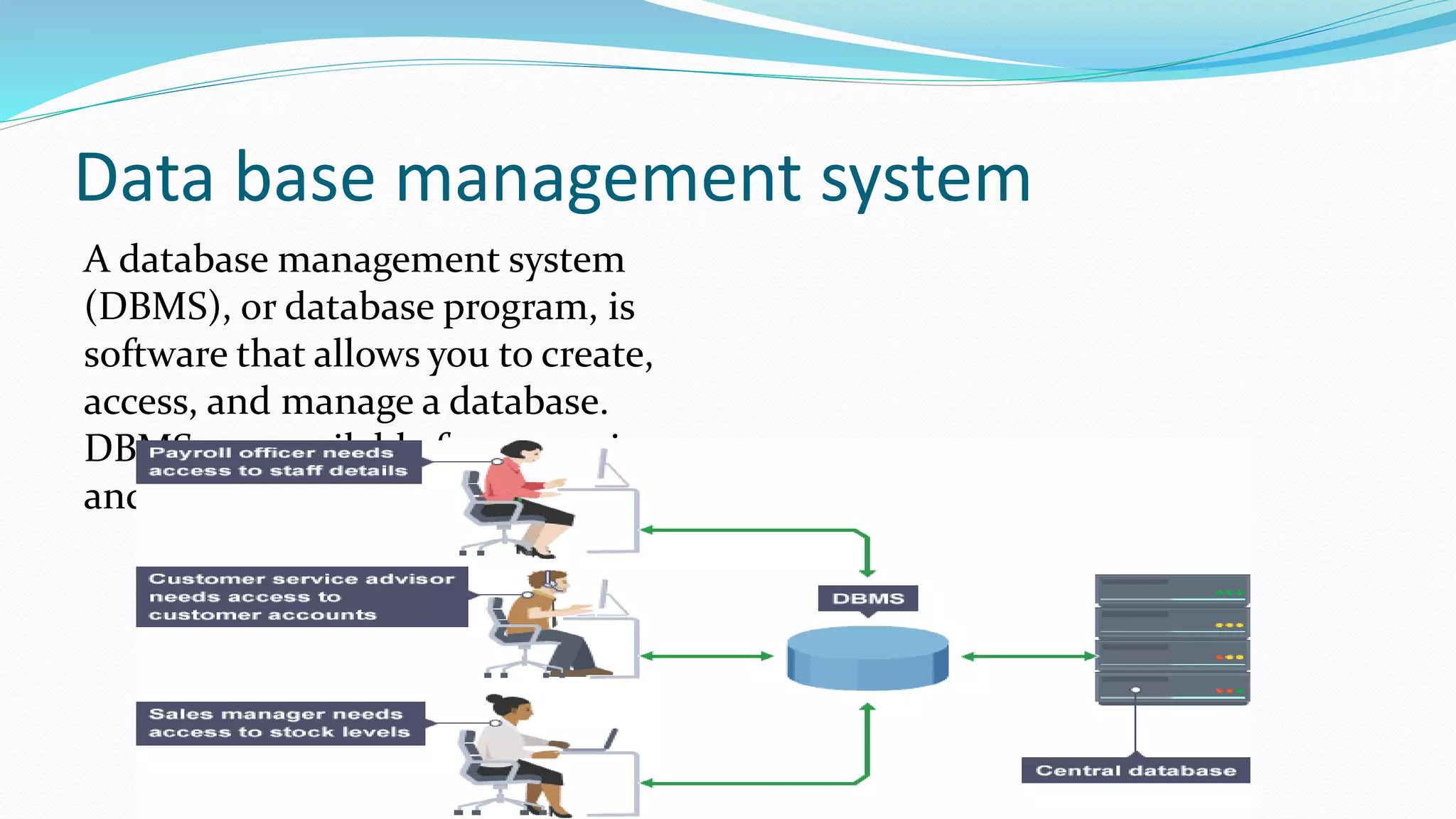
The document discusses database concepts and components. It lists the group members working on the project as Raja Muhammad noman, Muhammad aqib, Haider abbas, and Farhad abbas. It then covers topics such as the hierarchy of data, maintaining data through adding, changing and deleting records, and validating data. It also compares file processing and database approaches. The roles of database analysts and administrators in managing the database are also summarized.