The document discusses several topics related to computer hardware components:
1. It defines the system unit or tower as housing the main internal components like the motherboard, CPU, RAM, and case.
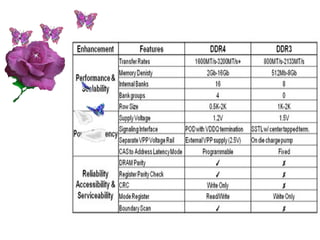
2. It provides a table comparing the differences between DDR1 and DDR2 memory.
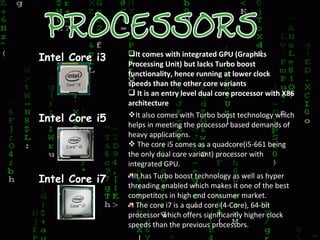
3. It summarizes the key differences between Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processors.
4. It lists the main components that are included on modern motherboards.
5. It describes the sequence of operations when a computer executes an instruction.
6. It provides more details on what is contained within the system unit, including the motherboard, power supply, cooling fan