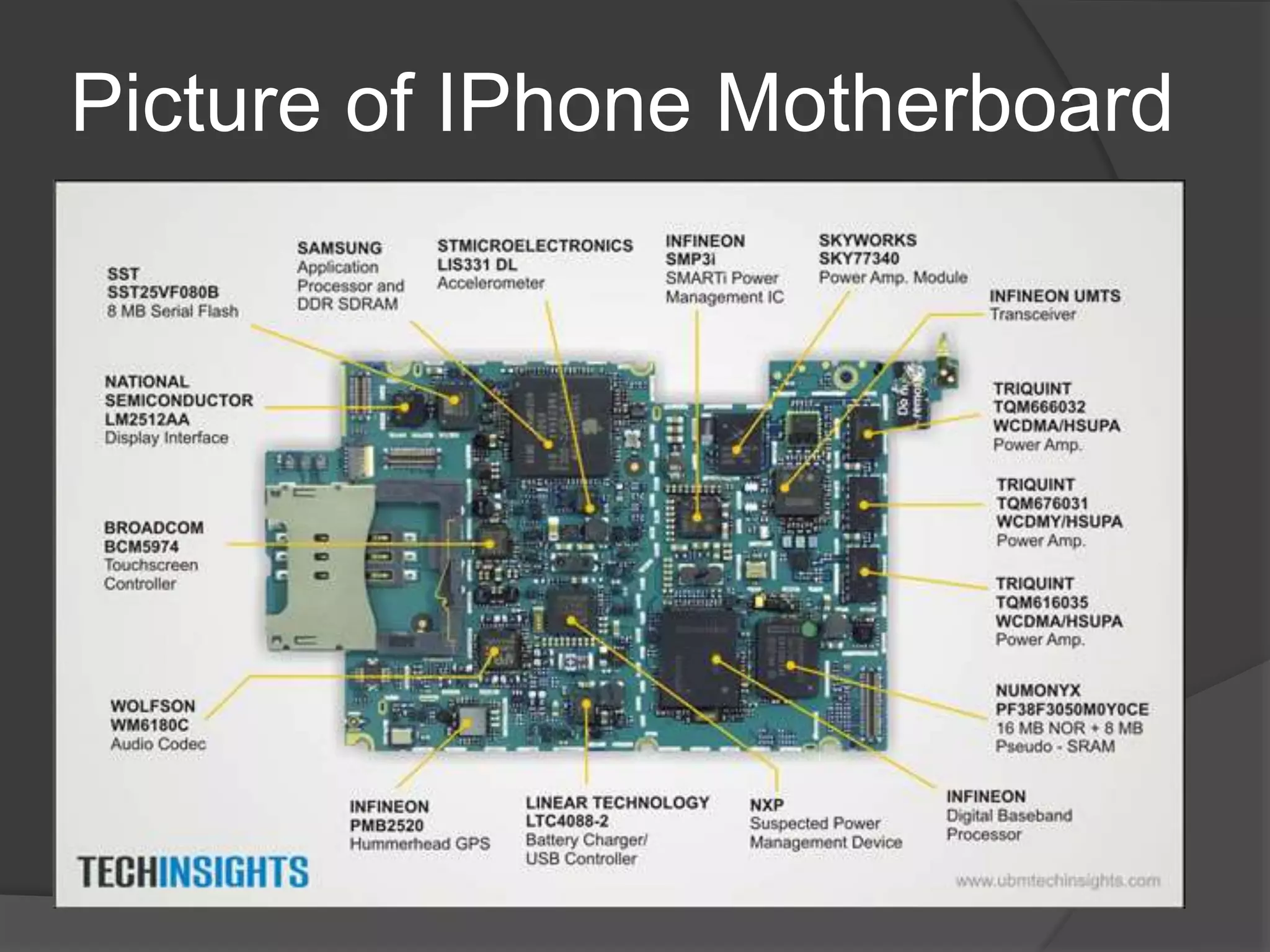
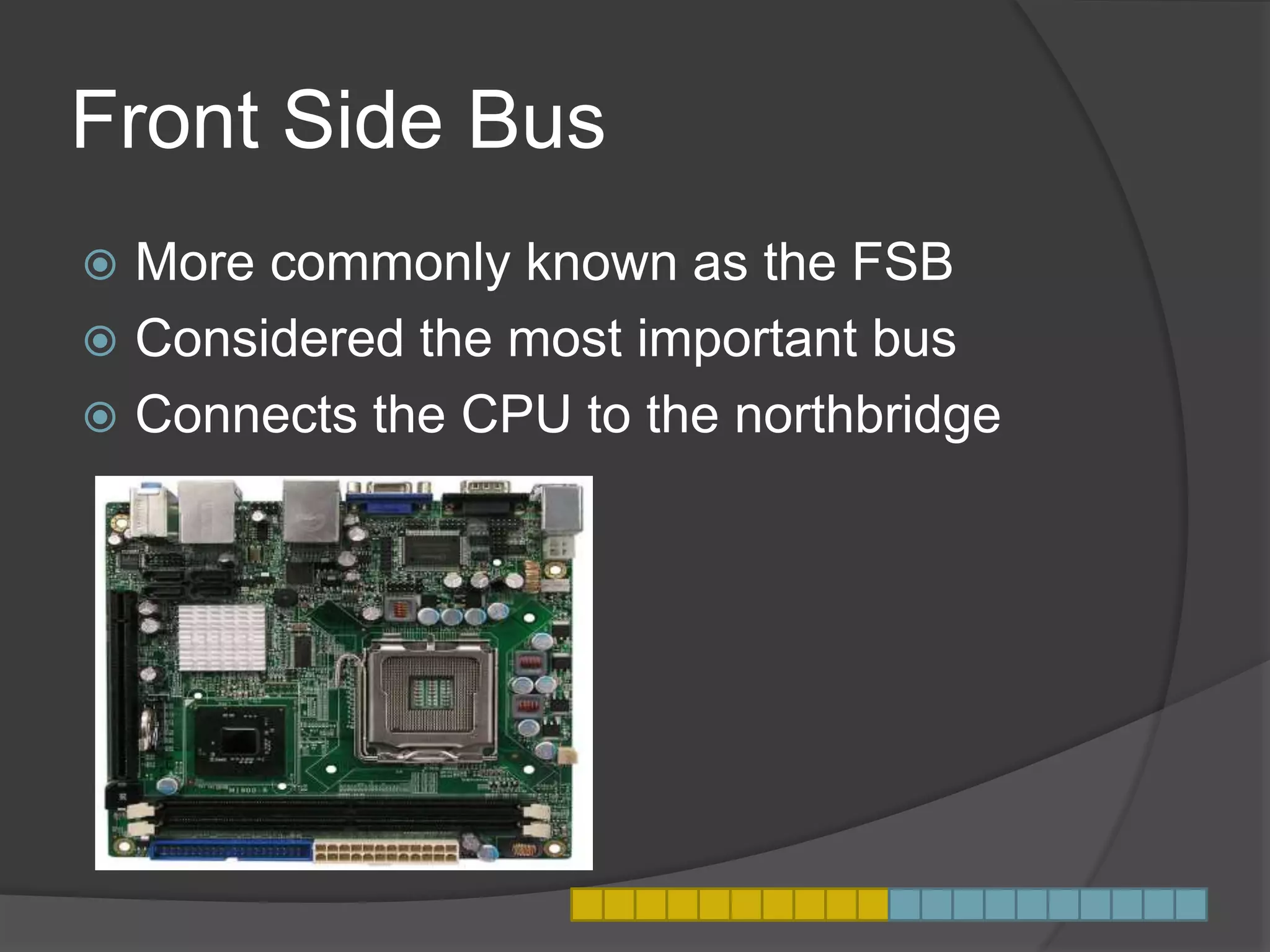
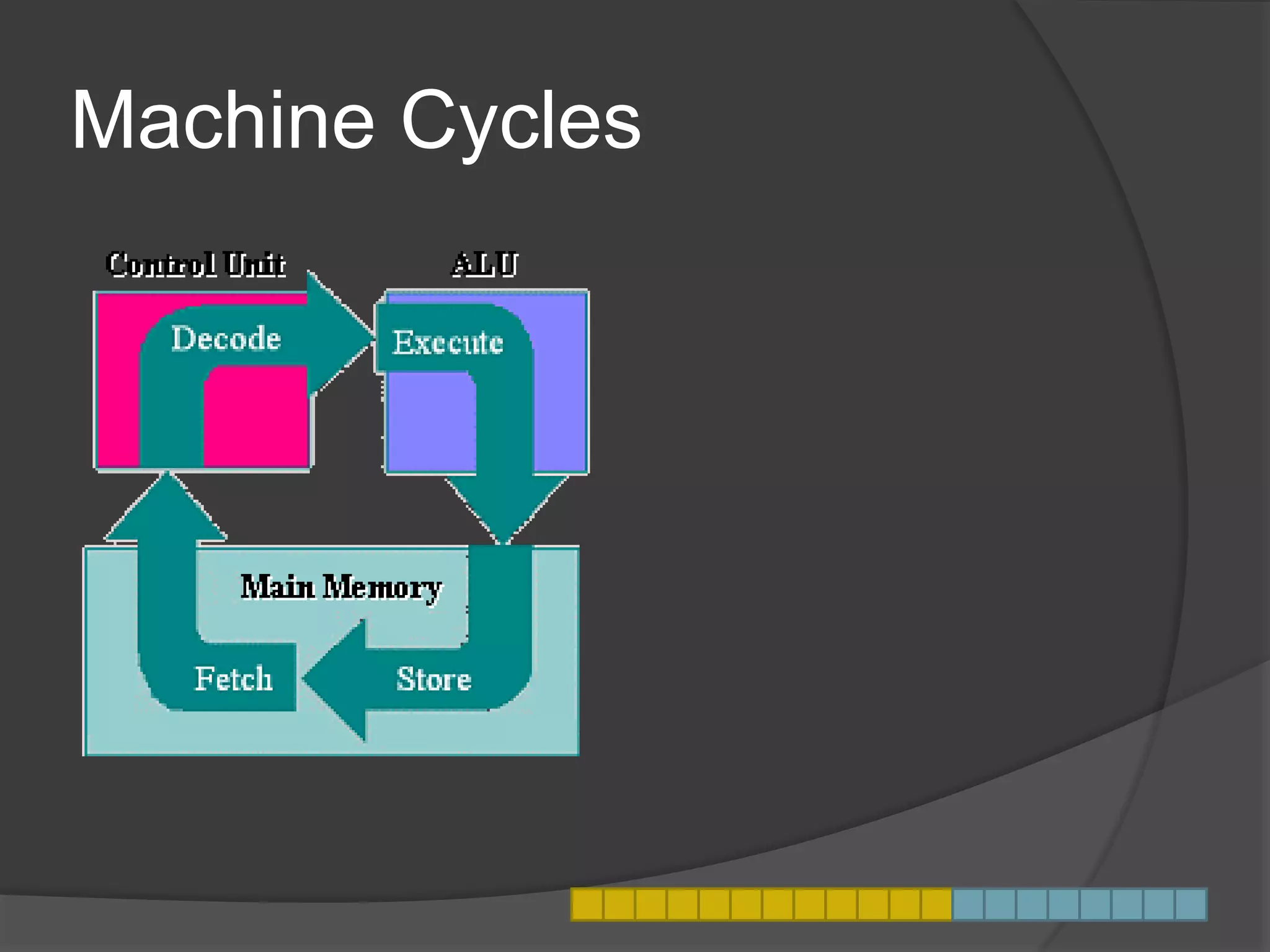
This document defines and explains what a motherboard is and its importance. A motherboard is the primary circuit board that connects all the core components of a computing device. It allows the components to communicate and work together. Motherboards are found in devices like desktop and laptop computers, phones, tablets, servers, and supercomputers. The document discusses different types and sizes of motherboards and describes the various buses that connect components via the motherboard, such as the front side bus. It also explains what a machine cycle is and how it provides an orderly method for a processor to execute software instructions.