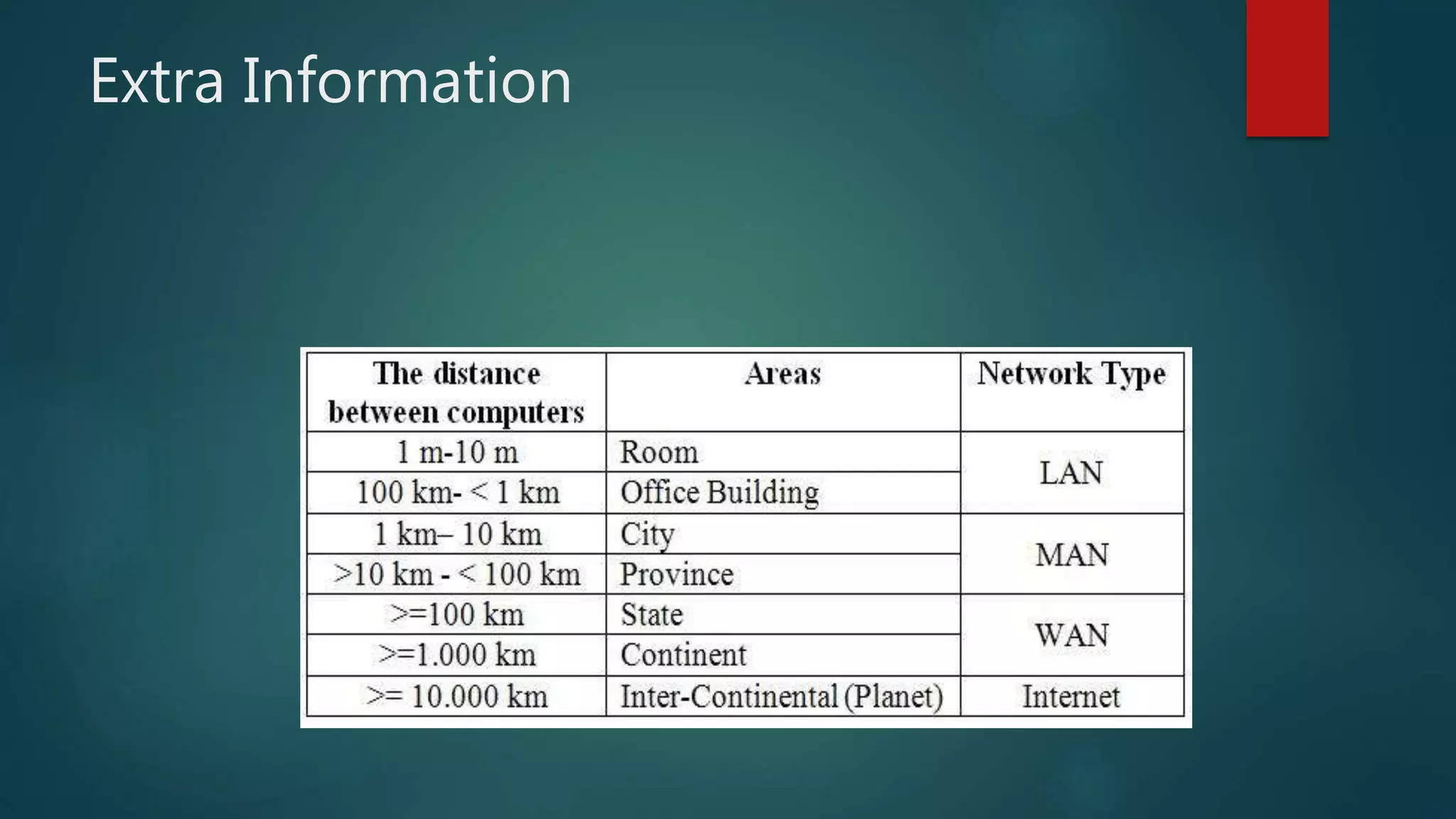
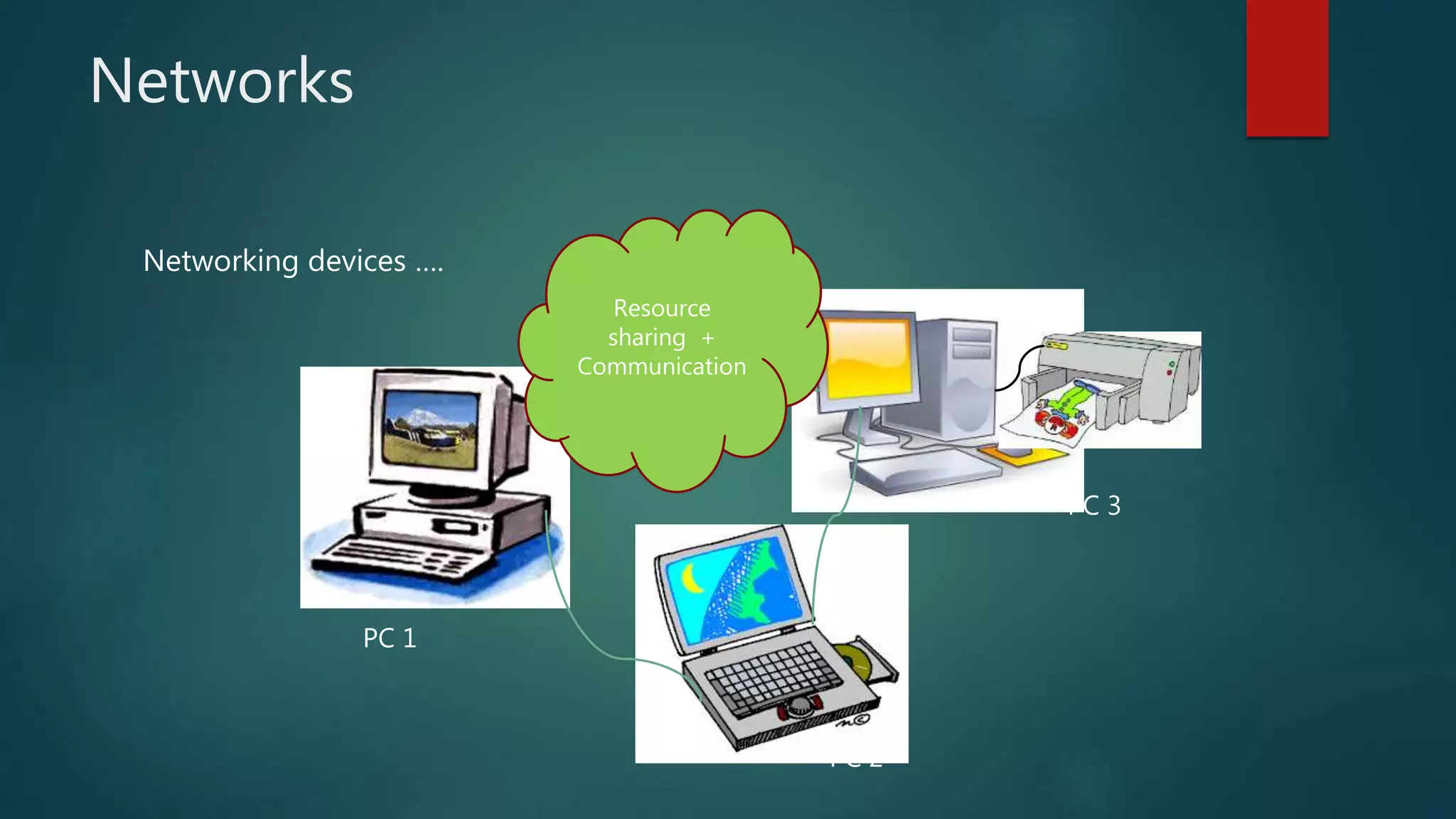
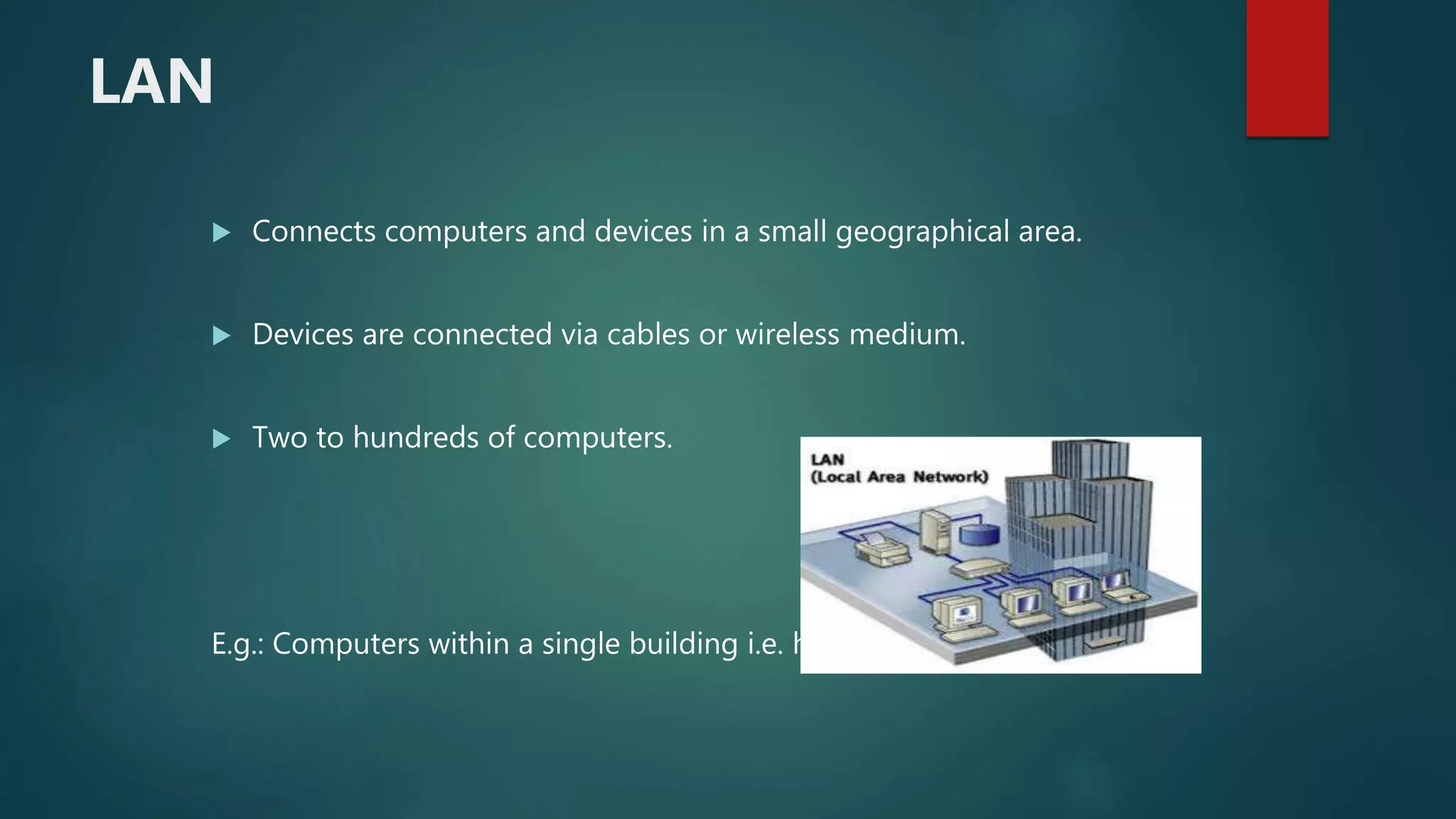
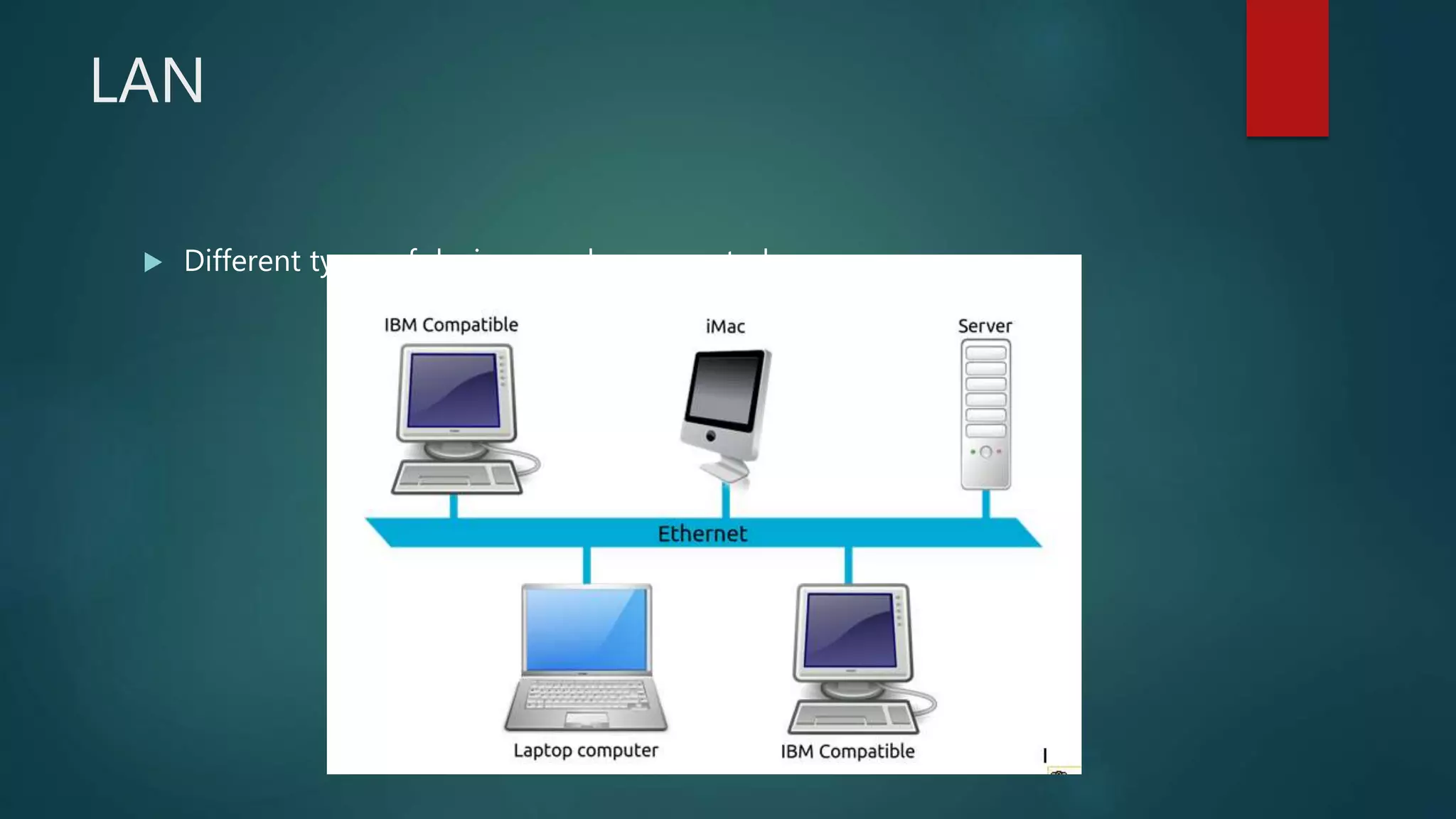
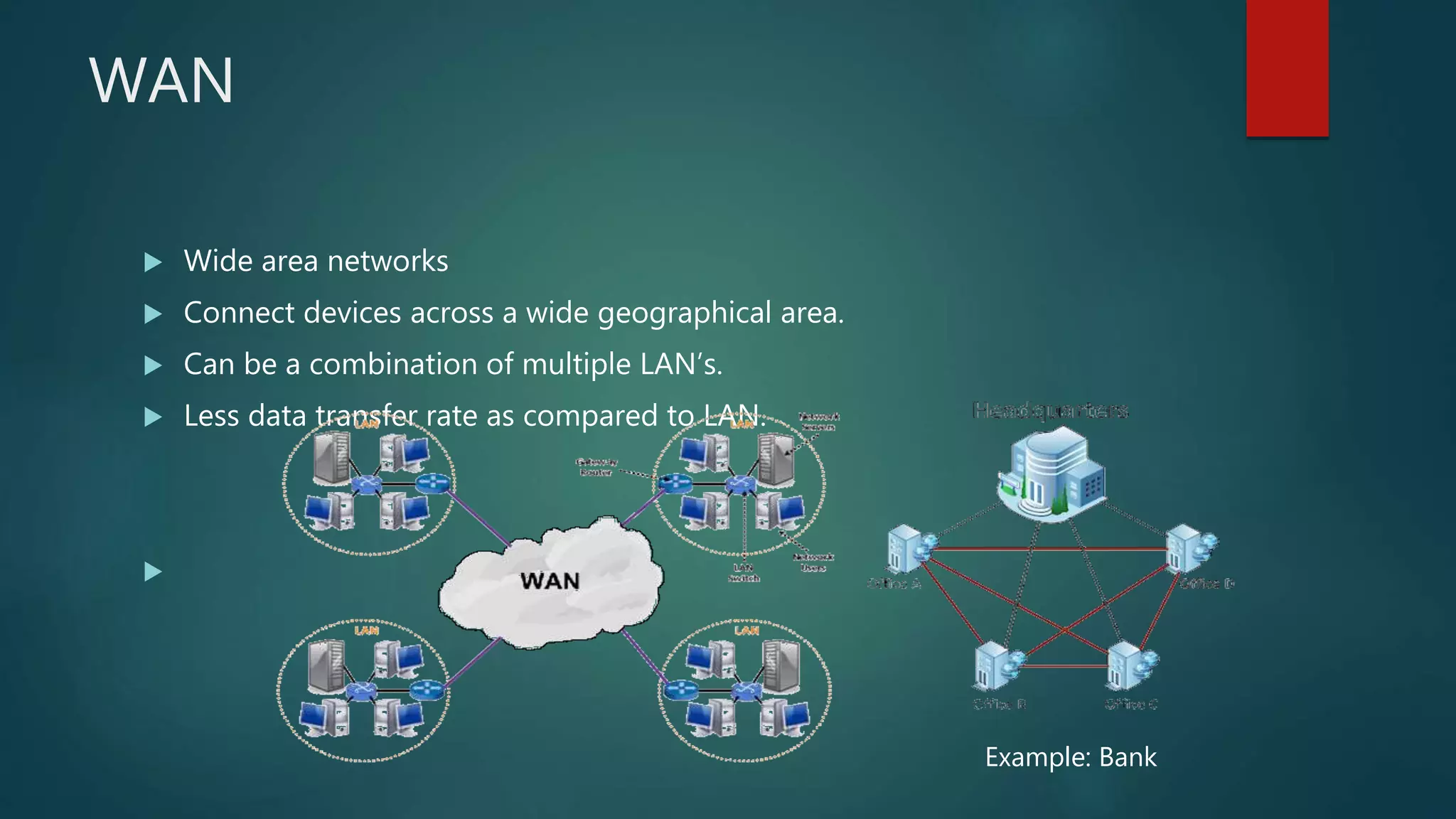
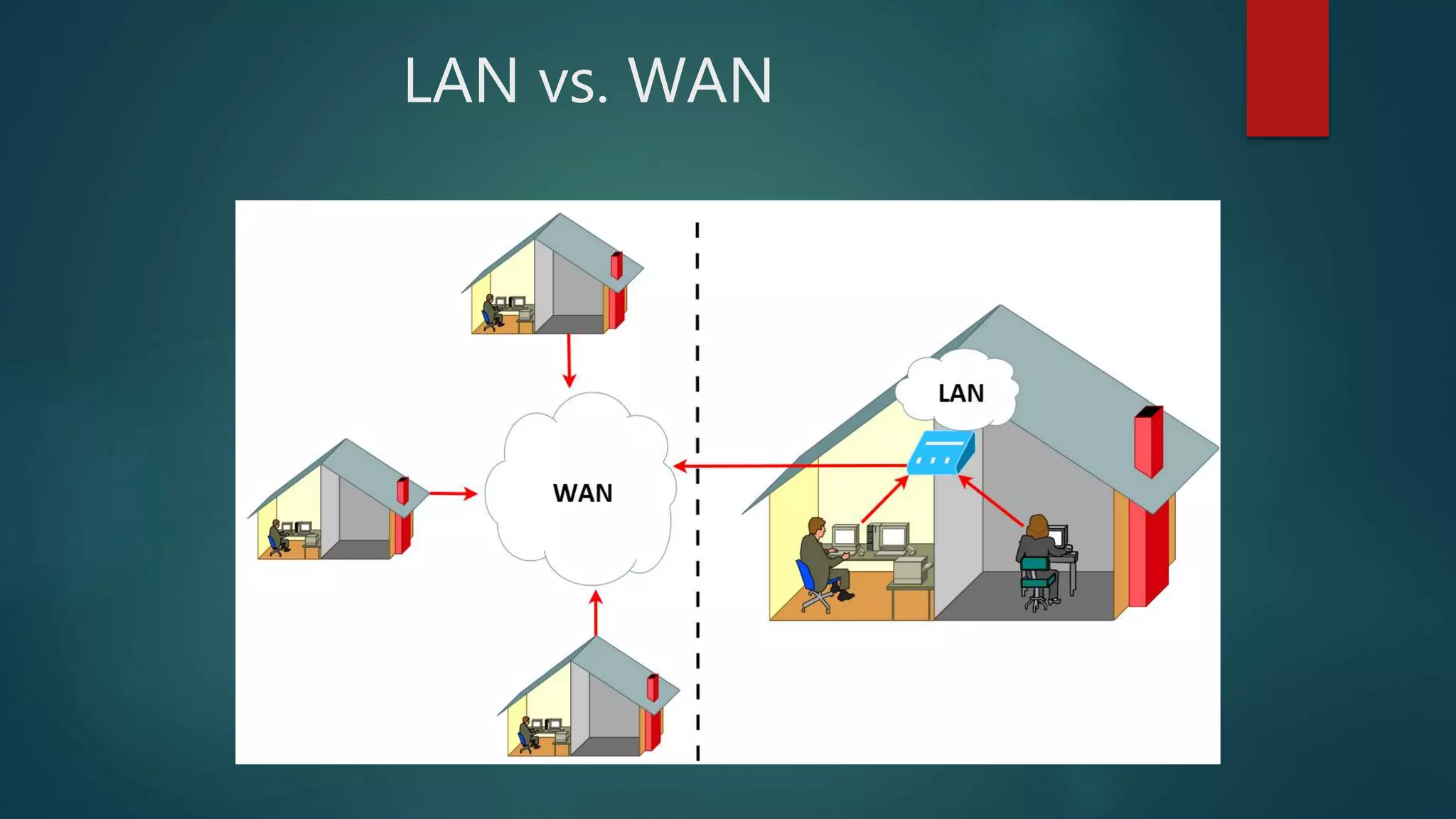
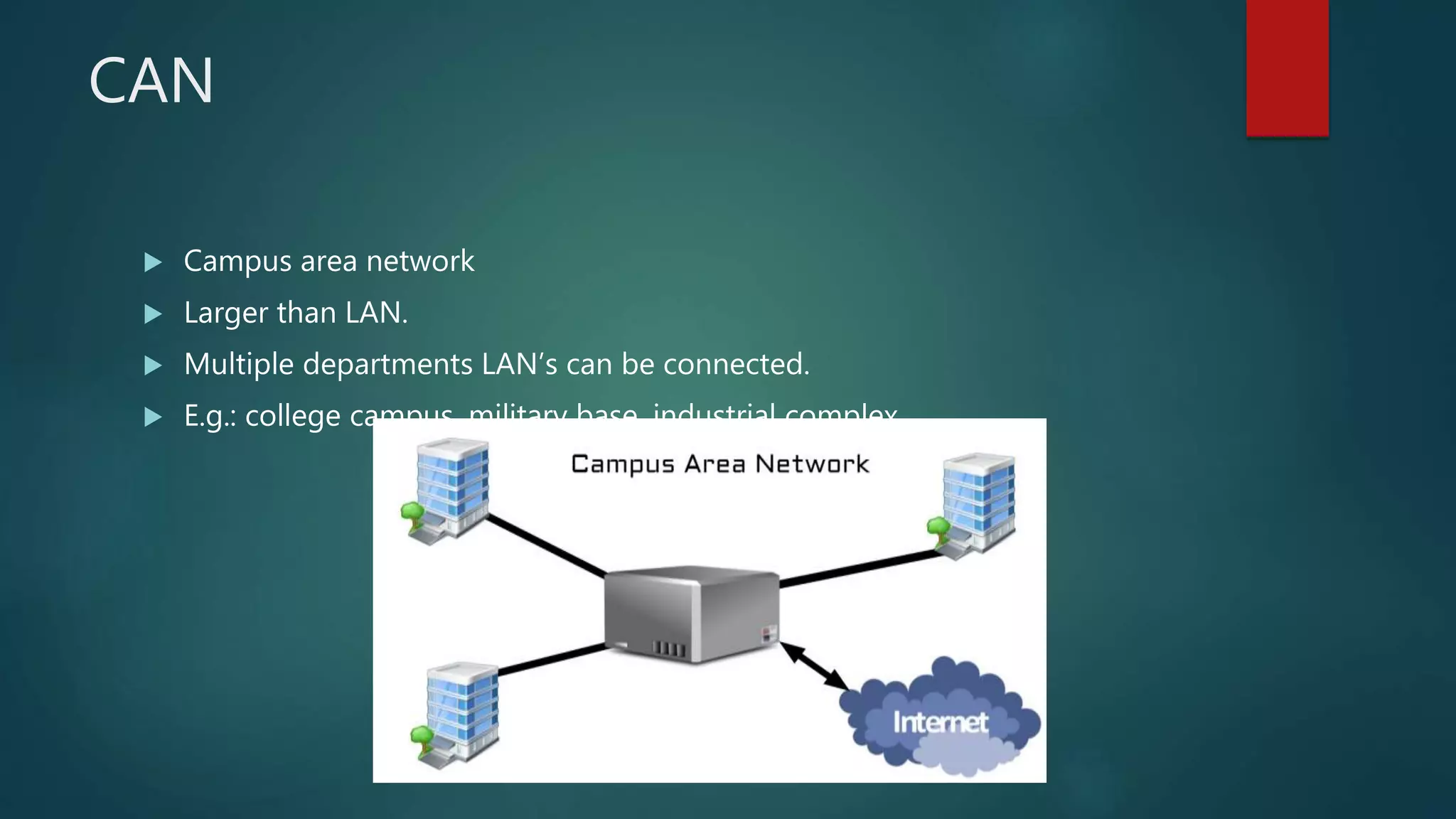
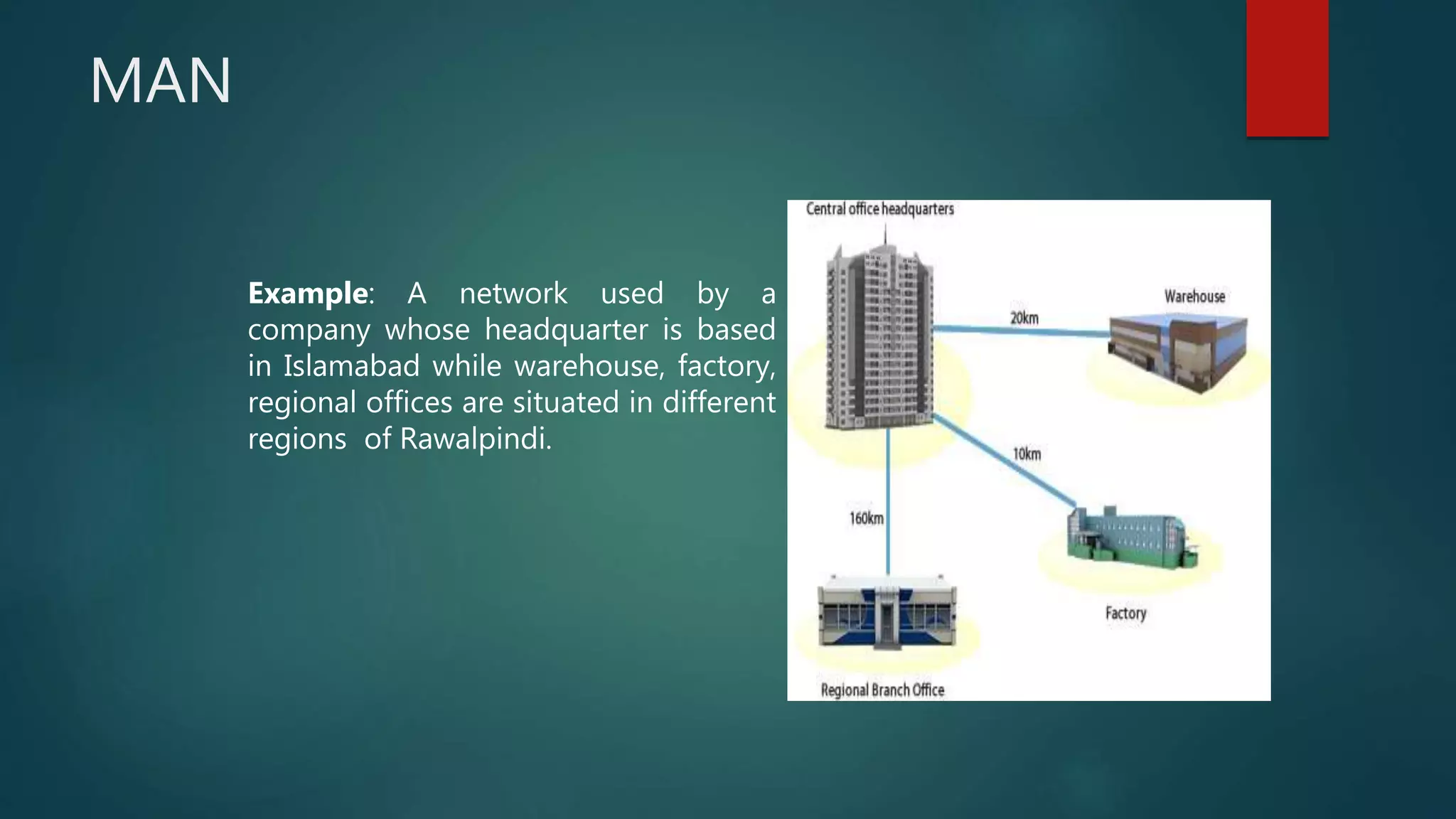
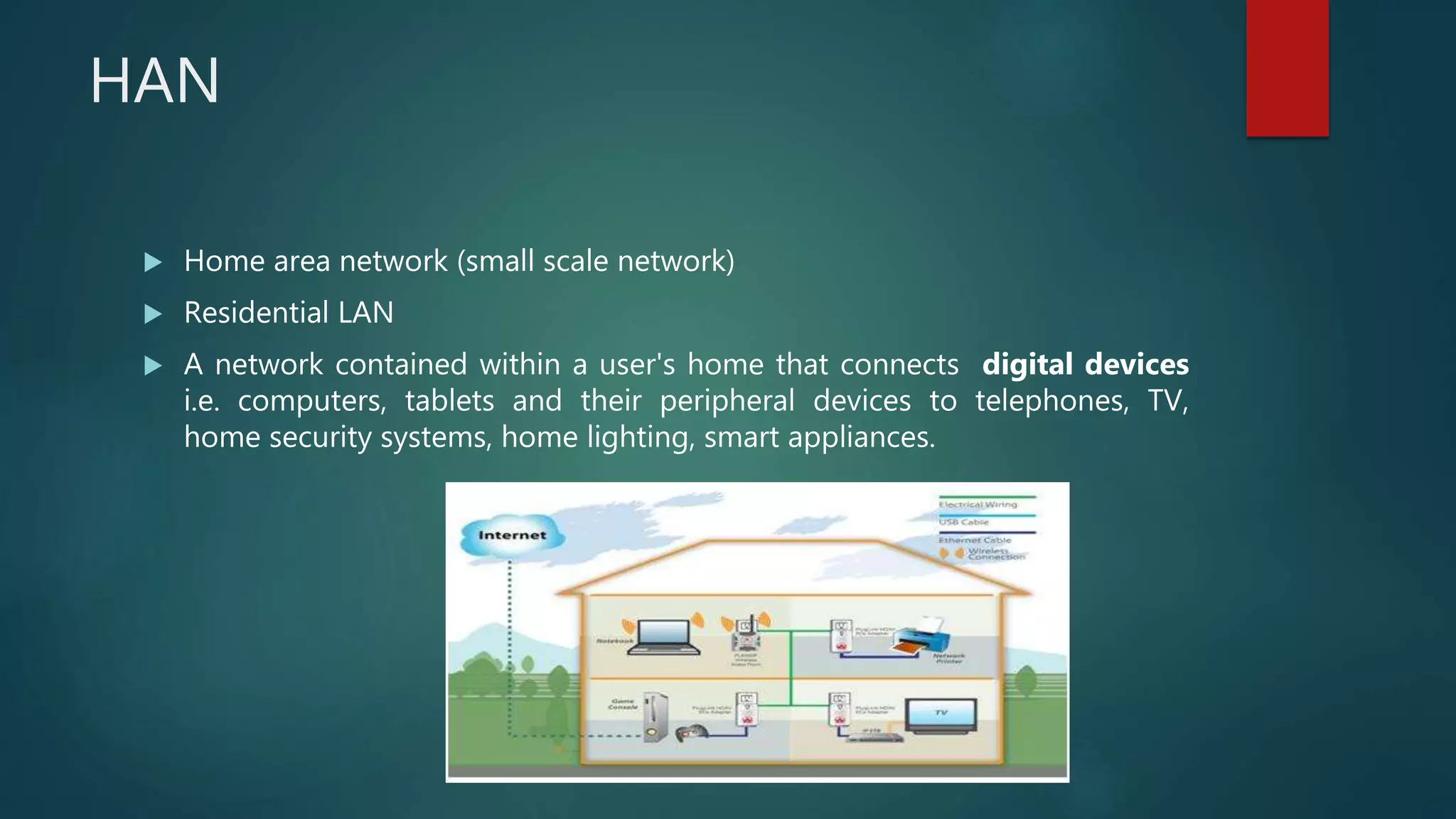
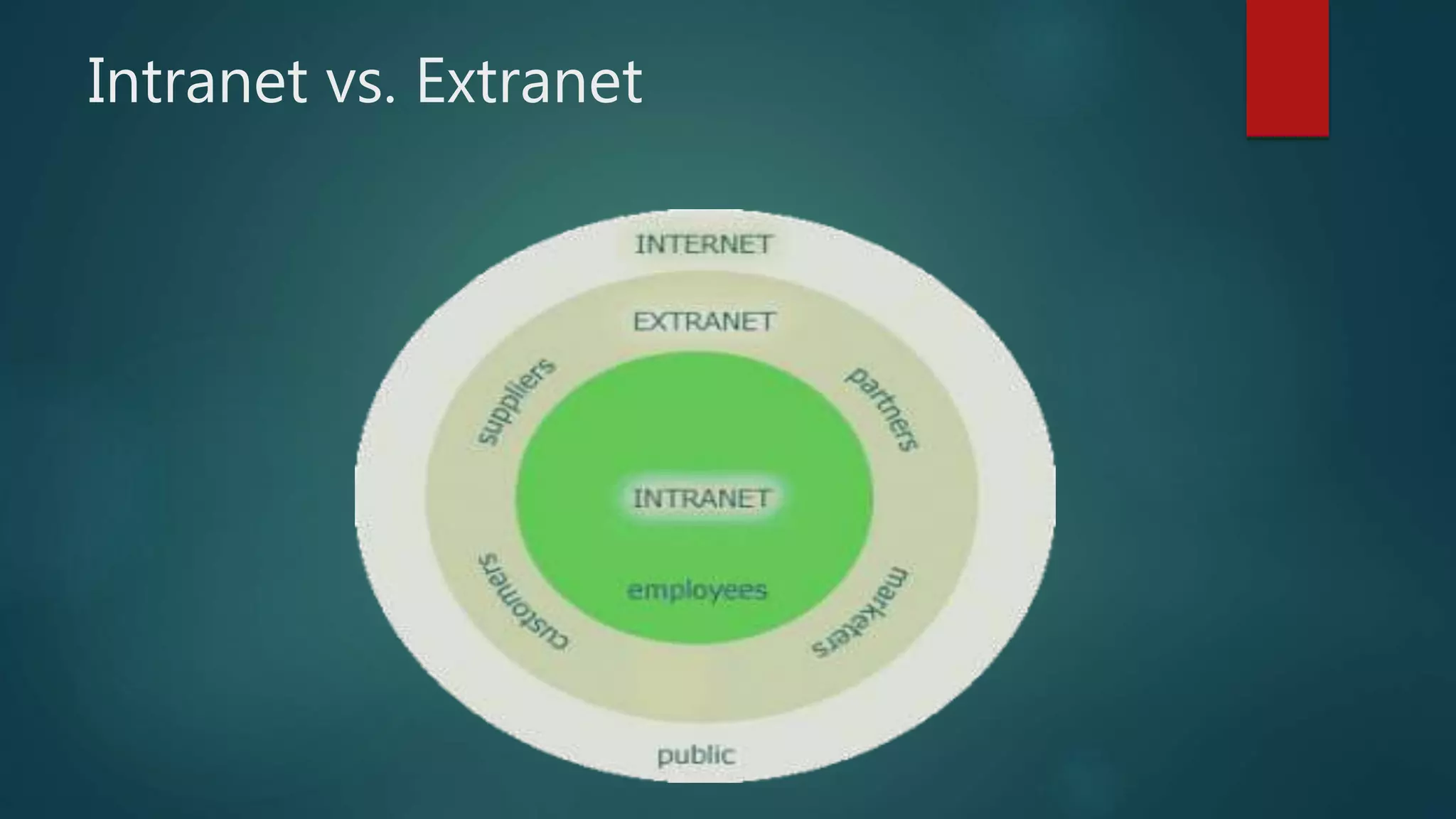
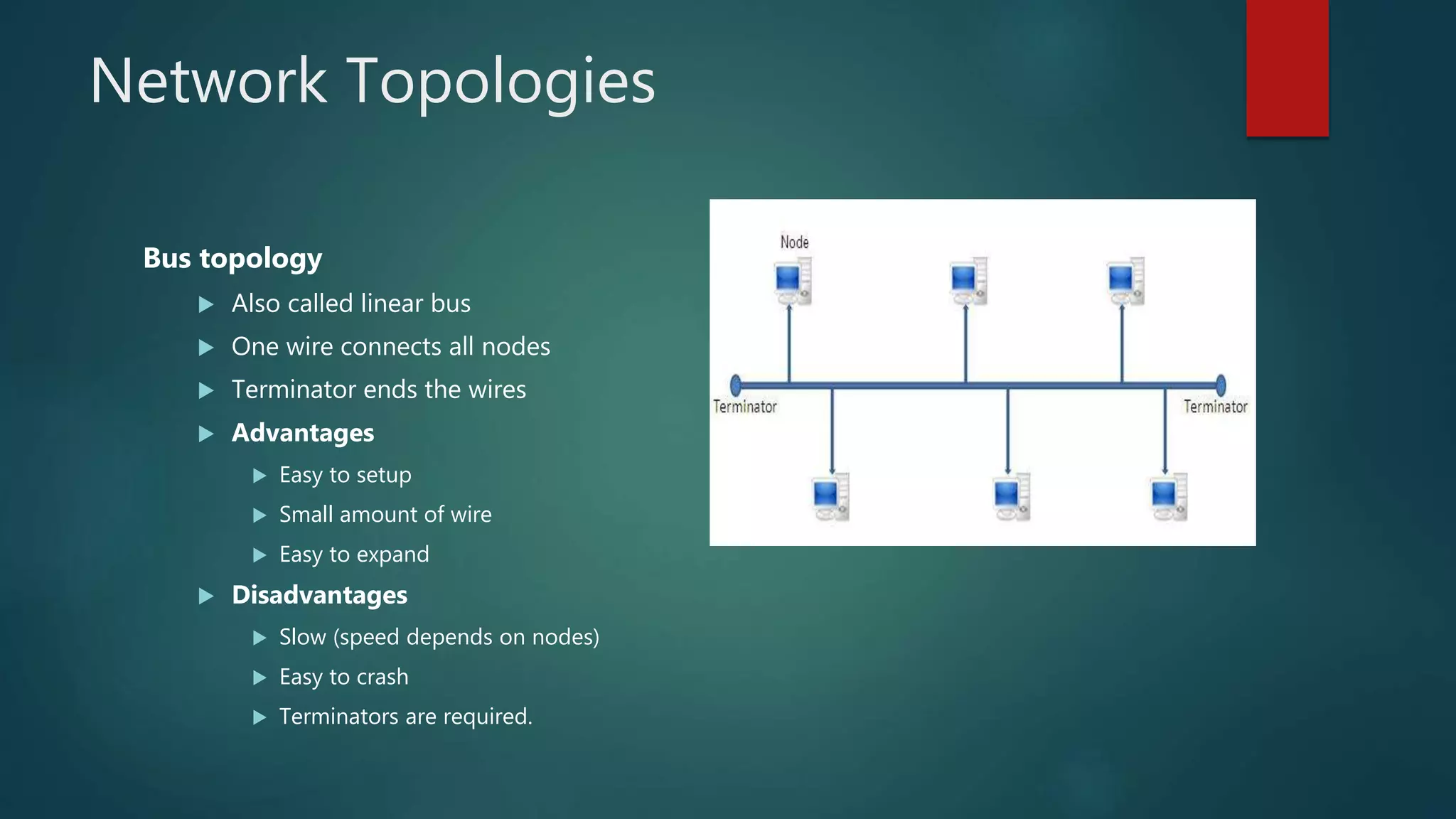
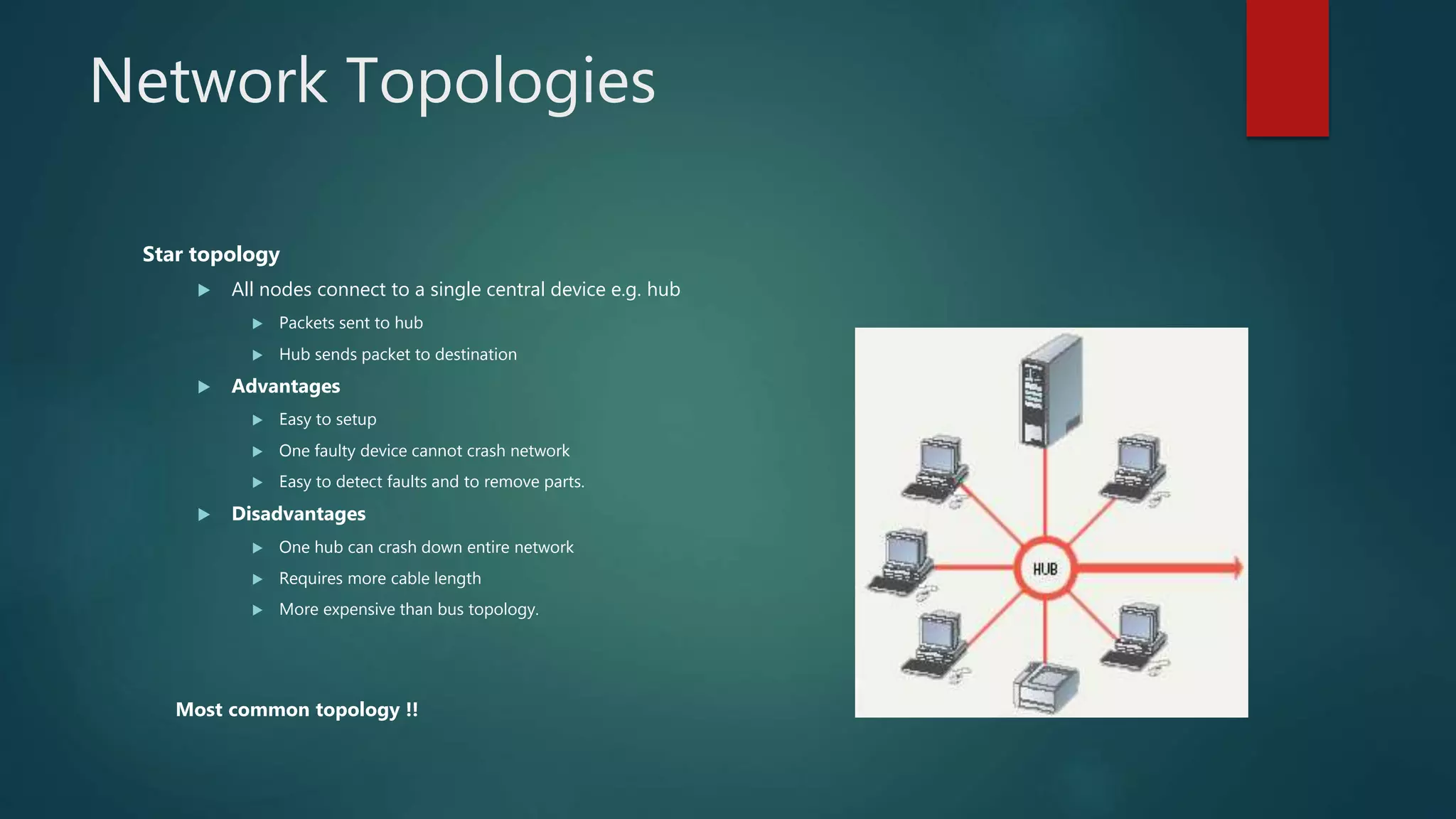
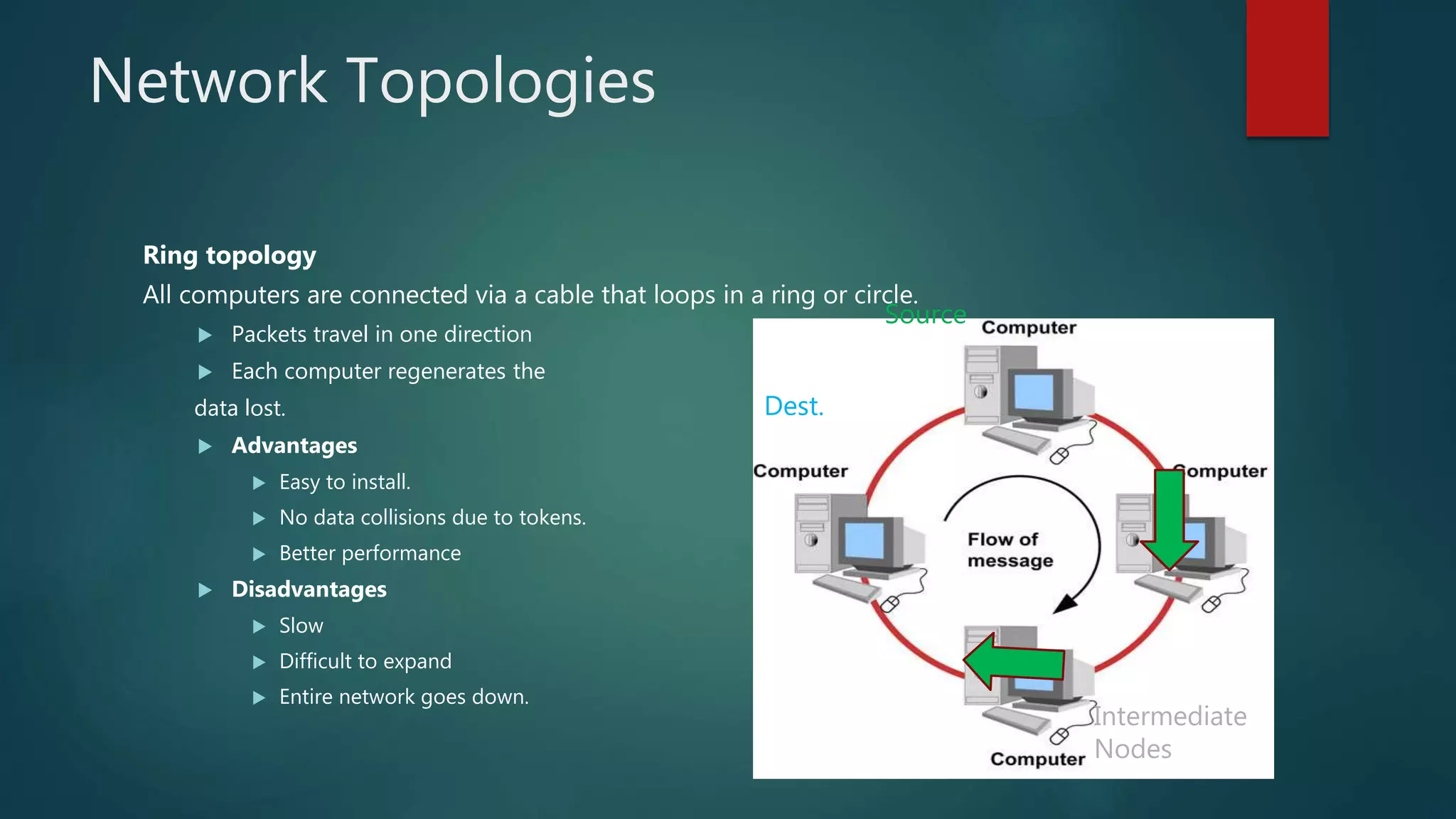
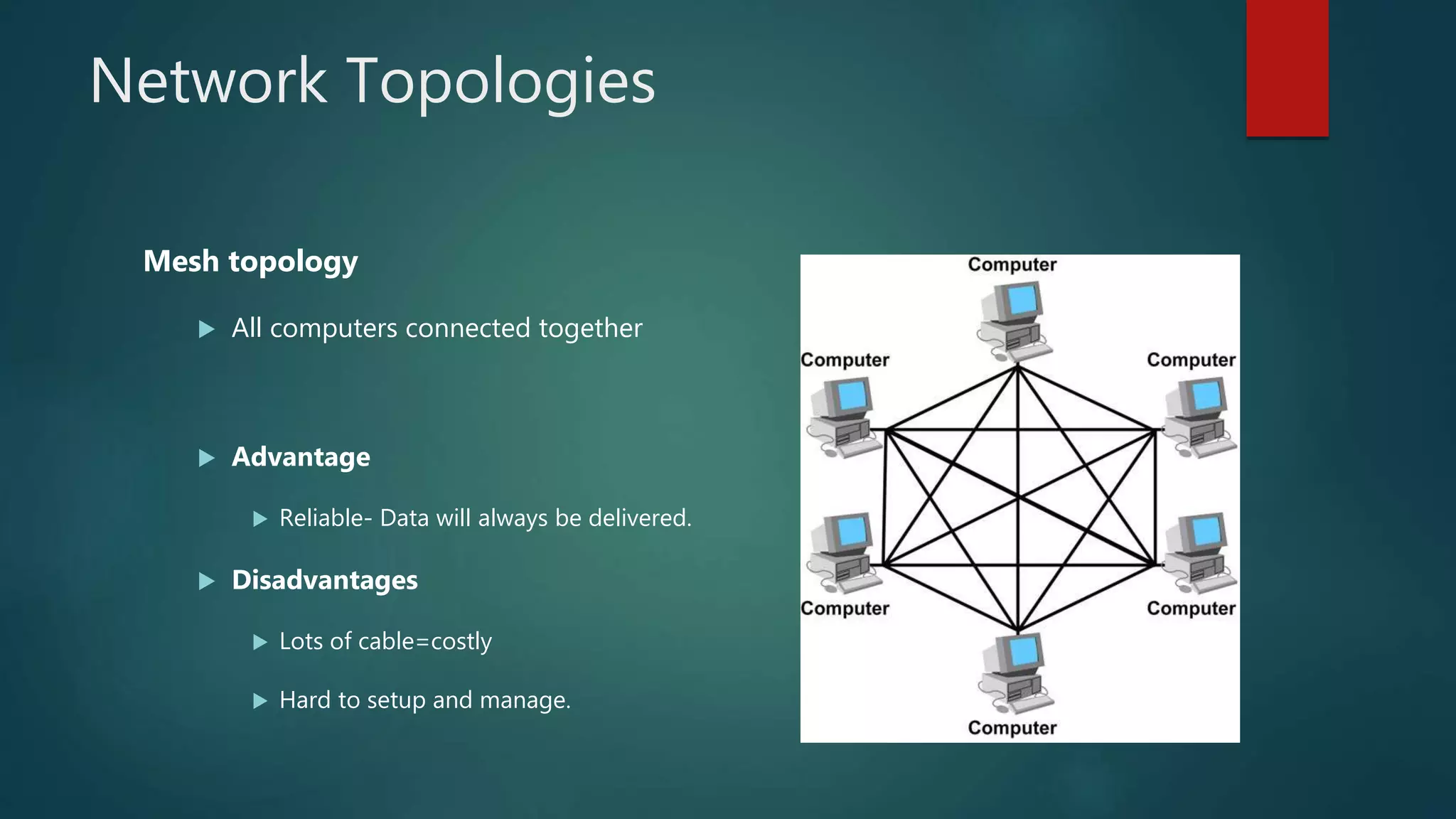
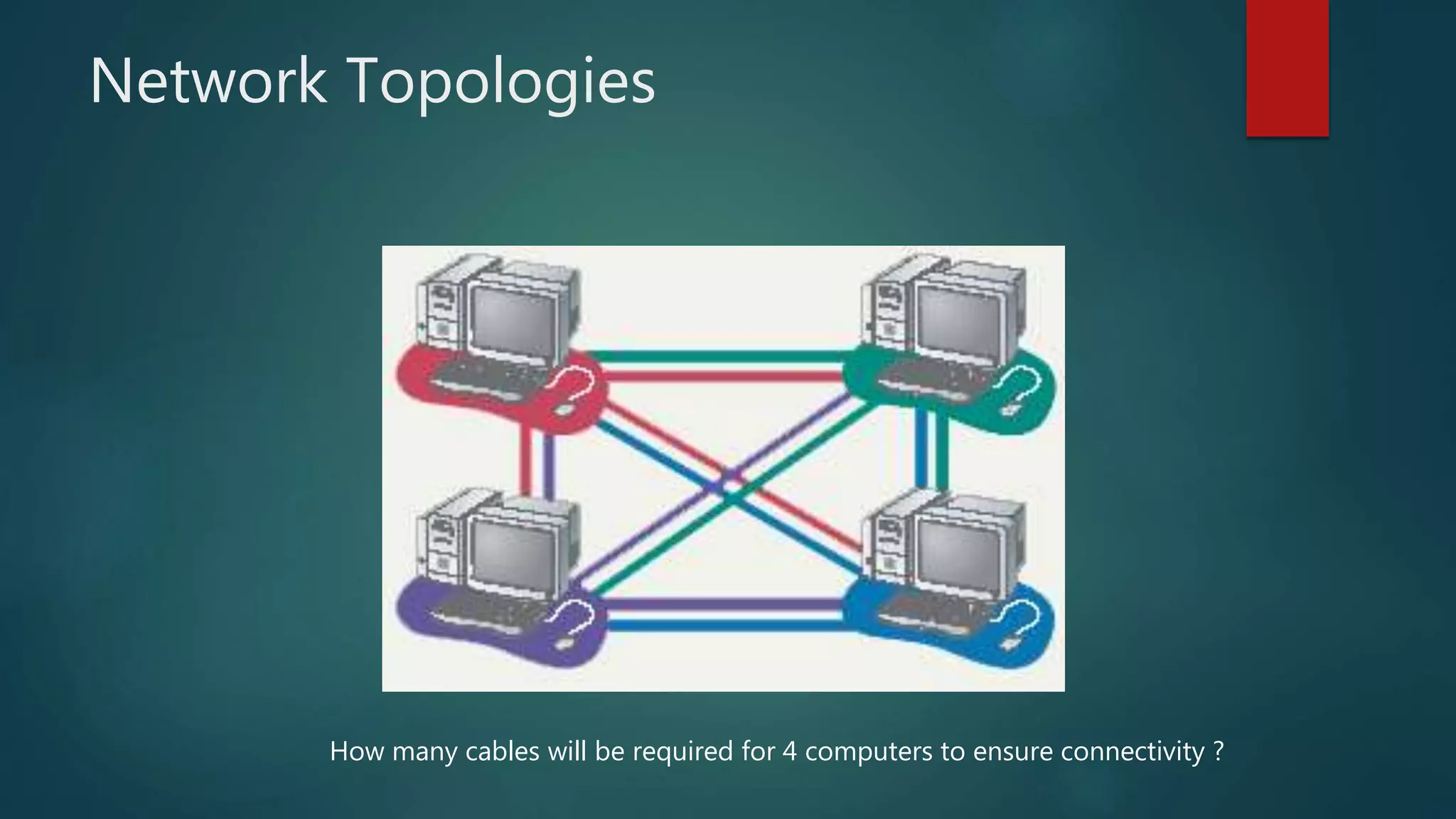
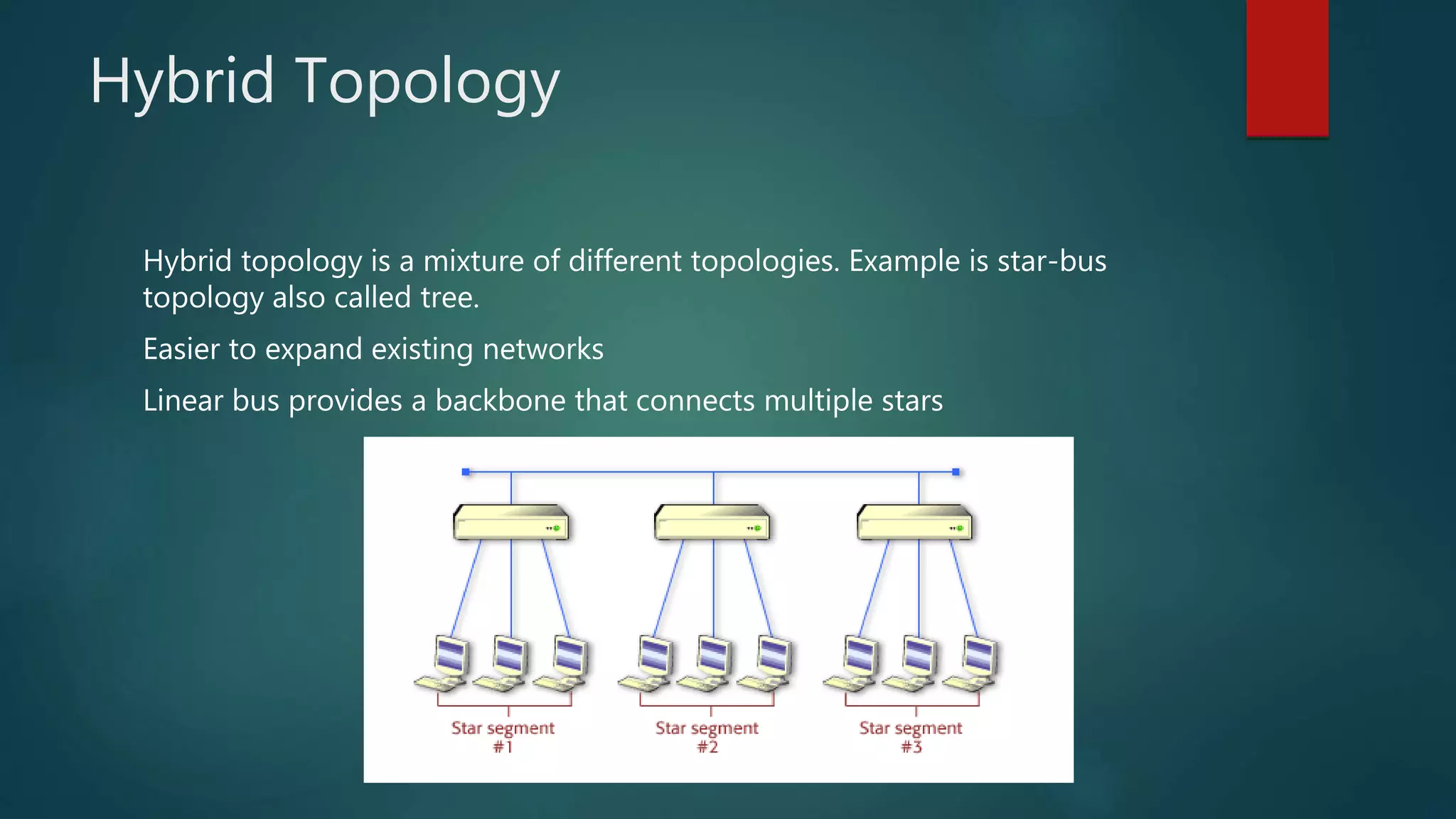
The document provides information about computer networks and networking devices. It begins with definitions of networks and their benefits, including resource sharing, file sharing, and communication. It then discusses different types of networks classified by size (LAN, WAN), structure (client-server, peer-to-peer), and topology (bus, star, ring). Various networking devices are also defined, such as hubs, switches, routers, bridges, firewalls, and wireless access points. The document concludes with examples and diagrams to illustrate key network concepts.

































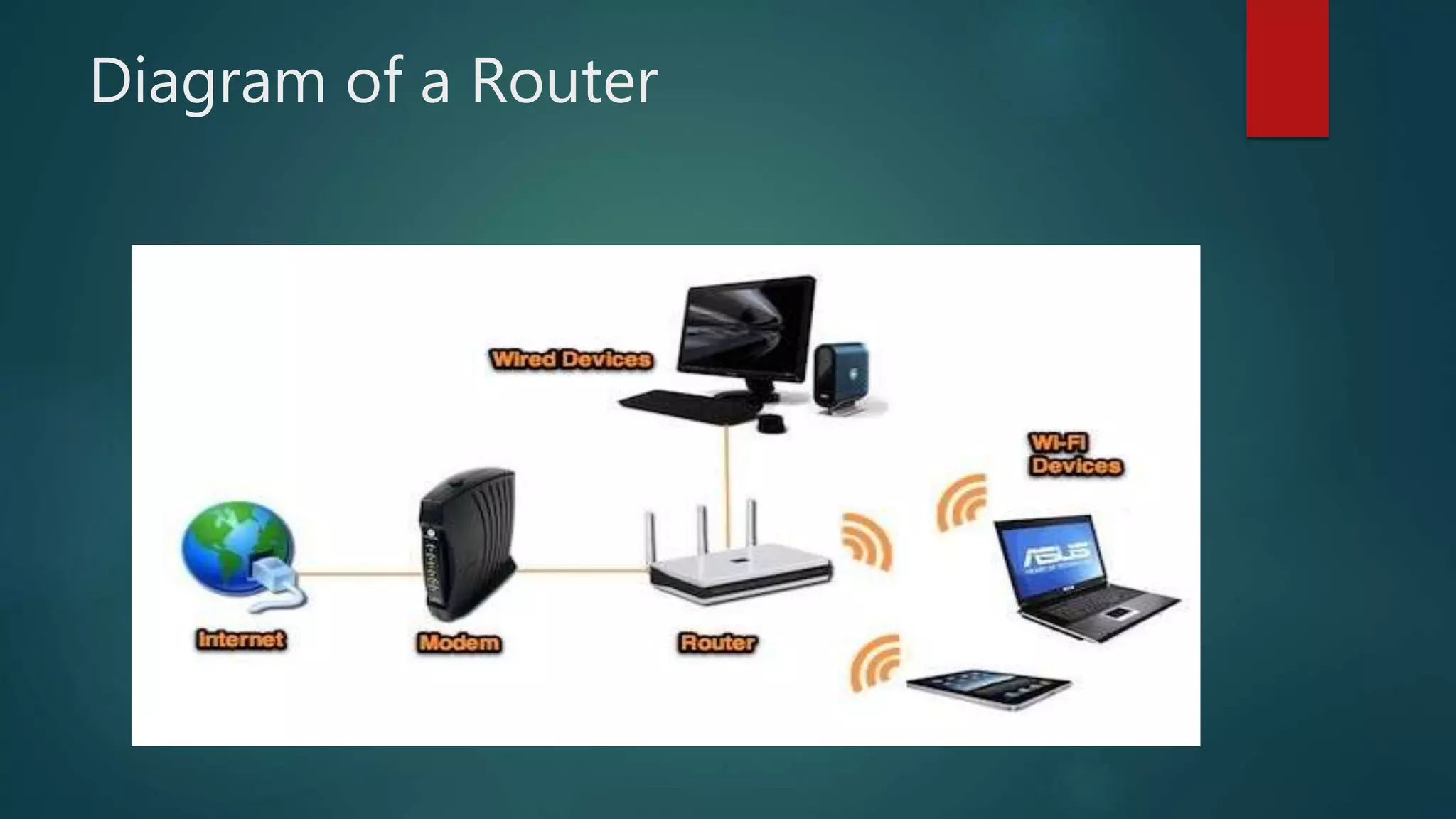

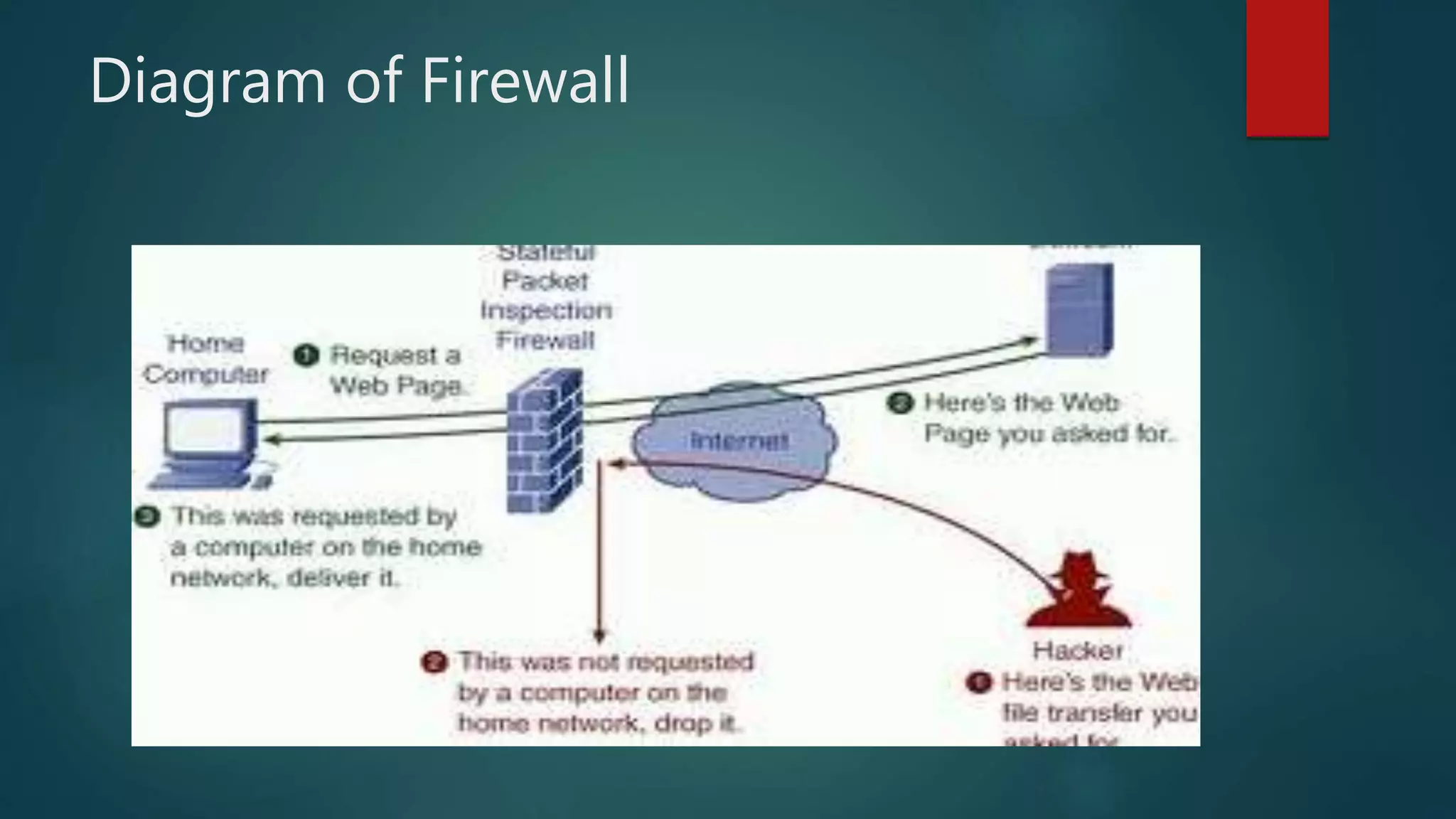

![Diagram of Wireless Access Point
RxNT – The eprescribing System. [online image]. Available www.rxnt.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture9-190122145511/75/computer-networks-62-2048.jpg)