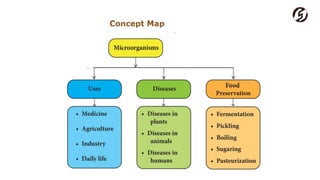
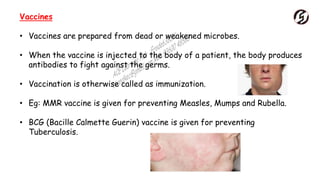
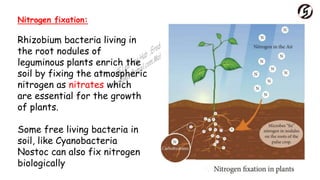
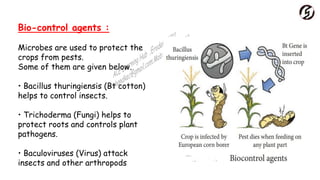
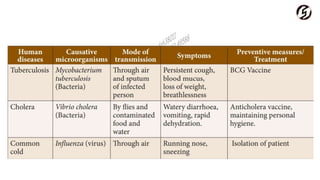
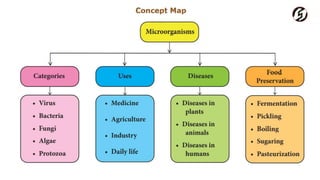
Microorganisms are useful in medicine, agriculture, and industry. In medicine, they are used to produce antibiotics like penicillin and vaccines. In agriculture, they act as natural fertilizers by fixing nitrogen, and as bio-control agents to protect crops. In industry, microbes are used for sewage treatment, production of alcohol, and food processing through fermentation.