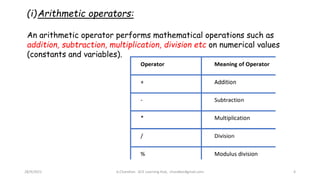
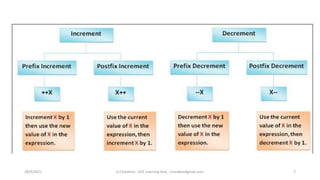
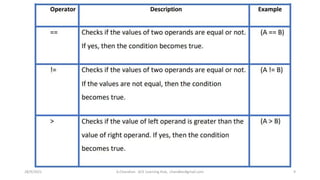
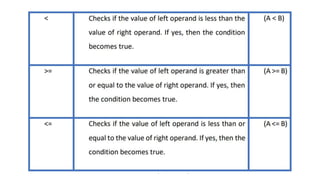
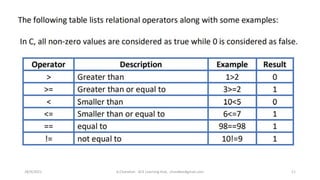
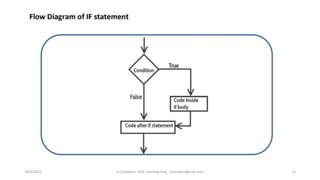
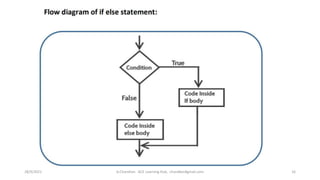
This document discusses operators and conditional statements in C programming. It describes different types of operators like arithmetic, assignment, relational, and increment/decrement operators. Conditional statements like if and if-else are also covered. The if statement executes code if a condition is true, while if-else executes one code block if true and another if false. An example uses an if-else statement to check if a user's age makes them eligible to vote.