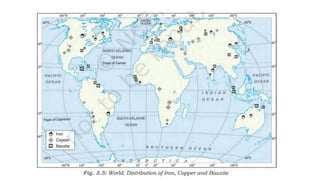
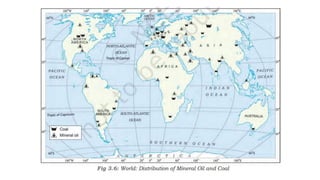
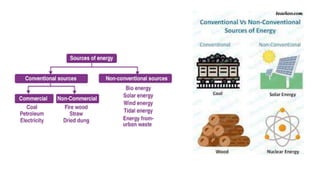
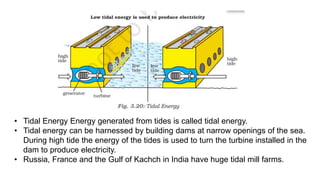
The document provides an overview of minerals, their types, distribution, and mining processes, explaining that minerals are non-renewable resources formed naturally with varying geological conditions. It also discusses conventional and non-conventional energy sources, highlighting the urgency of conserving mineral resources and the need for cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels. Additionally, it outlines the global distribution of mineral and energy resources across different continents and emphasizes the significance of sustainable energy practices.