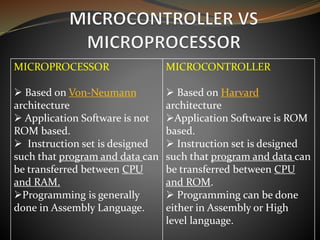
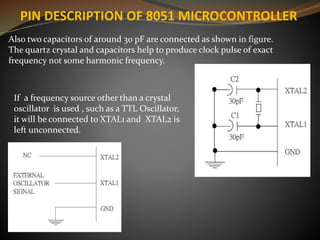
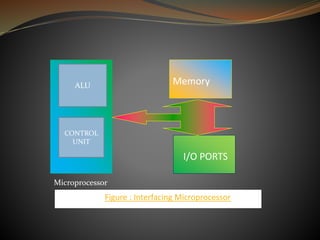
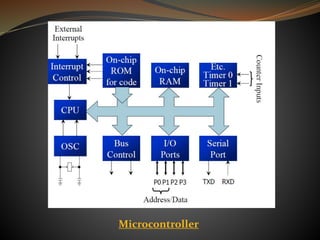
The document compares microprocessors and microcontrollers, highlighting that microprocessors are general-purpose CPUs requiring external interfacing for memory and I/O, while microcontrollers are dedicated computers on a chip with embedded RAM, ROM, and I/O ports for specific applications. It elaborates on the architecture differences, with microprocessors following von-Neumann architecture and microcontrollers using Harvard architecture, along with examples of applications for each. The text specifically details the 8051 microcontroller family, its features, pin descriptions, and operational aspects.