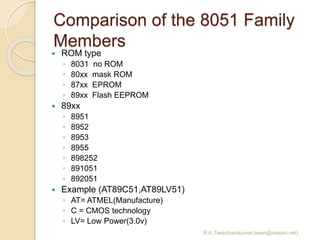
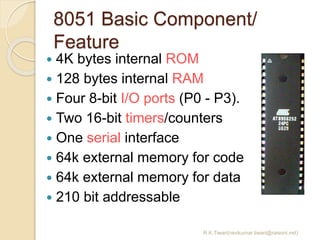
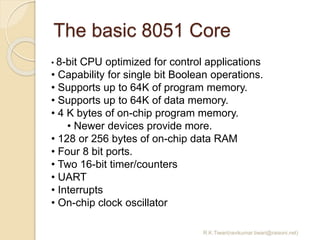
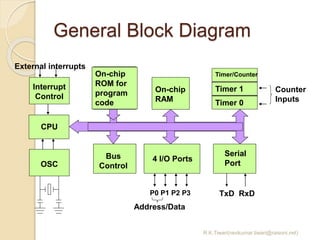
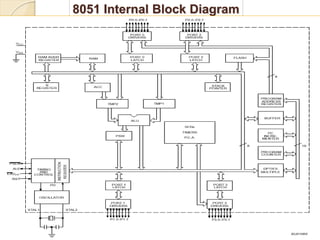
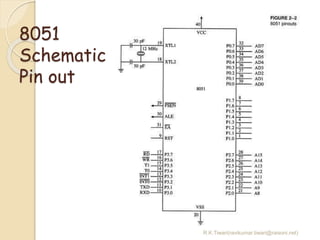
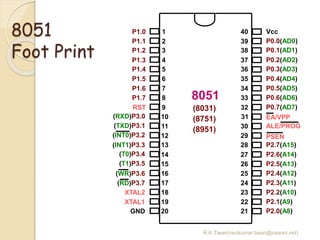
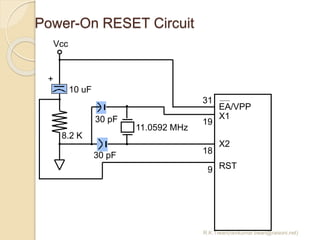
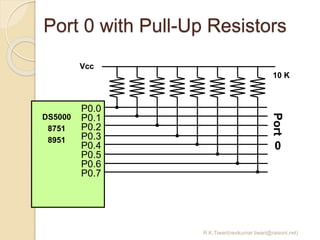
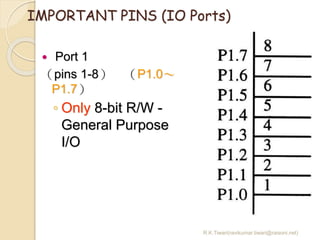
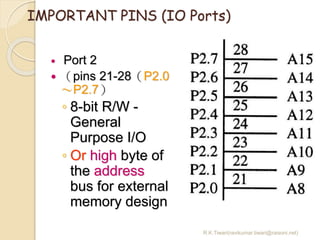
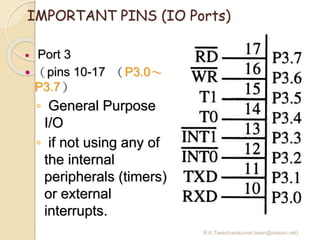
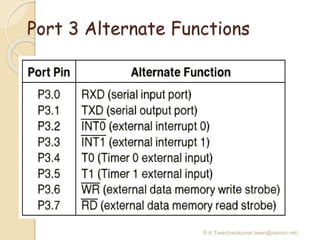
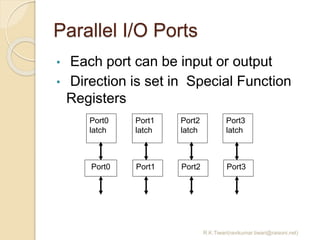
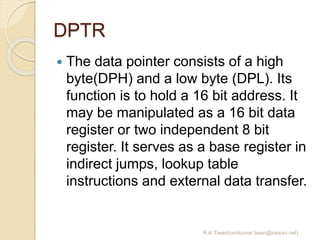
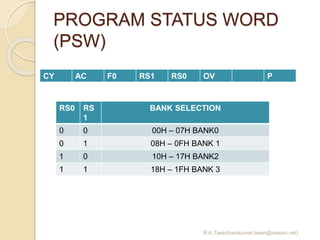
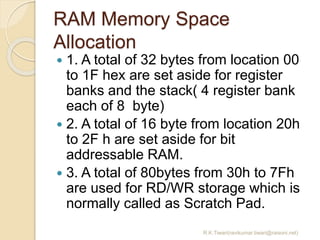
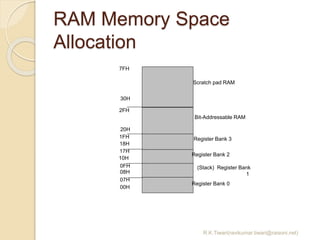
The document discusses the 8051 microcontroller. It provides three key criteria for choosing a microcontroller: 1) meeting computing needs efficiently and cost effectively, 2) availability of software development tools, and 3) reliable sources. It then describes the basic components and features of the 8051, including 4K bytes of ROM, 128 bytes of RAM, four 8-bit I/O ports, two timers/counters, a serial interface, and support for external memory. Finally, it explains the memory organization and allocation of the 8051, distinguishing program memory, data memory, and external RAM.