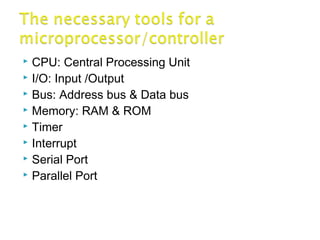
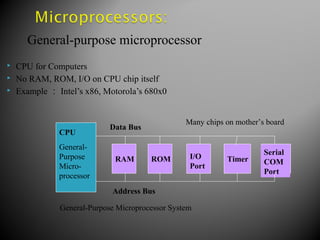
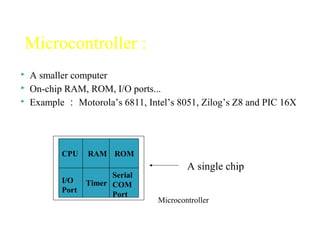
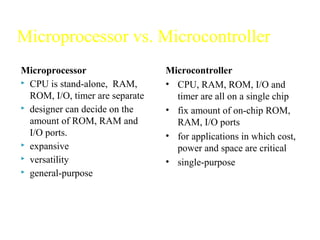
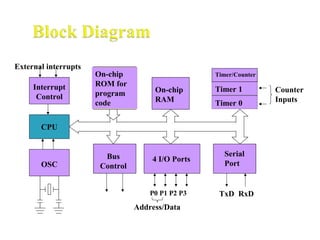
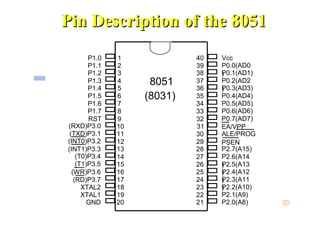
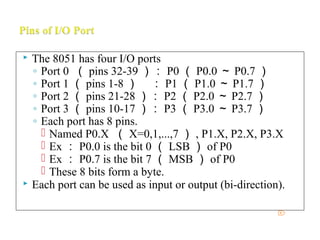
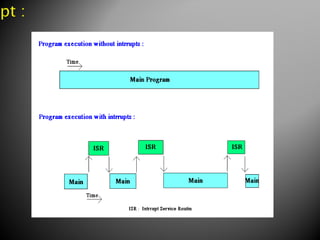
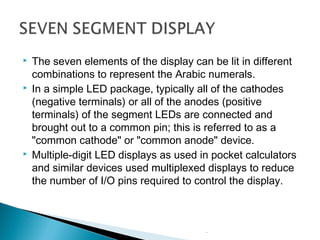
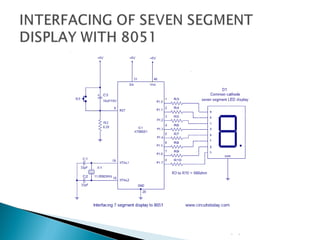
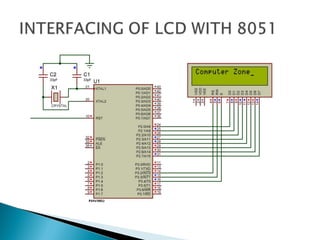
The document discusses microprocessors and microcontrollers. It begins by explaining that microprocessors are the core of modern computer systems and devices, and that they control communication, entertainment, and portable devices. It then contrasts microprocessors and microcontrollers, noting that microprocessors have external memory and I/O components while microcontrollers have these components integrated on a single chip. The document also provides details on the 8051 microcontroller, including its architecture, ports, memory organization, and interrupts.