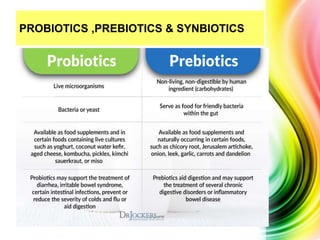
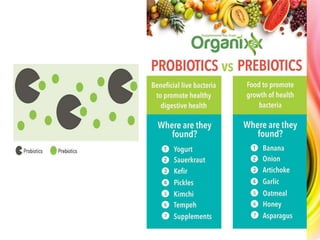
The gut microbiome refers to the microorganisms that inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract. The gut microbiome begins developing at birth and is influenced by factors like diet, geography, and age. Approximately one third of gut bacteria are common across people, while two thirds vary individually. The gut microbiome plays important roles in digesting food, producing vitamins, protecting against other microbes, and influencing conditions like depression, autism, and schizophrenia through the gut-brain axis. Managing the gut microbiome through prebiotics, probiotics, and diet can positively impact health and disease.