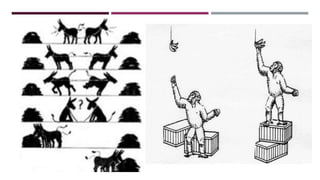
There are four main methods of learning discussed in the document: learning by trial and error, learning by imitation, learning by insight, and learning by doing. Learning by trial and error involves repeatedly trying solutions to a problem until finding one that works. Learning by imitation occurs when observing and replicating the behaviors of others. Learning by insight is solving a problem suddenly without gradual trial and error. Learning by doing means gaining skills and knowledge directly from carrying out and practicing a task.