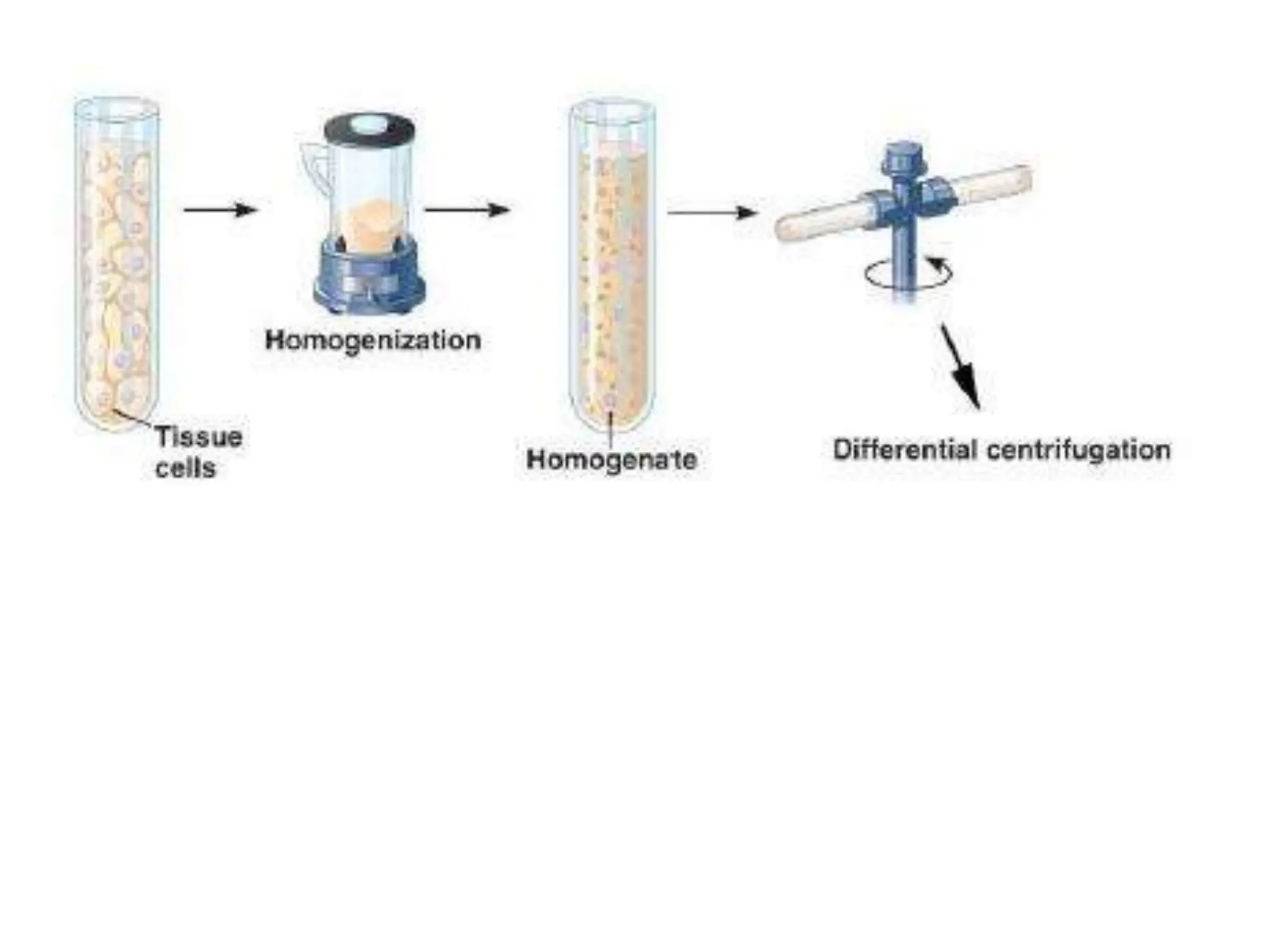
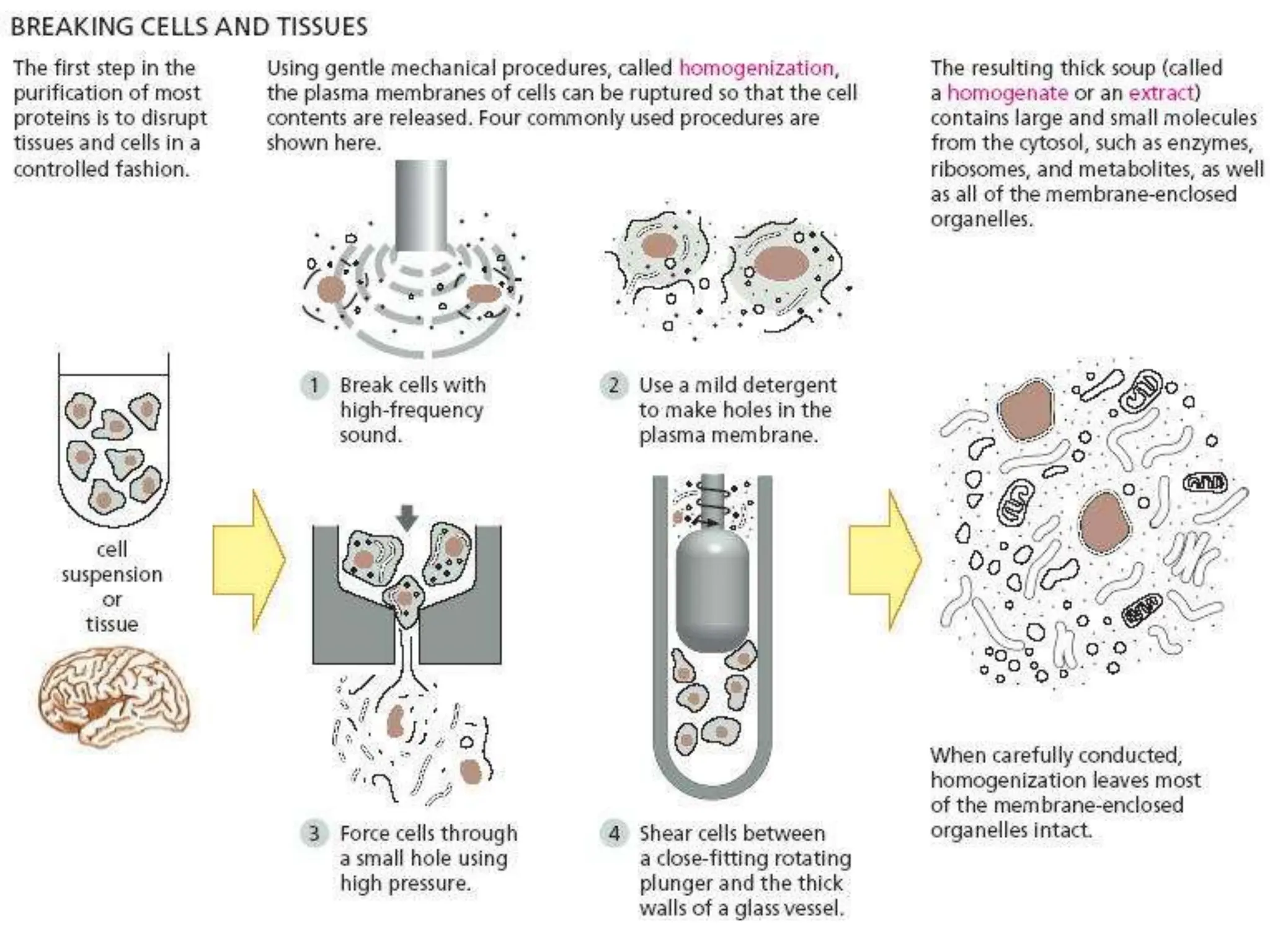
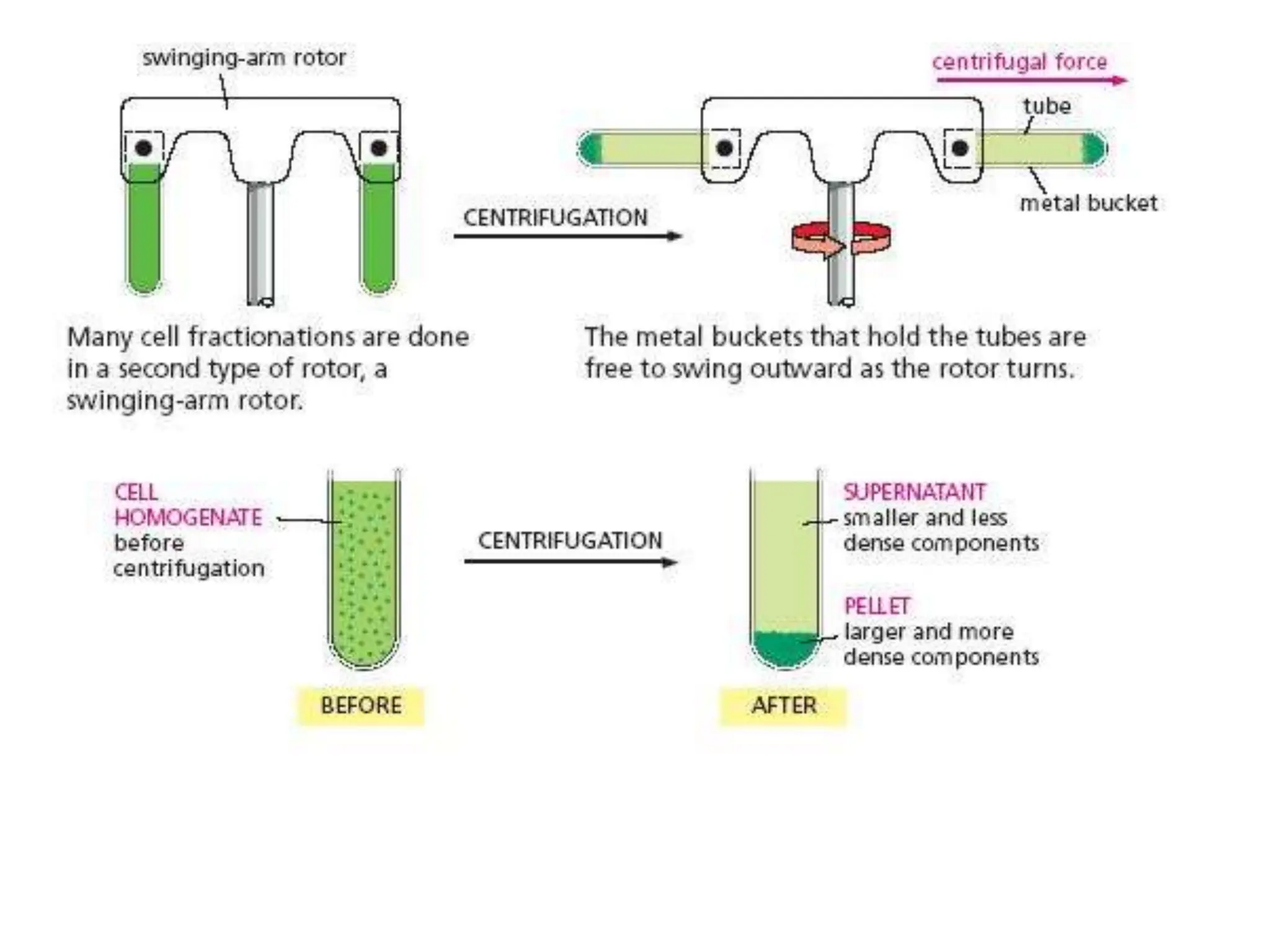
Cell fractionation is a process that separates cellular components while maintaining their functions, involving tissue disruption and centrifugation. Tissue disruption can be achieved through methods like homogenization, sonication, and osmotic lysis, while centrifugation uses relative centrifugal force to separate components based on size and density. Differential centrifugation progressively isolates cellular components by sequentially spinning a lysate at increasing forces, producing pellets of mixed components and supernatants for further processing.