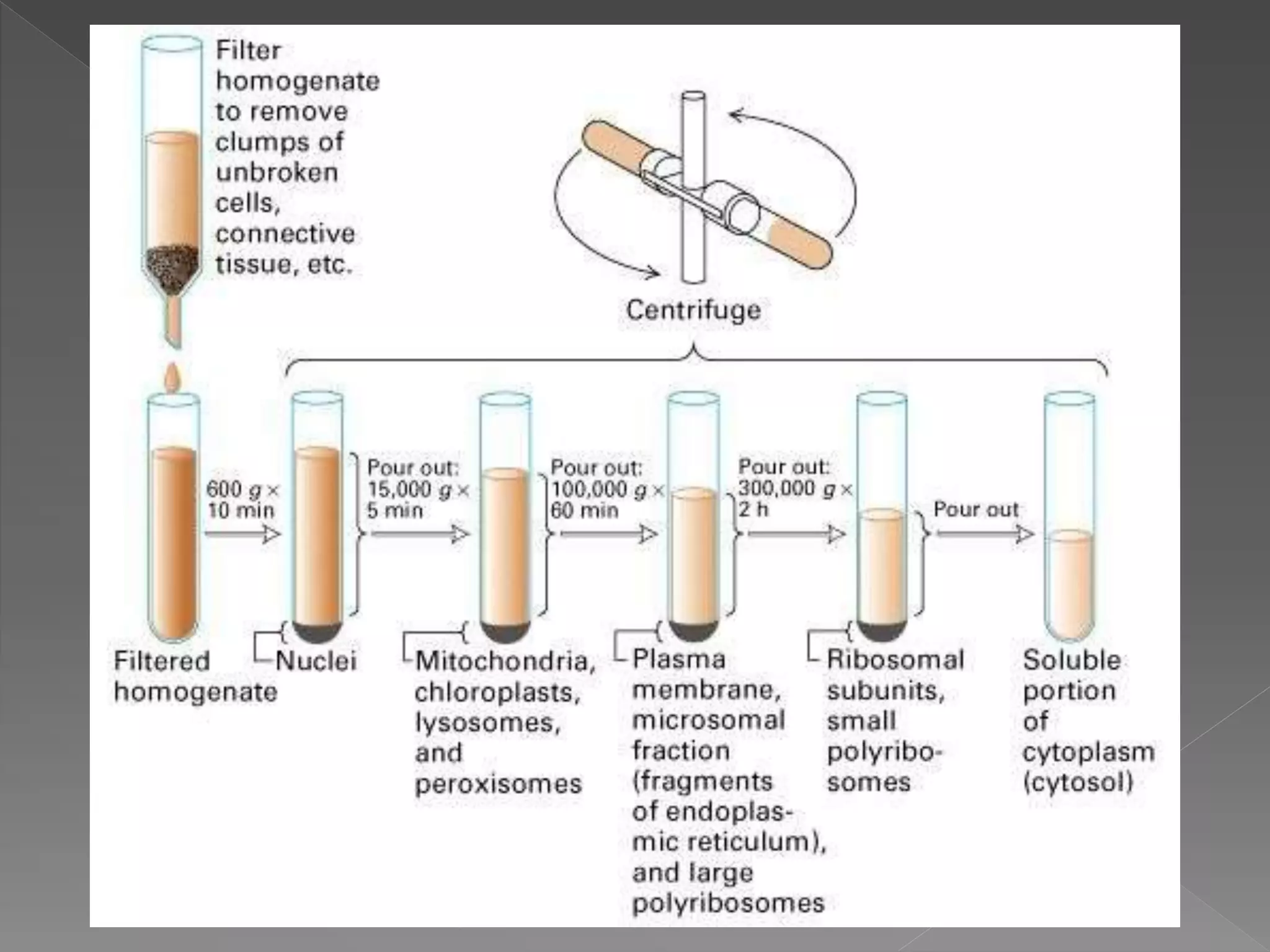
Cell fractionation is a three step process to rupture cells and separate their constituents in isotonic medium to study structure, composition and function. The steps are extraction, homogenization, and centrifugation. Extraction suspends cells in a mild isotonic solution to maintain biological activity. Homogenization then disrupts the cells using grinding, high pressure, osmotic shock, or sonication. Lastly, centrifugation separates the various components by density through sequential centrifugation at increasing forces in an ultracentrifuge. Equilibrium density gradient centrifugation further separates particles based on differences in buoyant density.