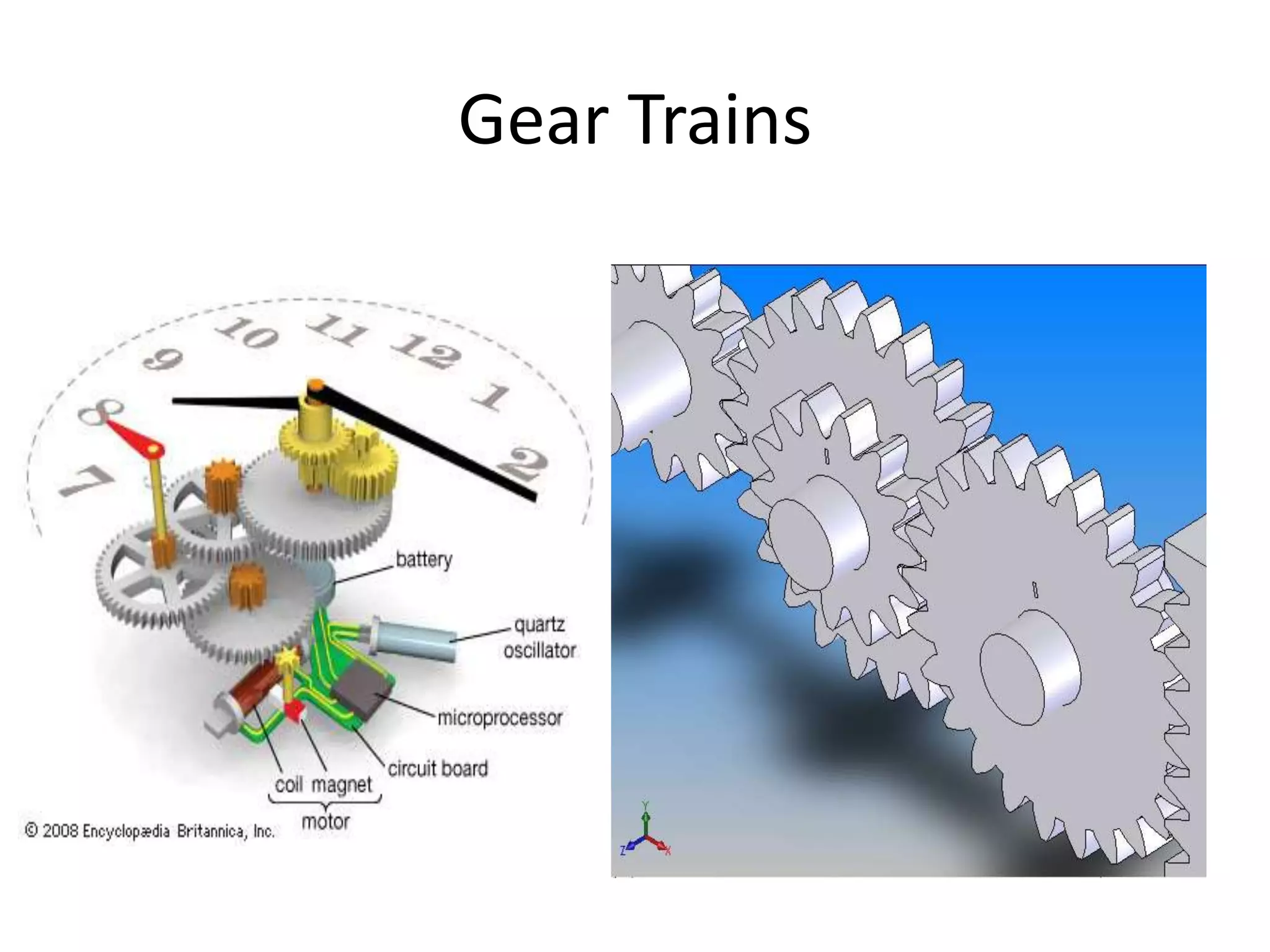
Power needs to be transmitted from where it is generated to where it is used. Bearings are components that support rotating or moving parts and reduce friction. They come in plain and rolling element types, with the most common being journal bearings that support a rotating shaft using lubrication between surfaces. Gear trains use successively engaging teeth to transmit rotational motion between parts of a mechanical system. Belt, rope, and chain drives are also used to transfer power between rotating shafts.