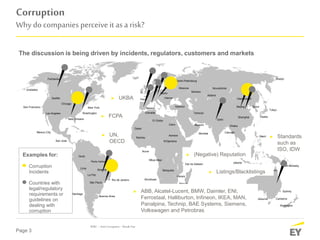
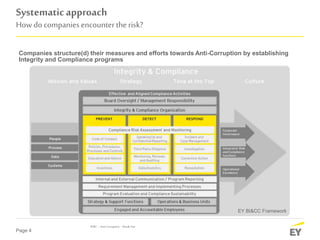
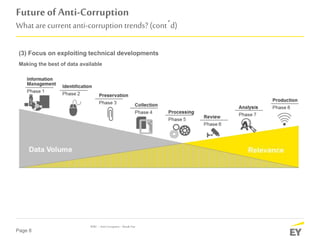
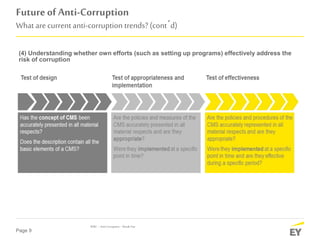
The document discusses the evolving landscape of anti-corruption measures, emphasizing the need for companies to establish integrity and compliance programs in response to regulatory pressures and competitive environments. It highlights current trends focusing on improving business effectiveness, corporate culture, and leveraging technical advancements to mitigate corruption risks. The content aims to provide insights into how organizations can adapt their compliance frameworks to enhance performance and stakeholder trust.