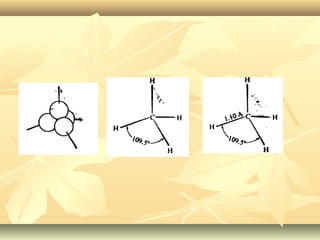
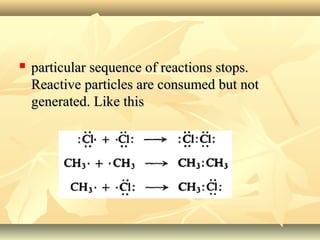
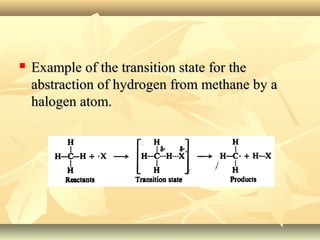
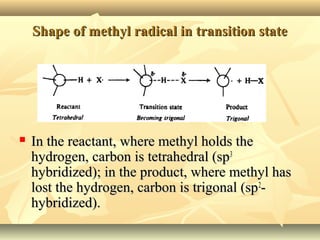
Methane is the simplest alkane and consists of one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms in a tetrahedral structure. It is a colorless, odorless gas that is nonpolar and has a low boiling point. Methane is produced from the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter and is the primary component of natural gas. It typically only reacts under vigorous conditions with substances like oxygen, halogens, or at high temperatures. When methane reacts with chlorine, it undergoes a substitution reaction where a chlorine replaces a hydrogen to form methyl chloride, in a chain reaction where reactive radicals continually form and react.