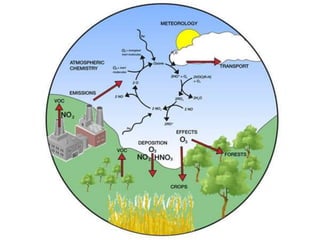
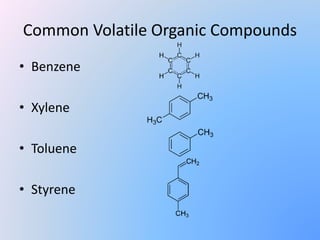
VOCs are organic chemicals that evaporate at room temperature and are both naturally occurring and human-made. They are emitted through processes like combustion and evaporation from products like paints, solvents, and fuels. Exposure can cause short term effects like headaches and dizziness or long term health issues like cancer, organ damage, and central nervous system effects. Common VOCs include benzene, xylene, toluene, and styrene. Reducing VOC sources, increasing ventilation, and using pollution control devices can help mitigate exposures.