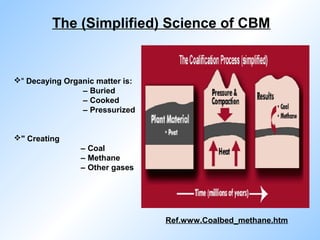
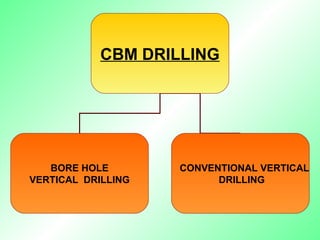
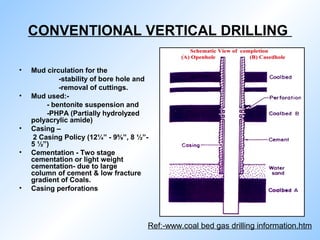
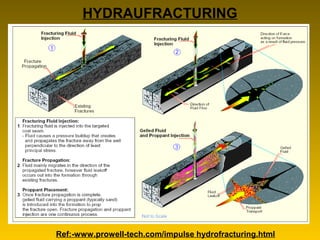
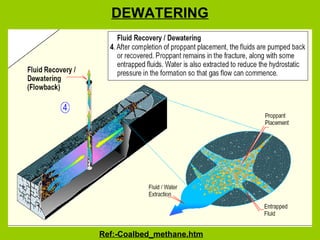
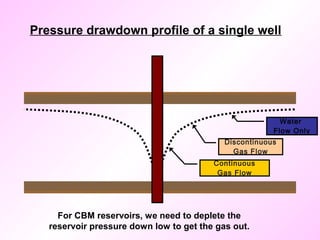
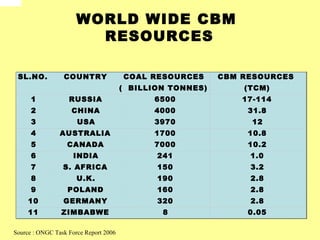
Coal bed methane is natural gas formed during the coalification process and stored in coal seams. It is held in place by water pressure. CBM exploration involves mapping coal seams to determine their extent, thickness, permeability and gas content. Drilling uses mud circulation to remove cuttings and install casing for stability. Production involves hydraulic fracturing to increase permeability followed by dewatering to reduce water pressure and release the gas. Major CBM resources are found in Russia, China, the US, Australia and Canada while India has an estimated 1 TCM of reserves. Uses of CBM include fuel, electricity generation and supporting mine operations.