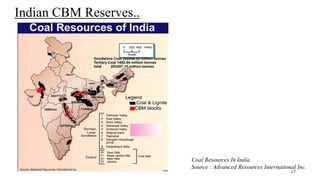
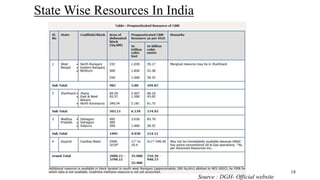
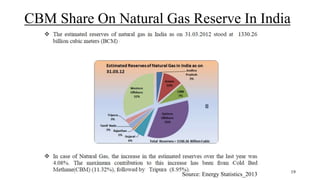
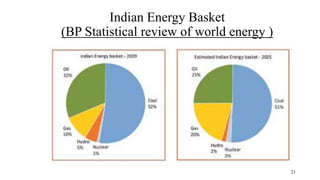
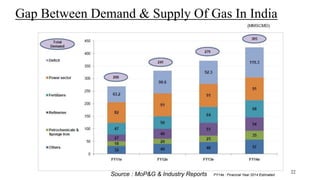
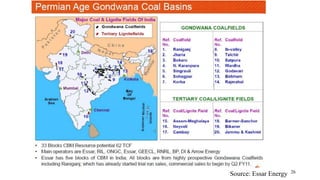
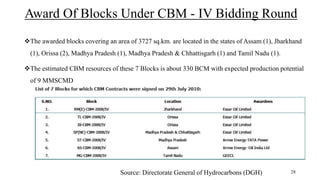
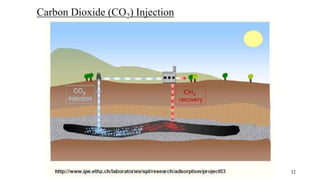
Coal bed methane (CBM) refers to natural gas trapped in coal beds. CBM was previously considered a mining hazard but is now seen as a potential energy source. Global CBM production has increased in recent decades in countries like the US, Australia, and China. India has significant estimated CBM reserves of around 70 trillion cubic feet. While CBM development has faced challenges in India, it could help meet the country's growing energy demand and reduce reliance on imports. Enhanced recovery techniques using carbon dioxide injection may further increase CBM production potential in the future.



![Global Scenario
Extracting coal bed methane (CBM) from underground coal seams like a gift to a world in need of
clean energy supplies.
Today’s oil and gas industry recognizes the value of this unconventional resource, CBM exploration and
development, once uniquely North American, are now under way on a global scale.
In recent years, CBM projects have rapidly proliferated.
Australia had no CBM production in 1995, but in 2008, 4 billion m3 [141 Bcf] was extracted from its
extensive underground coal reserves.
China had in excess of 1.4 million m3[49 Bcf] of CBM production in 2006.
These amounts are small compared with US production in 2007—61 billion m3 [2.15 Tcf], more than
10% of the US domestic natural gas supply
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coalbedmethanewithreferencetoindia-150330084237-conversion-gate01/85/Coal-bed-methane-with-reference-to-india-4-320.jpg)