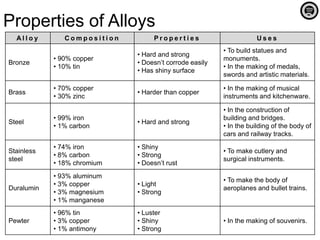
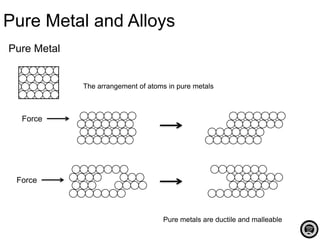
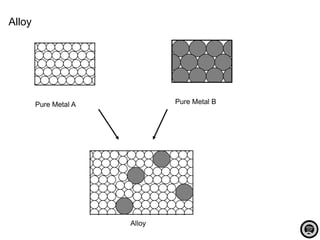
Alloy is a mixture of two or more elements where the major component is a metal. Alloys are created to increase hardness and strength, prevent corrosion, and improve appearance over pure metals. Common alloys include bronze, brass, steel, stainless steel, duralumin, and pewter. Alloys have specific compositions that influence their properties and determine their common uses.