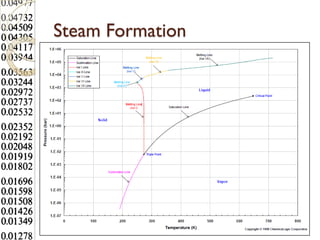
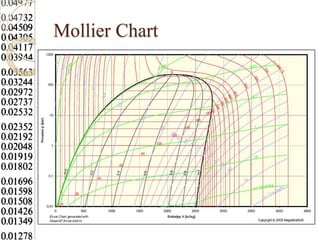
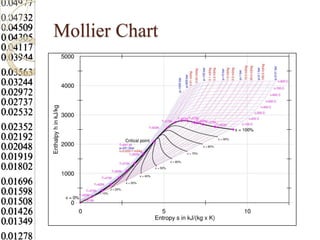
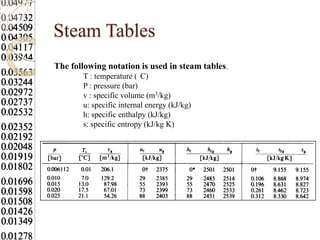
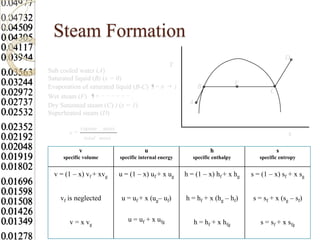
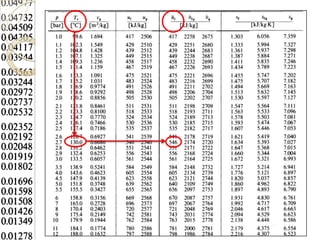
Steam tables provide thermodynamic property values like pressure, temperature, specific volume, internal energy, enthalpy and entropy for water and steam from the triple point to the critical point. Saturated steam tables give properties for saturated liquid and vapor states, while superheated steam tables cover superheated vapor. Steam tables use common notation and are essential for analyzing steam systems and processes that involve phase changes of water.