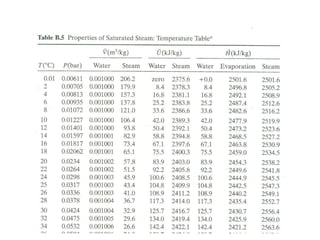
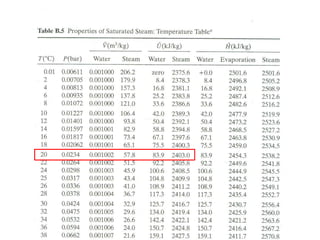
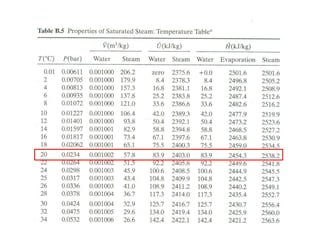
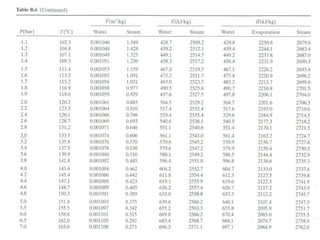
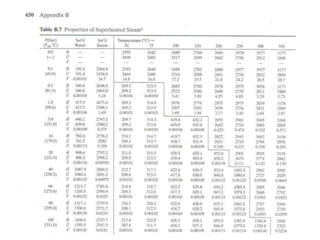
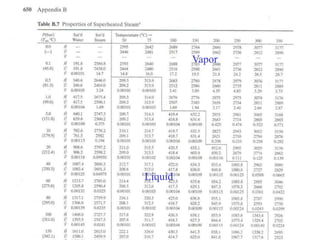
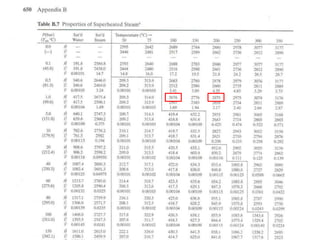
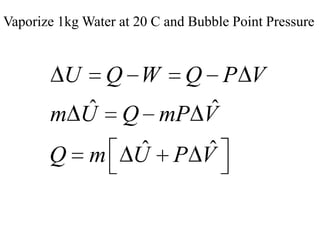The document discusses the use of steam tables to determine properties of water and steam under different conditions. It provides examples of using steam tables to calculate:
1) The heat required to vaporize 1kg of water at 20°C and the bubble point pressure
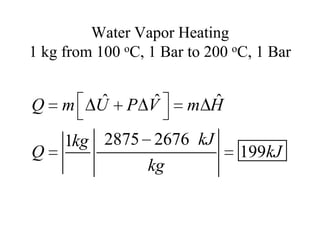
2) The internal energy change and heat transfer for heating 1kg of steam from 100°C to 200°C at a constant pressure of 1 bar
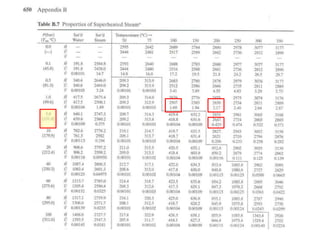
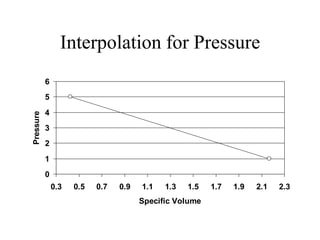
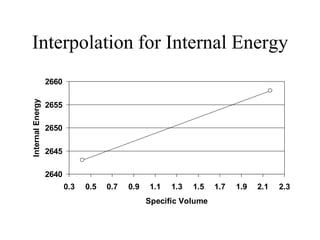
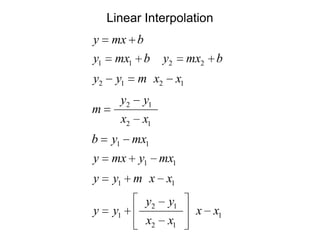
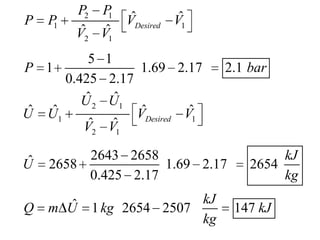
3) Using interpolation in steam tables to find the pressure and internal energy for constant volume heating of 1kg steam from 100°C to 200°C.