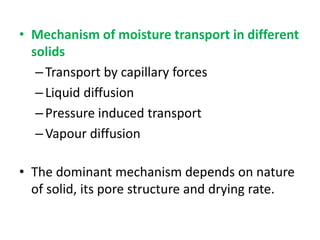
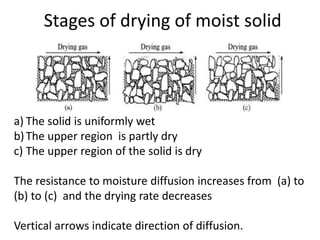
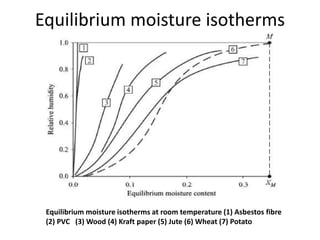
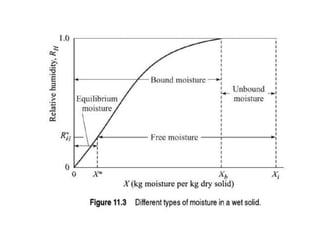
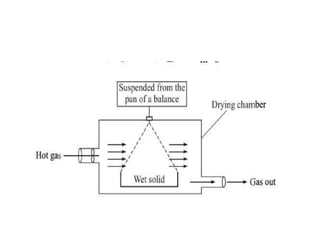
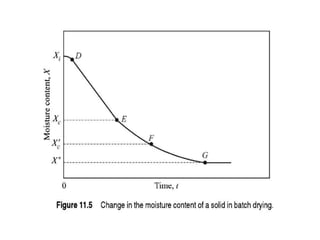
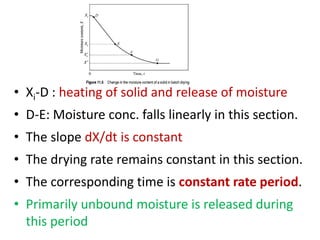
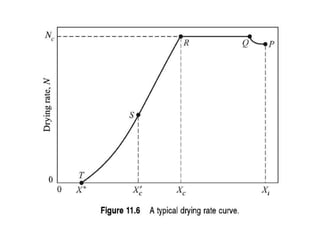
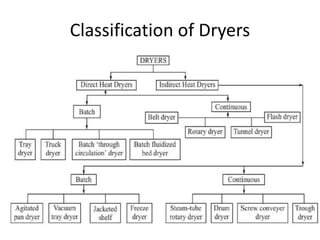
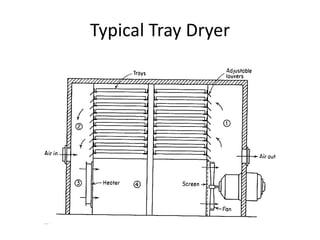
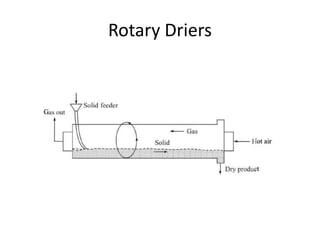
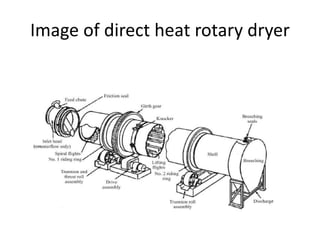
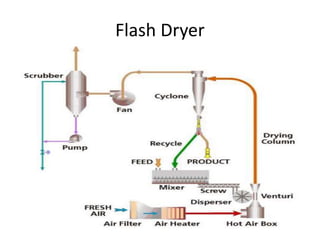
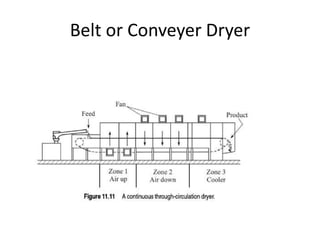
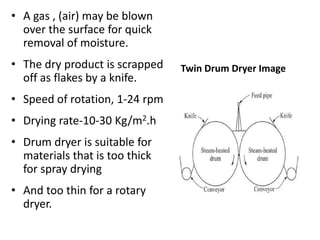
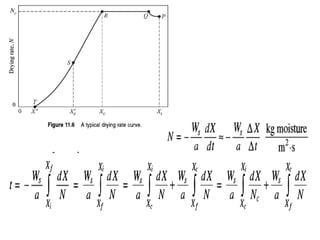
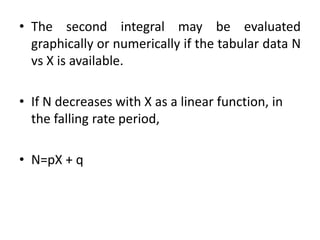
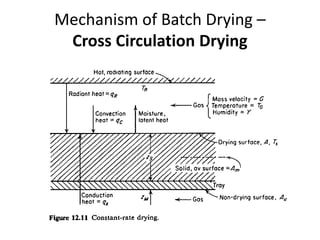
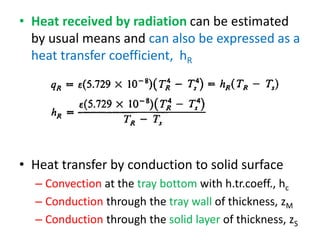
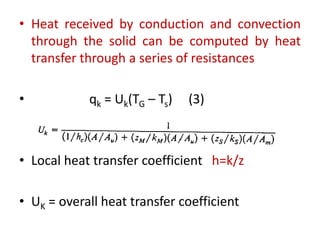
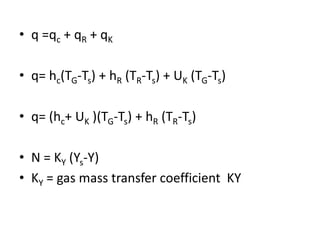
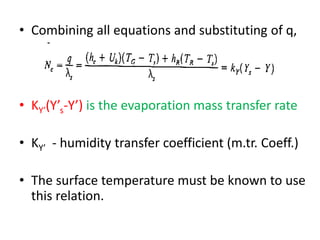
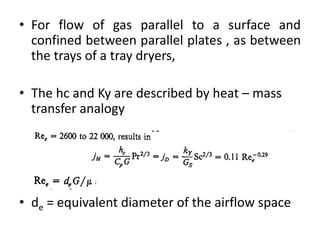
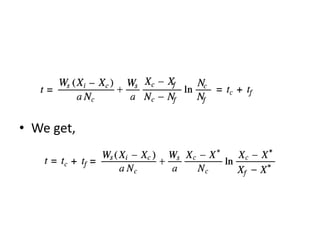This document discusses drying of wet solids. It begins by defining drying as the removal of liquid, generally water, from a wet solid to produce a relatively dry product. Examples of industrial drying processes are provided. The various mechanisms of moisture transport within solids during drying are described, including capillary forces, liquid diffusion, and vapor diffusion. The stages of drying and how the drying rate changes over time are explained. Factors that influence the critical moisture content and equilibrium moisture content are discussed. Different types of industrial dryers used for drying solids, including tray dryers, rotary dryers, flash dryers, and drum dryers are described. Heat and mass transfer principles governing batch and continuous drying are outlined.