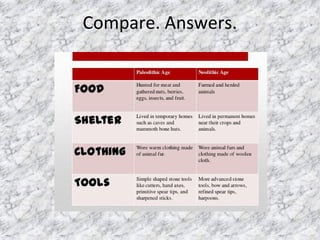
The document discusses the distinction between the Paleolithic and Neolithic periods, also known as the Old and New Stone Ages. The Paleolithic period began around 2.6 million years ago with the advent of stone tools and lasted until around 10,000 BCE. It was characterized by nomadic hunter-gatherer societies using chipped stone tools. The Neolithic period began around 10,000 BCE and lasted until around 2,000 BCE, characterized by more settled agricultural societies using polished stone tools and domesticating plants and animals. Key differences included permanent dwellings, private property, more advanced tools and weapons, clothing, and the development of trade networks and organized religion/government in the Neolithic period.