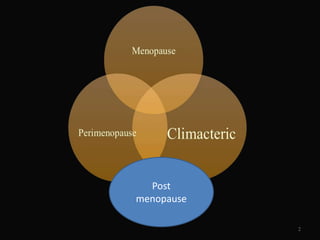
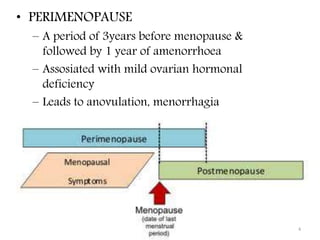
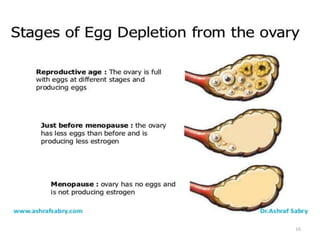
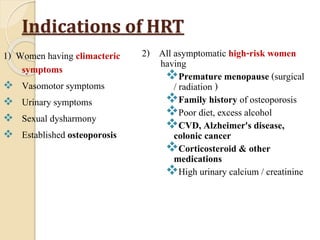
This document discusses menopause and postmenopause. It defines menopause as the permanent cessation of menstruation due to loss of ovarian activity, usually occurring between ages 45-50. The document describes the hormonal changes, symptoms, risks, diagnosis, and treatment options associated with menopause including hormone replacement therapy and lifestyle modifications.