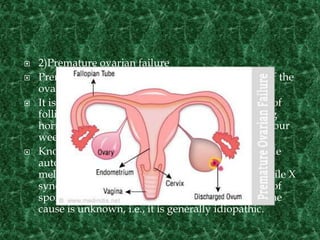
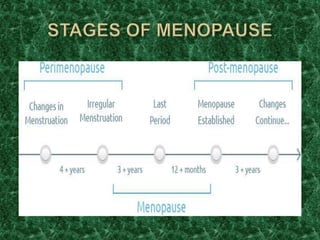
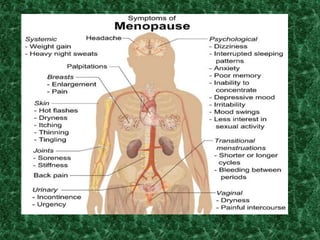
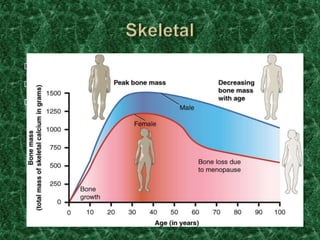
Menopause typically occurs between ages 49-52 as the ovaries gradually slow production of eggs and reproductive hormones, causing menstrual periods to stop. It may be induced by surgery or occur prematurely under age 40. Symptoms include hot flashes, mood changes, and increased risk of osteoporosis and heart disease due to hormonal changes. Hormone replacement therapy can help treat symptoms but also carries risks if used long term. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through diet, exercise, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol can also help manage menopausal effects.