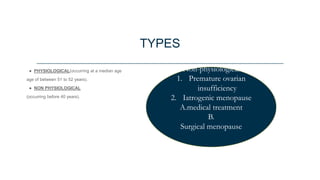
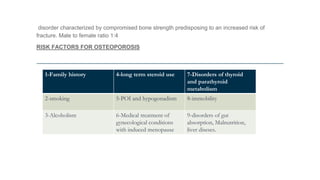
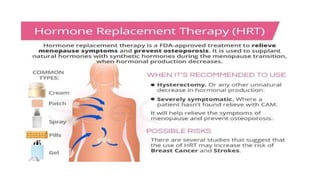
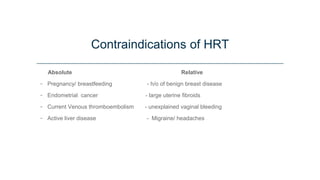
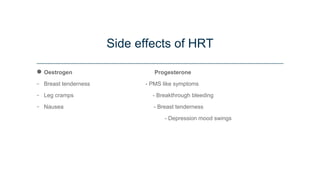
This document discusses menopause and hormone replacement therapy (HRT). It defines menopause and the stages surrounding it. It describes the endocrine changes that occur and various symptoms women may experience physically, psychologically, and with their sexual/reproductive systems. The document also outlines the risks and benefits of HRT, how it is administered, contraindications, and potential side effects.